
The power of evolution is undeniable, and one such example is the human body.
Over time, the size of our brains has increased, enabling advanced cognitive abilities like language, problem-solving, and cultural development, whereas changes in our diet have led to smaller jaws and teeth. Moreover, certain body parts that were once considered useful serve no purpose in modern times. These are also called vestigial organs, referring to body parts that you can do without.
Table of Content:-
Listed below are five such body parts that you can survive without:
Also Read: 10 Foods That Look Like The Body Parts They Benefit The Most
Appendix

The appendix is a tiny pouch attached to the cecum, which is a part of the large intestine. It is believed to have played a role in the digestive process for early humans, but today, it can be easily removed with the help of an appendectomy, usually in the case of appendicitis or an inflamed appendix, which affected an estimated 1.77 crore people in 2019, as per a study published in the World Journal of Surgery.
For a long time, the appendix has been considered a vestigial organ, until recently, when studies indicated that it may act as a 'safe house’ for good bacteria in the digestive system. More recent research, published in Comptes Rendus Palevol, suggests that it might be involved in immunity due to its link to immune tissue in the cecum.
Tonsils
Tonsils are a part of the immune system, located at the back of the throat. They help protect against infections, especially during childhood, but are also prone to turning against the body, leading to various health complications.
Tonsillitis is a common issue, especially in kids, leading to frequent tonsil removal surgeries, also called tonsillectomy. While they're also considered a vestigial organ, studies show mixed results about whether or not they're completely useless. In fact, a study published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology suggests that tonsillectomy could be associated with an increased risk of infections or chronic diseases.
Gallbladder
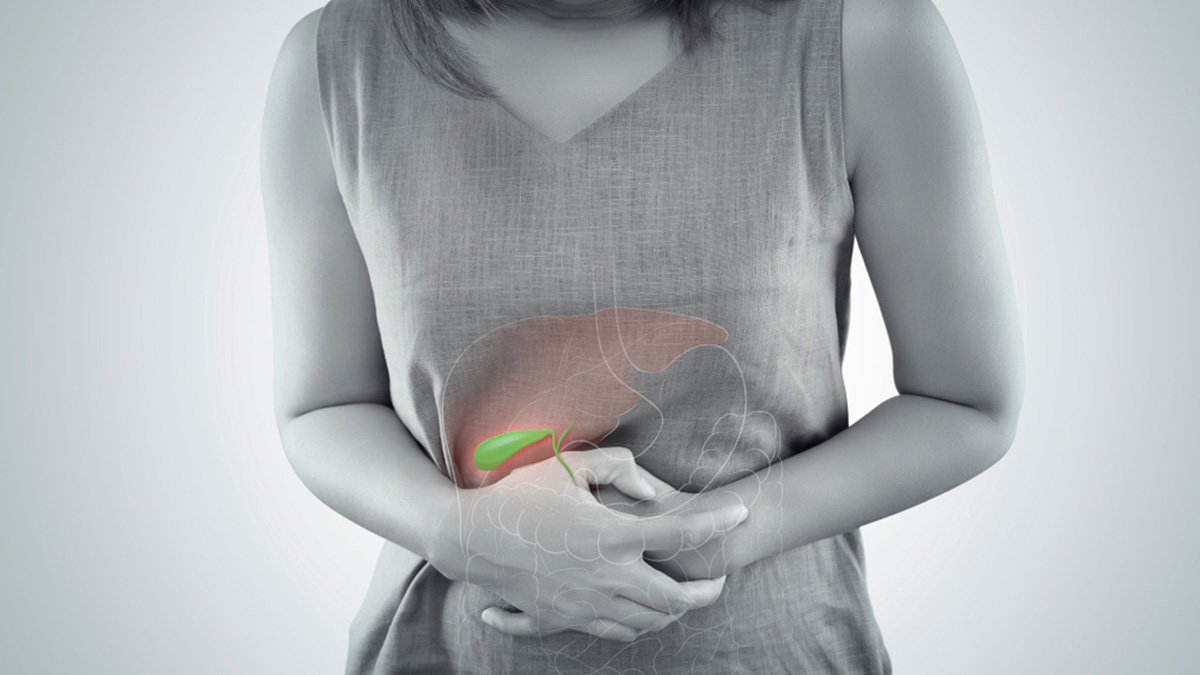
The gallbladder is located under the liver on the upper-right side of the abdomen. It stores bile produced by the liver and releases it to aid in digestion. However, the gallbladder can be removed when it causes trouble. The most common reason is gallstones, which are hardened cholesterol deposits that can block bile flow and lead to pain, inflammation, and infection. After removal, the only difference noticed is that the bile is directly released into the small intestine.
Also Read: From Curd To Almonds, Here Are Some Foods Best For Your Gut Health
Adenoids
Adenoids are located in the back of the nasal cavity and, like tonsils, are part of the immune system. They’re usually more useful in children, but they shrink and disappear by the time most children turn 13, according to the Cleveland Clinic. This is why removing them doesn't affect the body's ability to fight infections.
Spleen
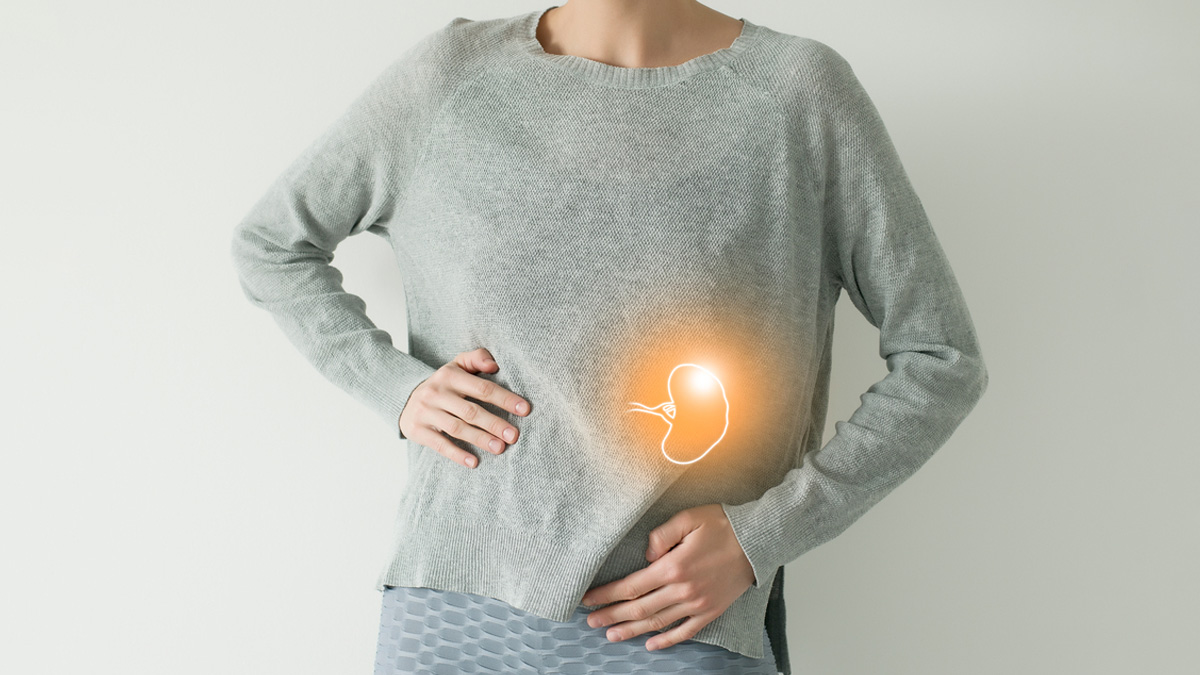

The role of the spleen is to filter our blood and help with immune responses. It acts as a reservoir for White Blood Cells (WBCs), helping us fight infections. However, humans can live without the organ, as other organs can compensate for its absence. In certain situations where the spleen is damaged, diseased, or enlarged, it can be removed with the help of a splenectomy.
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
