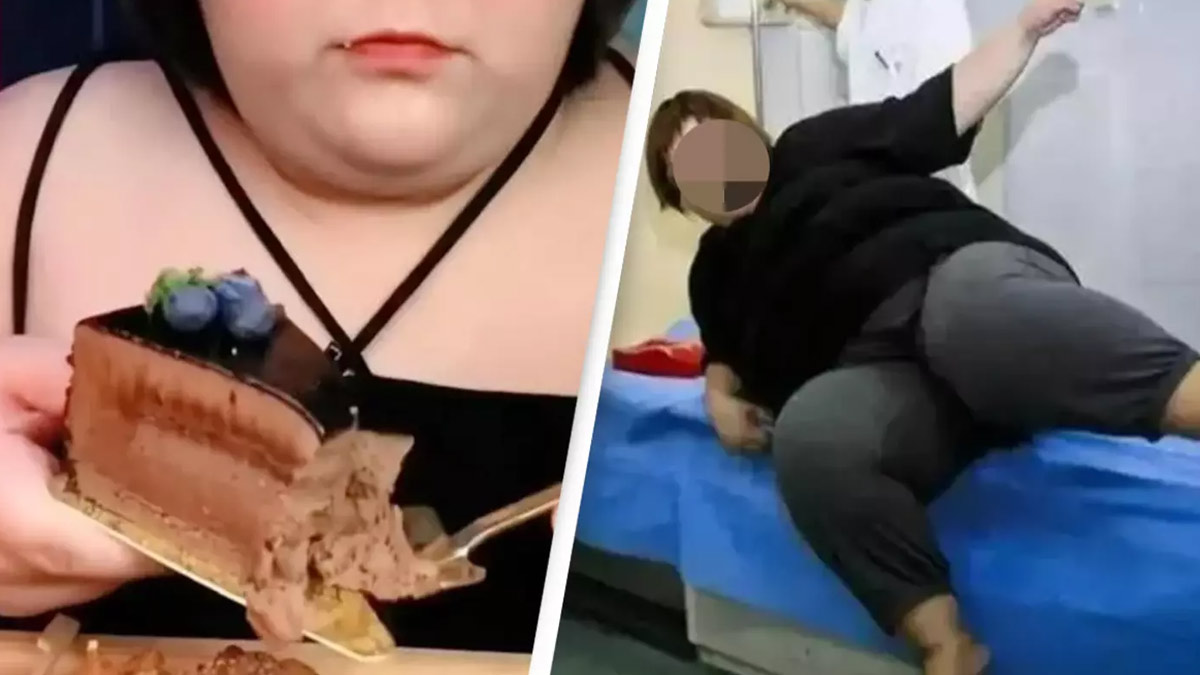
A tragic incident unfolded on July 14, when Pan Xiaoting, a 24-year-old influencer from China, lost her life during a live-streamed eating challenge. Known for her extreme eating feats, Xiaoting often participated in marathon sessions, consuming vast quantities of food over extended periods. Reports from the local portal Hankyung and Creaders.com indicate that Xiaoting's eating challenges frequently involved consuming up to 10 kilograms of food in one sitting.
Table of Content:-
Despite numerous warnings from her family and friends, Xiaoting persisted with these dangerous stunts, ultimately leading to her untimely demise. Her autopsy revealed a severely deformed stomach filled with undigested food, highlighting the severe strain her body endured. This tragic event has sparked widespread health concerns on social media, prompting discussions about the risks associated with overeating and extreme eating challenges.
The Harmful Effects of Overeating

Disrupts Hunger Regulation
The body's hunger regulation relies on two hormones: ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, and leptin, which signals fullness. Overeating can disrupt this balance by overriding these hormonal signals. Consuming foods high in fat, salt, and sugar releases dopamine, a feel-good hormone, which can lead to a cycle of eating for pleasure rather than hunger. To counteract this, portioning out high-calorie foods and eating slowly can help the body recognize when it is full.
Also Read: Mirzapur Fame Harshita Gaur Opens Up About Her Bout With Depression
Promotes Excess Body Fat
Overeating can significantly contribute to the accumulation of excess body fat. When the number of calories consumed exceeds those burned, the body stores the surplus as fat. This calorie surplus, particularly from high-fat and high-carbohydrate foods, can lead to obesity. To prevent this, it is essential to focus on consuming lean proteins and non-starchy vegetables, which help in maintaining a balanced diet and controlling calorie intake.
Impairs Brain Function
Overeating and obesity have been associated with cognitive decline in older adults. Studies indicate that continual overeating can negatively impact memory and overall brain function. Given that the brain is composed of approximately 60% fat, consuming healthy fats such as those found in avocados, nut butters, fatty fish, and olive oil may help preserve mental function and prevent cognitive decline.
Increases Disease Risk
Chronic overeating is closely linked to an increased risk of various diseases. Obesity, defined by a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or above, is a significant risk factor for metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, insulin resistance, and inflammation. This syndrome increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Reducing the intake of high-calorie, processed foods and incorporating fiber-rich vegetables into the diet can help mitigate these risks.
Leads to Excessive Gas and Bloating
Overeating can strain the digestive system, leading to gas and bloating. This is especially true for foods that are spicy, fatty, or carbonated. Eating too quickly can exacerbate these symptoms by allowing large amounts of food to enter the stomach rapidly. Eating slowly, drinking fluids after meals, and moderating portions of gassy foods can help alleviate these issues.
Causes Nausea and Indigestion
Regularly overeating can lead to uncomfortable feelings of nausea and indigestion. The human stomach, roughly the size of a clenched fist when empty, can expand to hold about one quart of food. Consuming large quantities can stretch the stomach to its limits, causing nausea and, in severe cases, vomiting. To avoid these symptoms, it is crucial to regulate portion sizes and eat at a slower pace.
Bottomline
The tragic death of Pan Xiaoting serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of extreme eating challenges and chronic overeating. It underscores the importance of understanding how overeating affects the body and adopting healthier eating habits. By being mindful of portion sizes, focusing on nutritious foods, and listening to the body's hunger signals, individuals can avoid the harmful effects of overeating and promote long-term health and well-being.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version