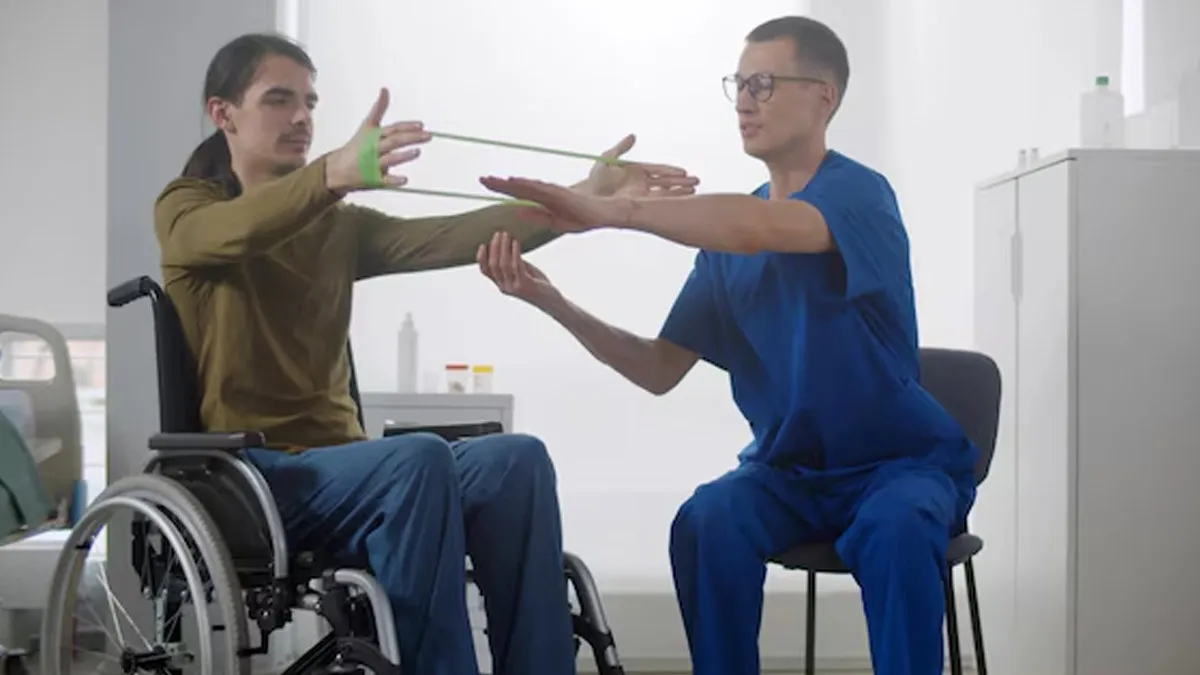

Orthopaedic care is focused on diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions, such as bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons from going into dysfunction or being injured. It plays a leading role in managing the pain and making mobility possible for such individuals and their entire life experience. The impending disability makes orthopaedic care more complex for such individuals as they usually have challenges, such as joint deformities, fractures, or mobility problems and are thus affected in many different aspects of their daily functioning.
Table of Content:-
We spoke to Dr Jayakrishnan Pillai, MBBS, DNB - Orthopedics/Orthopedic Surgery, Orthopedic surgeon, Joint Replacement Surgeon, Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Bengaluru, who explained treatment options for people with such disabilities.
Disabilities may arise from a congenital deformity, neuromuscular disease, traumatic injuries, or a chronic illness. "These conditions present several orthopaedic challenges, including bone deformity, muscle weakness, and functional joint problems. These orthopaedic care kinds provide solutions encountered by pain relief, mobility restoration, and enhancing independence," said Dr Pillai.
Understanding Joint Deformities in Individuals with Disabilities
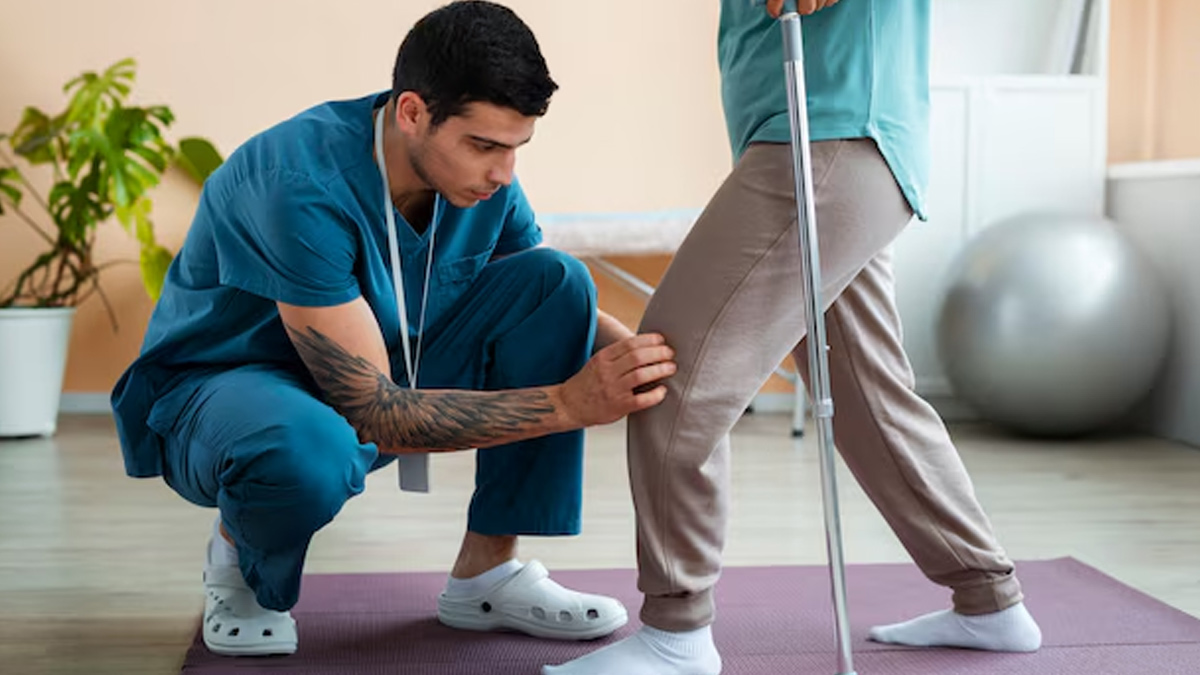

Joint deformities, often associated with conditions like cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and osteogenesis imperfecta, usually entail pain, restriction of movement, and an overall loss of functionality. Physical therapy, orthotic devices, and medications help in managing these deformities.
- Physical Therapy: Increases flexibility of joints, strengthens muscles, and reduces spasticity.
- Orthotic Devices: Braces and splints provide support to joints, and they also help in alignment.
- Medications: Muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin injections reduce spasticity.
Surgery is considered when conservative measures become ineffective. "Procedures, such as osteotomy, tendon release, and joint reconstruction aim to correct the deformity and enhance function. Such procedures include innovations like minimally invasive surgery and robot-assisted techniques for precision and faster recovery," explained Dr Pillai.
According to the Journal of Physical Therapy and Sports Medicine, adjusting to life with an orthopaedic disability requires the development of new techniques and the use of assistive technologies. Mobility aids like wheelchairs, crutches, and canes promote independence. Additionally, technology innovations, such as voice-activated devices and smart home solutions, enable individuals to manage daily activities with ease.
Also Read: Orthopaedic Physical Therapy: Expert Insights On Its Role In Managing Musculoskeletal Issues
Fracture Management for the Disabled
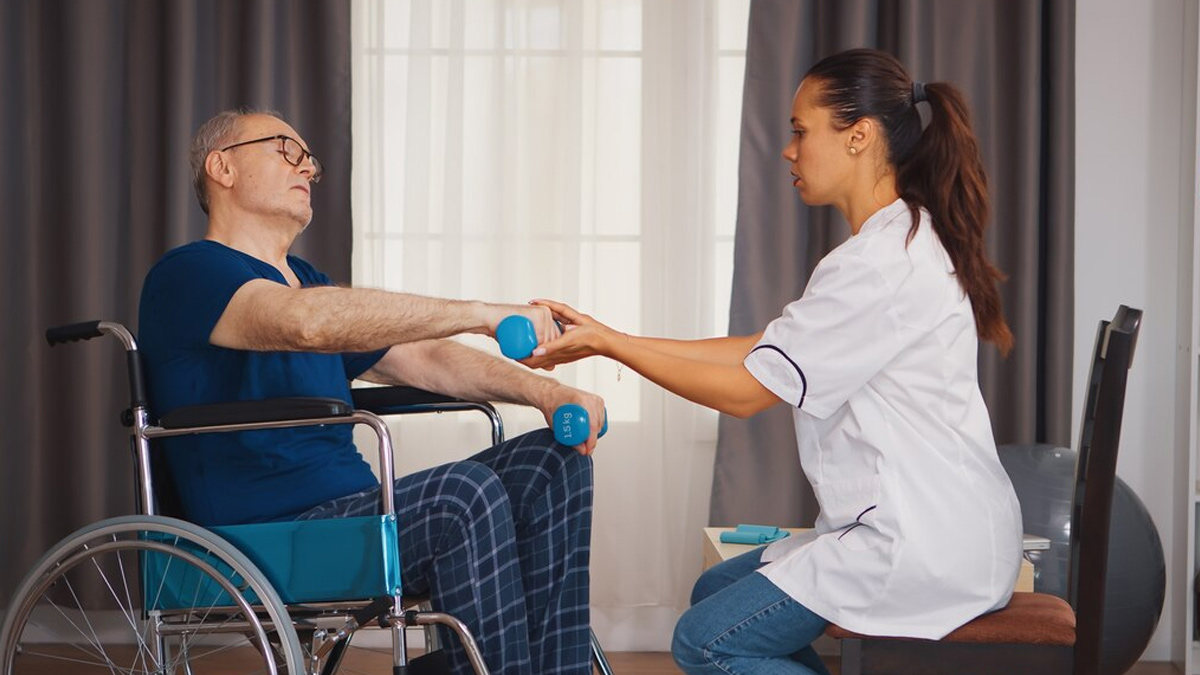

- Approaches to the management of fractures in the disabled have to be most appropriate because of factors, such as poor bone quality, abnormal bone alignments, and limited healing capacity.
- Immobilisation by a plaster cast or functional brace forms the first treatment line for a stable fracture.
- Unstable or complicated fractures usually require surgical intervention, such as internal fixation with plates, screws, or intramedullary nails.
- In cases, such as osteogenesis imperfecta where the bones are brittle, prevention of fractures is paramount.
Also Read: Struggling With A Sports Injury? 4 Kinds Of Therapy To Help You Recover Faster
Addressing the Problems of Mobility
Mobility impairments among the disabled are due to several issues, including stiff joints, weakness in one's muscles, and/or due to neurological conditions. Multi-pronged, multi-disciplinary care comes into play, as listed by the expert:
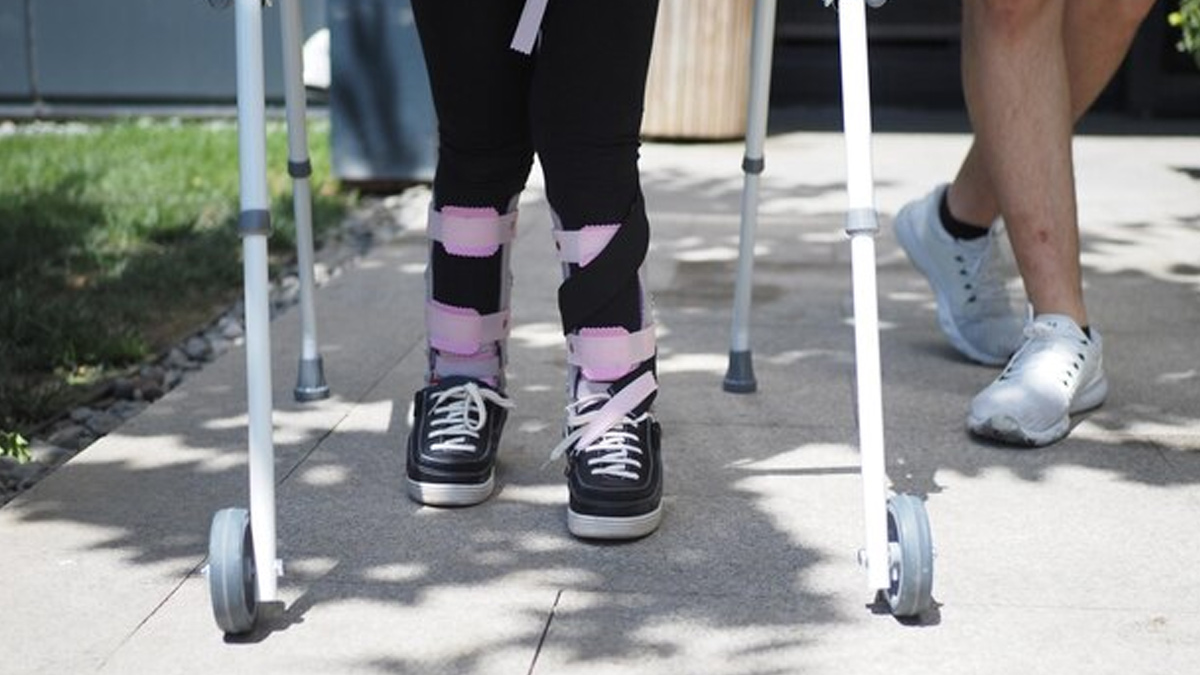
- Assistive Devices: Use of independence-regaining aids, such as wheelchairs, crutches, walkers, and prosthetics. Advances in prosthetic technology like microprocessor-controlled knees, allow for another degree of mobility and adaptability.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: Personalised therapy plans are effective for treating problems with mobility. There will be some training to enhance gait, balance, and endurance.
- Surgical procedures: For people dealing with severe mobility disorders, joint surgeries like total hip or knee arthroplasty are modalities that can be very useful.
- Neuromodulation Advanced Therapies: Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) improves muscle activity in neuromuscular deficits.
Bottomline
Dr Pillai concluded, "All orthopaedic treatment for disabled people requires well-formed knowledge regarding medical, physical, and psychosocial factors. An increasing proportion of orthopaedic specialists nurture the notion of empowering individuals with disabilities to lead active and fulfilling human lives through patient-centred services."
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your professional if you are dealing with any health issue to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
