We live in a world full of invisible stressors: pollution, poor diet, lack of sleep, and chronic stress. Over time, these pressures can keep the body in a state of low-grade inflammation, not the kind you see with a cut or infection, but the kind that smoulders quietly, damaging cells and disrupting metabolism. Many modern diseases, like heart problems, insulin resistance, and even accelerated ageing, share inflammation as a common thread.
Table of Content:-
That’s why omega-3 fatty acids have gained so much attention. Read ahead, Dr Shyam Ramakrishnan, Director, R&D for India & Southeast Asia, Amway, explains what inflammation is, how omega-3s work, the real benefits, and how to include them safely.
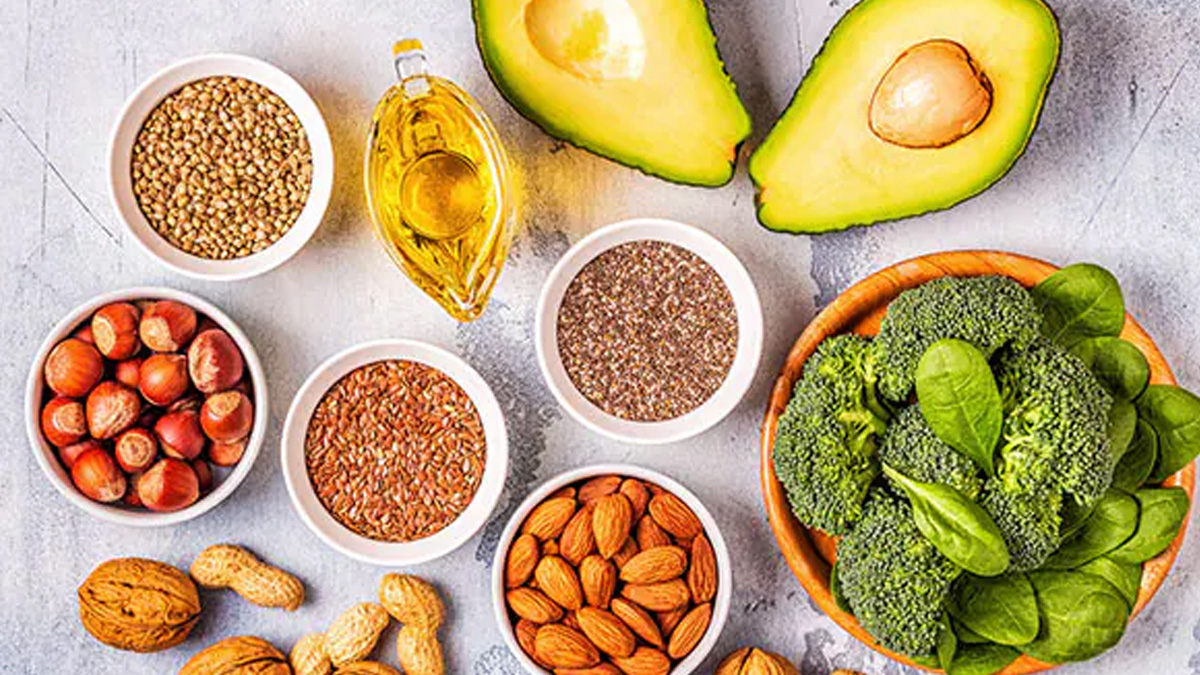
Understanding Inflammation and Omega-3![omega 3 1 - 2025-10-06T162156.902]()
Dr Ramakrishnan explains, “Omega-3 fatty acids are vital polyunsaturated fats that play key roles in reducing inflammation at the root. They influence cell membranes and immune responses, helping to keep the body’s system balanced and healthy.”
He notes that omega-3s not only prevent the production of harmful pro-inflammatory agents like cytokines, but also encourage the creation of resolvins compounds that actively calm inflammation and promote tissue repair.
Inflammation shows up as redness, swelling, and heat, signalling the body’s defence mechanisms. Dr Ramakrishnan explains, “While acute inflammation is necessary, factors like a busy lifestyle, stress, pollution, poor diet, smoking, and irregular sleep can cause chronic low-grade inflammation. This persistent inflammation quietly harms tissues and can lead to metabolic disorders.”
ALSO READ: 10 Low-Calorie Foods That Support Weight Loss
How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Control Inflammation![3 - 2025-10-06T162155.909]()
Omega-3s belong to the polyunsaturated group of fatty acids. According to Dr Ramakrishnan, “They integrate into cell membranes and change their structure, improving immune cell communication. This helps reduce excessive inflammatory signalling and supports immune balance.”
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are especially potent omega-3 types found mainly in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel.
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) is a plant-based omega-3 but converts only a limited amount into EPA and DHA.
Benefits of Omega-3 for Inflammation Management
Dr Ramakrishnan highlights multiple benefits:
- Supports cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation-related damage.
- Helps cognitive function and brain health.
- May reduce joint and bone inflammation, easing stiffness and pain.
- It can improve insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes, supporting metabolic balance.
Research highlights that EPA and DHA omega-3s reduce inflammatory cytokines, enhance immune regulation, and promote the production of specialised pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) such as resolvins and protections. These compounds help resolve inflammation naturally, fostering tissue repair without suppressing the immune system
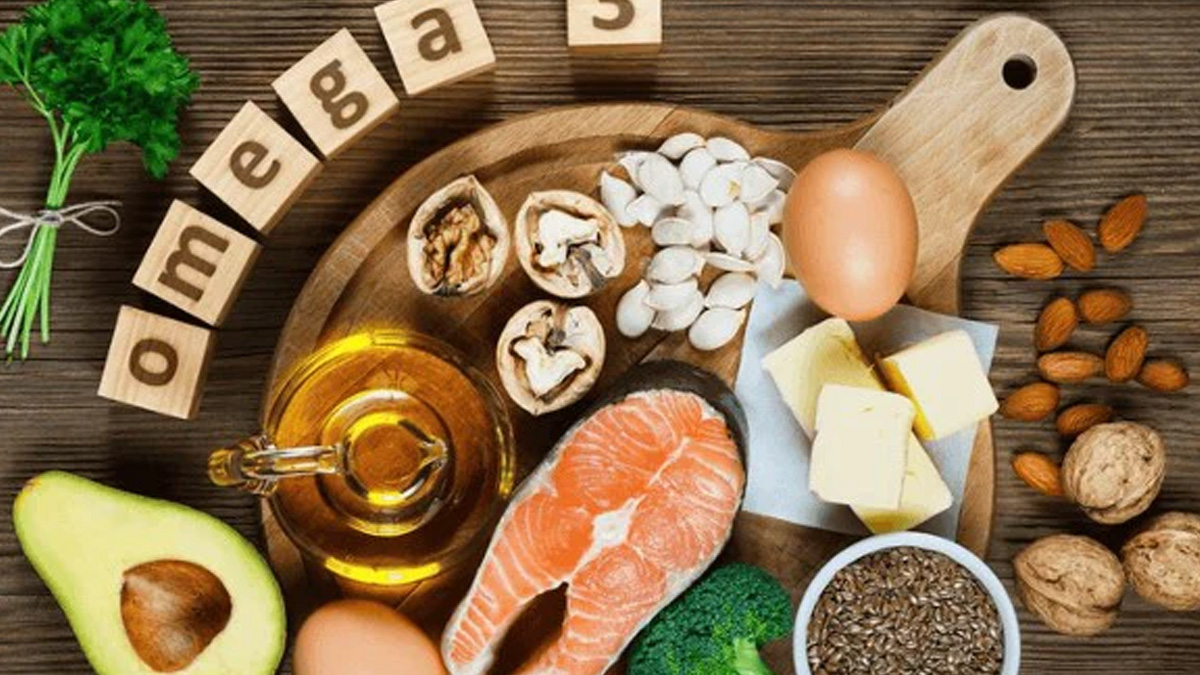
How to Add Omega-3s to Your Diet![2 - 2025-10-06T162154.752]()
Dr Ramakrishnan emphasises prudence, saying, “Don’t just take high doses blindly. First, look at your diet. Then, augment with clean, tested supplements if needed. Make sure your omega-6: omega-3 balance improves, not just add omega-3 in isolation.”
Here are practical steps:
- Eat oily fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) 2-3 times a week
- For vegetarians/vegans, use algae-based EPA/DHA supplements
- Include ALA sources (flaxseed, chia, walnuts), but know conversion is limited
- Choose high-quality, purified supplements (third-party tested)
- Monitor with your doctor, especially if on blood thinners or with immune conditions
- Pair with an anti-inflammatory diet: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-processed foods
ALSO READ: Omega-3s And The Male Heart: Do Supplements Live Up To The Hype?
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids offer a compelling, science-backed route to tame chronic inflammation not by masking it, but by influencing how your body responds at the cellular level. Insights from Dr Shyam Ramakrishnan help clarify that their action is deep and systemic: reshaping membranes, moderating genes, and producing metabolites that resolve inflammation.
If you approach omega-3 thoughtfully as part of a balanced diet, proper dosing, and medical guidance, it can become a powerful ally in supporting metabolic balance, cellular health, and resilient well-being.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
Oct 06, 2025 16:27 IST
Published By : Vivek Kumar