
Former West Bengal Chief Minister Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee, a prominent figure in Indian politics and a key leader of the Communist Party of India (Marxist), has passed away at the age of 80. His death occurred at his residence in Kolkata early Thursday morning. Bhattacharjee's health had been declining for some time, with recent reports indicating that he was suffering from a severe lower respiratory tract infection and Type 2 respiratory failure.
Table of Content:-
A Brief Overview of Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee's Life and Career
Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee, who served as the Chief Minister of West Bengal from 2000 to 2011, was a significant figure in the Indian political landscape. Taking over from Jyoti Basu, he led the Communist Party of India (Marxist) through a pivotal period in the state's history. Bhattacharjee's tenure ended in 2011 when the Trinamool Congress, led by Mamata Banerjee, emerged victorious in the state elections, marking the end of a 34-year era of Communist governance.
Throughout his career, Bhattacharjee was a respected leader within the CPM and was a member of its Politburo, the party’s top decision-making body. His political journey was marked by both achievements and challenges, and his contributions to West Bengal’s political and social landscape were widely acknowledged.
View this post on Instagram
Understanding Type 2 Respiratory Failure
Type 2 respiratory failure, also known as hypercapnic respiratory failure, is a critical condition that occurs when there is an excess of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood. This form of respiratory failure can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
What Is Respiratory Failure?
Respiratory failure refers to a state where the respiratory system is unable to supply sufficient oxygen to the body’s tissues or remove carbon dioxide from the blood effectively. This can result in two main types of respiratory failure:
- Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (Type 1): Characterized by low levels of oxygen in the blood.
- Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (Type 2): Characterized by high levels of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Type 2 respiratory failure specifically involves an elevated level of carbon dioxide, which can impede the ability of the blood to carry oxygen.
Also Read: WHO Calls For Emergency Meet As Deadliest Mpox Virus Spreading Rapidly In African Countries
Causes of Type 2 Respiratory Failure
Type 2 respiratory failure can arise from various underlying conditions:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Often seen in patients with long-term lung conditions, COPD can severely affect breathing and gas exchange.
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Conditions affecting the muscles involved in breathing, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), can lead to respiratory failure.
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome: Severe obesity can impair lung function and lead to an accumulation of carbon dioxide.
- Severe Asthma: Asthma exacerbations can sometimes result in respiratory failure if not managed properly.
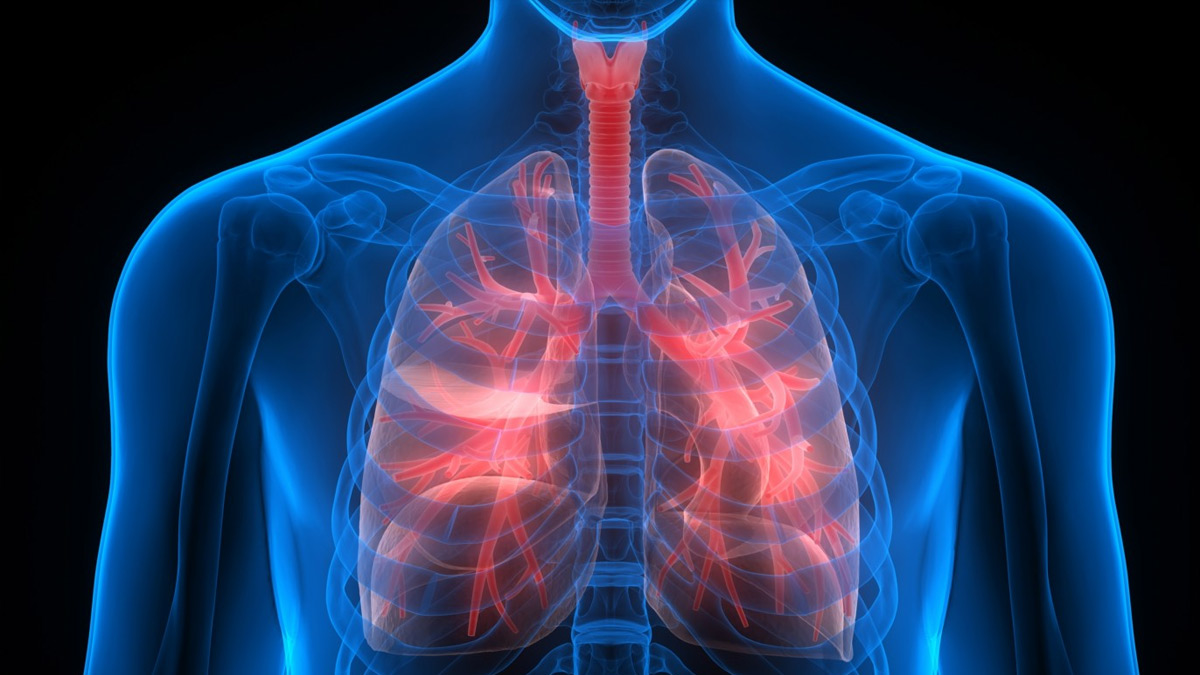
Symptoms of Type 2 Respiratory Failure
The symptoms of Type 2 respiratory failure can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea): Difficulty in breathing or feeling that you cannot get enough air.
- Rapid Breathing (Tachypnea): Breathing faster than normal in an attempt to get more oxygen.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness or a feeling of weakness.
- Heart Palpitations: A racing or irregular heartbeat.
- Bluish Skin or Lips (Cyanosis): Discoloration indicating low oxygen levels.
- Confusion or Agitation: Difficulty thinking clearly or becoming unusually restless.
Also Read: Listeria Outbreak In United States And Canada; Symptoms To Look Out For
Management and Treatment
Managing Type 2 respiratory failure typically involves addressing the underlying cause and supporting the respiratory system. Treatments may include:
- Oxygen Therapy: To help increase oxygen levels in the blood.
- Ventilatory Support: Devices such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) can assist with breathing.
- Medications: To treat underlying conditions such as infections or chronic diseases.
- Lifestyle Modifications: For conditions like obesity, weight loss and exercise can improve respiratory function.
Remembering Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee
As the political world reflects on the passing of Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee, his legacy as a leader and his contributions to West Bengal’s development are remembered. Despite his illness, Bhattacharjee's impact on the state’s politics and society remains significant. Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has expressed her condolences, acknowledging Bhattacharjee’s long-standing influence and announcing plans to honour him with full respect during his final rites.
Bottomline
The passing of such a prominent leader underscores the importance of understanding and managing complex health conditions like respiratory failure, which affect many individuals globally.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Vinesh Phogat Disqualified From Olympic Due to Overweight; Check Scientific Ways to Lose Weight Fast
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version