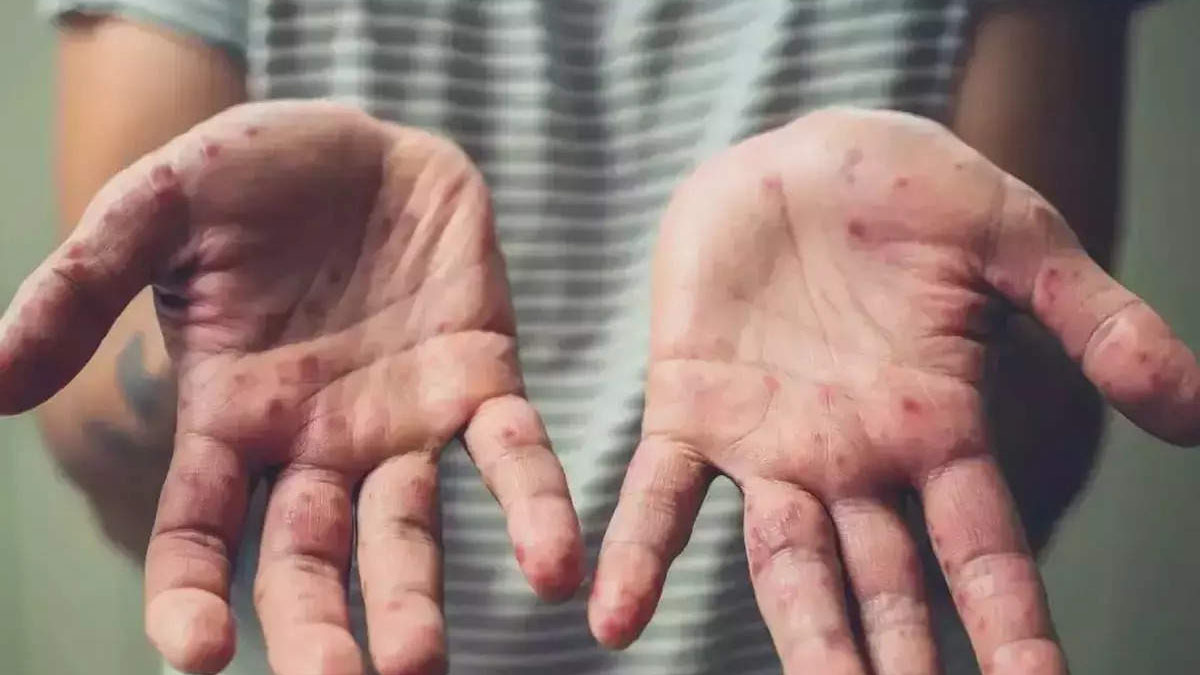

The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently called an emergency meeting of international health experts due to the alarming spread of a highly virulent variant of the Mpox virus across several African nations. The outbreak, which has escalated significantly, has prompted the WHO to take urgent measures to address the global health threat posed by this deadly strain.
Table of Content:-
WHO's Emergency Response
On Wednesday, WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus announced the convening of an emergency committee under the International Health Regulations. This decision reflects the severity of the situation, as the outbreak has rapidly extended beyond the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and exhibits the potential for further international spread. Dr Ghebreyesus emphasized the critical nature of the outbreak, stating, "In light of the spread of Mpox outside DRC and the potential for further international spread within and outside Africa, I have decided to convene an emergency committee under the International Health Regulations to advise me on whether the outbreak represents a public health emergency of international concern."
Understanding Mpox Virus
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is a viral disease that primarily manifests through painful skin lesions, fever, headache, and muscle pain. The virus, belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus—which includes the smallpox virus—poses a serious health risk due to its zoonotic nature, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. The virus primarily spreads through direct contact with infected animals or humans, and can also be transmitted through respiratory droplets during sneezing and coughing.
Also Read: Listeria Outbreak In United States And Canada; Symptoms To Look Out For
Transmission and Symptoms
Mpox is known for its ability to spread through close and skin-to-skin contact. Infected individuals may also transmit the virus through contact with contaminated surfaces or materials. The disease’s incubation period ranges from 2 to 4 weeks, with initial symptoms often appearing within 24-48 hours after exposure.
Current Outbreak Status
The ongoing Mpox outbreak in the DRC has been particularly devastating. Since the start of 2023, approximately 27,000 cases have been reported, with over 1,100 fatalities, the majority of whom are children. This alarming situation underscores the urgency of the WHO’s emergency response and the need for coordinated international efforts to curb the spread of the virus.
Also Read: Kerala On Alert After Health Ministry Confirms Rising Cases Of Deadly Brain-Eating Amoeba
Implications for Global Health
The rapid spread of this variant of Mpox raises significant concerns for global health security. The potential for the virus to spread beyond Africa necessitates immediate and comprehensive action. The WHO’s emergency meeting aims to assess the outbreak’s impact and determine whether it constitutes a public health emergency of international concern. This designation would mobilize additional resources and support from the global community to address the outbreak.
Measures to Combat the Outbreak
In response to the crisis, several measures are being considered and implemented to control the outbreak:
- Enhanced Surveillance and Reporting: Increased monitoring and reporting of cases are crucial for understanding the spread and impact of the virus.
- Public Health Interventions: Strategies to prevent transmission, such as public awareness campaigns, improved hygiene practices, and vaccination efforts, are essential in mitigating the spread of Mpox.
- International Collaboration: The outbreak highlights the need for global cooperation and resource-sharing to support affected regions and develop effective treatments and vaccines.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research is vital for understanding the virus better and developing targeted interventions to combat it.
Bottomline
The WHO's emergency meeting reflects the critical need to address the Mpox outbreak effectively. With the virus spreading rapidly across African countries and showing potential for global expansion, it is imperative for international health authorities to work collaboratively to contain the outbreak and protect public health. The response to this crisis will set a precedent for handling future infectious disease outbreaks and underscore the importance of global solidarity in the face of health emergencies.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
