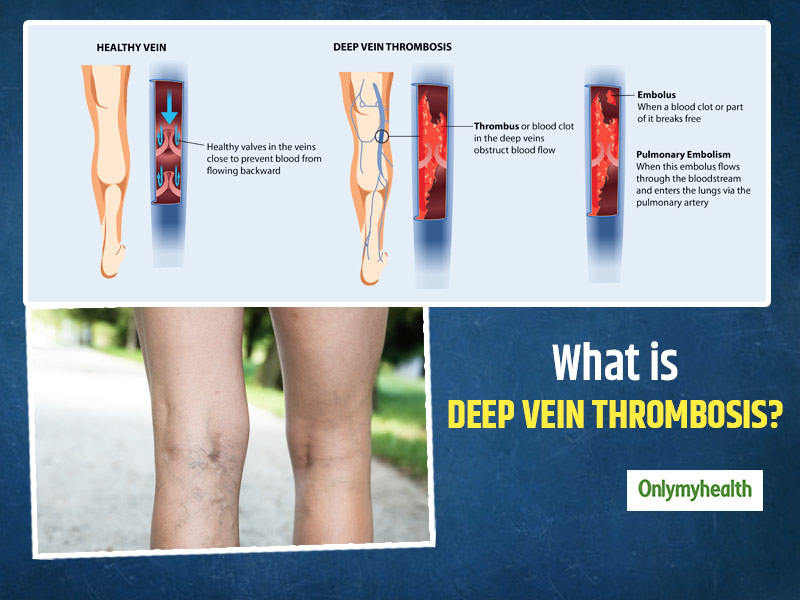
What is DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)? Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a formation of a blood clot in the deep vein. The clump of blood which converts into a tangible form is called a blood clot. Deep vein blood clots generally form in your lower leg, pelvis and thigh, but they can develop in other areas of your body too. How can one prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis? One can prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis by drinking many fluids, wearing loose-fitted clothes, and walking and stretching at regular intervals. Is there any self-treatment for deep vein thrombosis? Do not self-diagnose and never self-medicate for any severe ailment. Do medications cause fatal deep vein thrombosis? Some drugs add to the risk of DVT. It includes oral contraceptives, hormonal therapies, chemotherapeutic agent, etc. Patients on such medications should be aware of these side effects.
Table of Content:-
How to get rid of (DVT) deep vein thrombosis? Here are some medications and remedies
What are the risk factors related to deep vein thrombosis? Here's how you can manage complications?
What is the connection between diabetes and deep vein thrombosis?
Travelling for long could put you at risk for deep vein thrombosis every day
What are the signs of deep vein thrombosis?

Symptoms of DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS may include, swelling in the foot, ankle or leg, cramping pain in your affected limb, severe pain, and red/pale or discoloured skin over the affected area. Also, some DVT’s may have no symptoms. Sometimes DVT can lead to life-threatening complication of pulmonary embolism. DVT can have the life-threatening complication of pulmonary embolism and shock. It may travel through the bloodstream if a blood clot breaks off in a deep vein. The loose clot is called an embolus. It can block the flow of the blood and travel to an artery in the lungs. And the condition is called pulmonary embolism, or PE, a severe infection.
Also Read: 5 Major Eye Problems That Happen Due To Ageing With Tips To Manage The Conditions
What are the causes of deep vein thrombosis?
Damage to the blood vessel’s wall can narrow or block blood flow, and blood clot may form. Damage to a vein can be caused by surgery or trauma, and inflammation due to infection or injury. Reduced mobility or inactivity is a significant risk factor. When you frequently sit for prolonged durations, blood can collect in your legs, especially the lower parts. How to diagnose deep vein thrombosis? The diagnosis could be clinical and Duplex ultrasound is the gold standard for diagnosis. You may also need to do a test to rule out other problems or to confirm the diagnosis. D-dimer and markers of coagulation are frequently utilized.
Also Read: Fear Of Being Alone Or Lonely? BEWARE! You Might Be Suffering From Autophobia
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS: When Should One Seek Medical Advice?
Dr Yash Javeri (Critical Care, Anesthesia and Emergency Medicine, Regency Superspecialty Hospital, Lucknow) explains to be proactive. Contact your doctor promptly if you have a concern. Seek medical advice if you notice leg pain or swelling, sudden coughing, which may bring up blood sharp chest pain or chest tightness. Light-headedness, palpitations, pain in your shoulder, arm, back, or jaw, rapid breathing or shortness of breath could indicate complications of DVT.

How to get rid of (DVT) deep vein thrombosis? Here are some medications and remedies
DVT, deep vein thrombosis is most generally treated with blood thinners, also called anticoagulants. These drugs do not break up existing blood clots, but they can reduce your risk of developing more clots and prevent clots from getting more significant. Clot busters called thrombolytic, and these drugs might be prescribed if you have a more severe type of PE or deep vein thrombosis, or if other medications aren't working.
- Filters: If you cannot take medicines to thin your blood, you might have a filter inserted into Inferior vena cava.
- Compression stockings: These unique knee socks reduce the chances of swelling and other complications because of DVT. Sequential compression devices are used in hospitalized patients to prevent DVT.
Also Read: 4 Types Of OCD And Their Characteristics That You Should Know About
What are the risk factors related to deep vein thrombosis? Here's how you can manage complications?

Once you receive the treatment, it's essential to follow some lifestyle changes to manage your condition and prevent further episodes. Follow your medical practitioner, stringently. Certain factors can increase the risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis. These risk factors include age, sitting for long periods, prolonged bed rest, injury or surgery, pregnancy, overweight, smoking, heart failure and birth control pills. Risk factor reduction is the mainstay of treatment. Dietary modifications are needed if you have been initiated on warfarin. Foods rich in vitamin K, such as brussels sprouts, spinach, kale and other leafy greens can be good with warfarin. Take your medications as directed. Watch for excessive bleeding. If you have been on bed rest because of surgery or other factors, then the sooner you get moving will lower the chance that blood clots will develop. Wear compression stockings if advised.
Also Read: How Can Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Prevent Arachnophobia?
What is the connection between diabetes and deep vein thrombosis?
Dr Yash Javeri states that "research by defeat diabetes.org has shown that people with diabetes are nearly 30% more likely to develop recurrent DVT than non-diabetics. Smoking, inactivity, obesity, dehydration, and being pregnant are also known to be independent risk factors for DVT, as they are for developing type II diabetes." Hospitalization and deep vein thrombosis: What is the correlation? Immobilization, chemotherapy, pregnancy, severe covid, sepsis, critical illness, spine and lower limb surgeries are high-risk interventions for developing DVT. Prophylactic measures with drugs and sequential compression device are taken to reduce the risk. DVT prevention strategies are a must in the Intensive care unit.
How does it feel to be living with Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis has similar symptoms as many other health problems. However, often this blood clot in the veins display no signs at all. A smoker or someone with a sedentary lifestyle may have higher risks when living with deep vein thrombosis. Some ways through which one can tell that they are living with Deep Vein Thrombosis are swelling of legs, pain, or tenderness in the legs, red or discolouration of the legs, and swollen and problematic veins.
Also Read: What Is Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder?
Travelling for long could put you at risk for deep vein thrombosis every day
Travelling for long hours could be inconvenient for someone with DVT as in an aeroplane there might be little legroom, and traffic on the highway could add to the extra inconvenience. Hence, once can practice exercising in their seat, wearing compression socks, speaking to the doctor about blood-thinning medication and consuming a healthy diet. Besides, one should wear loose clothes for good blood flow and keep themselves hydrated. Exercise can also get you some relief from deep vein thrombosis (DVT), especially when you have been in bed for a long time. Obese people should lose their extra weight. Walking regularly will also help you a lot. This will prevent DVT from developing in your feet. Feet exercises, such as rotating your heels while sitting, should rotate the toes back and forth so that blood does not clot in the soles.
Also Read: Irritated From Excessive Eye Discharge? Know The Causes And Ways To Get Rid Of It
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Points to remember?
Once a person receives treatment for DVT, it is essential to follow a few lifestyle changes, which include:
- Asking the doctor about the diet: foods rich in vitamin K should be consumed
- Taking medications as directed
- Watch for excessive bleeding: one should speak to the doctor about what activities need to be avoided to prevent bruises and cuts
- Moving: the chances of developing DVT due to bed rest are high; therefore, one should get moving fast so that the chances of blood clot are lower
- Wear compression stockings: they can be worn to prevent blood clots in the legs.
Read More Articles in Other Diseases
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
