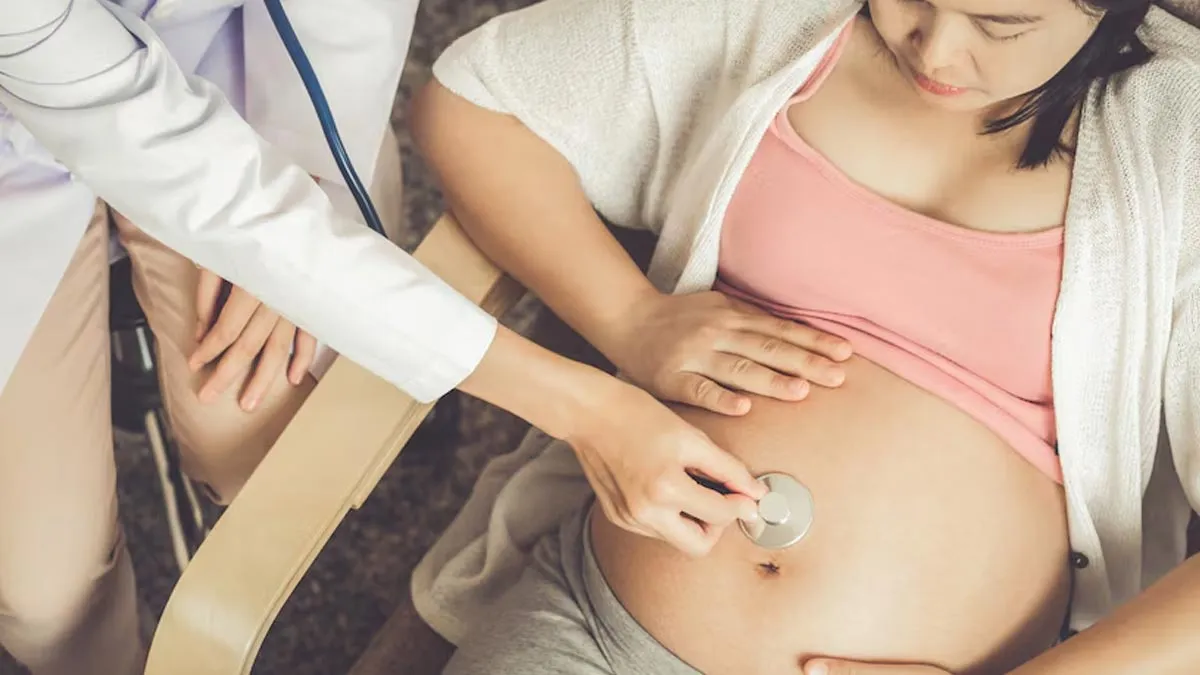

Pregnancy is often seen as a time of joy and anticipation, but for many women in India, it has become increasingly associated with complications and high-risk factors. A high-risk pregnancy occurs when the health of the mother or baby is at significant risk due to medical, lifestyle, or socio-economic factors. Alarmingly, the number of high-risk pregnancies in India is on the rise, posing a major public health challenge.
Table of Content:-
To understand why Indian women are facing more high risk pregnancies, OnlyMyHealth team spoke to Dr Vinatha Puli, Senior Consultant – Gynaecologist & Obstetrician at Cloudnine Group of Hospitals, Hyderabad.
She explains, "In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of high-risk pregnancies due to multiple factors, including lifestyle changes, rising maternal age, and inadequate prenatal care. Addressing these concerns requires a proactive approach to maternal healthcare."
1. Rising Prevalence of Lifestyle Diseases
A major contributor to high-risk pregnancies in India is the growing burden of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. These non-communicable diseases (NCDs) not only affect general health but also create severe complications during pregnancy.
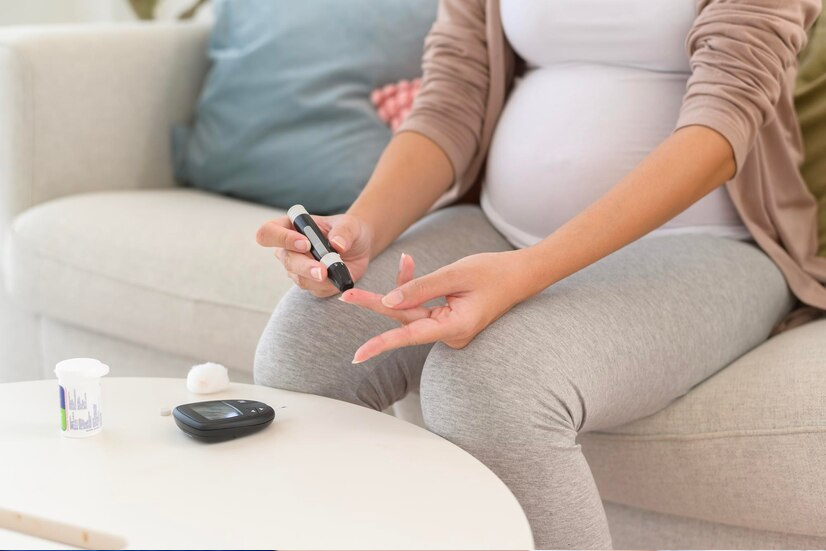

- Diabetes: Many women develop gestational diabetes, increasing the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and birth defects. Women with pre-existing diabetes face an even higher risk of complications, including stillbirth.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure during pregnancy, known as pre-eclampsia, can be life-threatening if left unmanaged, leading to organ damage, reduced blood supply to the placenta, and potential maternal or fetal mortality.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases the risk of gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and delivery complications, often necessitating C-sections, which have their own risks.
"Obesity and diabetes are two of the biggest challenges we face today in obstetrics. The increase in processed food consumption, sedentary lifestyles, and stress have contributed to these conditions, making pregnancy riskier than ever before," says Dr Puli.
Also read: Is Your Pregnancy High-Risk? Here’s What You Need to Know for a Healthy Delivery
2. Delayed Childbearing and Advanced Maternal Age
More Indian women are now prioritising careers, education, and financial stability before starting a family. While this trend is empowering, it comes with increased pregnancy risks.
According to a report published in the International Journal of Women’s Health, women over 35 are more prone to gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome. Advanced maternal age also raises the chances of multiple pregnancies, which are inherently high-risk.
"Many women today are having their first child in their late 30s, which increases the risk of complications. While medical advancements have made pregnancy safer at this age, women should still be aware of the risks and seek early medical intervention," advises Dr Puli.
3. Poor Access to Healthcare and Inadequate Prenatal Care
Despite government initiatives, access to quality maternal healthcare remains a challenge, particularly in rural areas. Many women either lack awareness of prenatal care's importance or cannot afford regular checkups.
Inadequate healthcare access leads to undiagnosed conditions such as high blood pressure, infections, and gestational diabetes, all of which could be managed if detected early. Even in urban areas, overcrowded hospitals and expensive private healthcare facilities make timely intervention difficult.
"Early and regular prenatal checkups are essential to detect complications in time. Unfortunately, many women either do not receive proper care or seek medical help too late, increasing their risk of adverse outcomes," explains Dr Puli.
Also read: 5 Things to Know If You Are Having a High-Risk Pregnancy
4. Cultural and Socio-Economic Factors
Social norms and economic constraints also contribute to high-risk pregnancies in India.
- Early Marriages and Teenage Pregnancies: Many young girls conceive before their bodies are fully developed, leading to preterm births and low birth weight babies.
- Malnutrition: A significant number of Indian women, especially in rural areas, suffer from malnutrition, making them more vulnerable to complications such as anaemia and stunted fetal growth.
- Social Stigma: Women facing unplanned or non-traditional pregnancies may avoid seeking medical care due to societal pressure, increasing their health risks.
"Nutrition plays a crucial role in maternal health. Many women enter pregnancy with nutritional deficiencies, which can impact both mother and baby. Proper diet and supplementation should begin even before conception," says Dr Puli.
5. The Overlooked Role of Mental Health
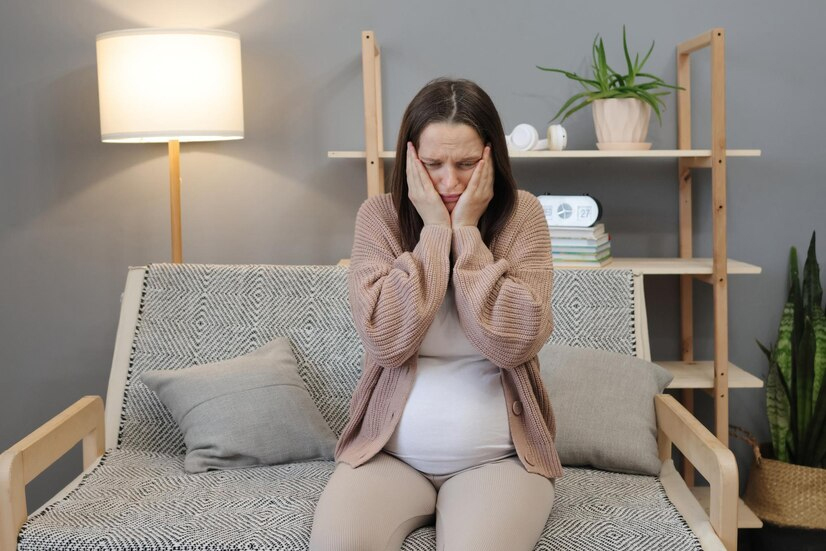

Pregnancy-related mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress are often ignored in India, particularly in rural communities where mental health is still a taboo subject.
Untreated mental health conditions can contribute to premature birth, low birth weight, and complications during labour. Moreover, chronic stress can exacerbate physical conditions such as hypertension and gestational diabetes.
"Mental health is just as important as physical health during pregnancy. Emotional well-being directly impacts both the mother and the baby. We need to normalise discussions around mental health and ensure women receive the support they need," stresses Dr Puli.
6. Gaps in Family Planning
While India has made progress in promoting contraception and reproductive health education, many women still lack access to effective birth control. This leads to unplanned pregnancies, which are often high-risk due to inadequate prenatal care and poor nutritional status.
"Family planning plays a vital role in reducing high-risk pregnancies. Proper spacing between pregnancies and access to contraception can significantly improve maternal health outcomes," says Dr Puli.
The Way Forward
The rising number of high-risk pregnancies in India is a complex issue requiring a multi-pronged approach. Steps to improve maternal health include:
- Expanding access to quality prenatal and postnatal care
- Raising awareness about lifestyle diseases and their impact on pregnancy
- Encouraging balanced nutrition and fitness for women of childbearing age
- Breaking the stigma around mental health in pregnancy
- Strengthening family planning initiatives
"Improving maternal health in India requires education, early intervention, and policy changes that support women's health at every stage of life. By addressing the root causes of high-risk pregnancies, we can work towards safer motherhood for all," concludes Dr Puli.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version