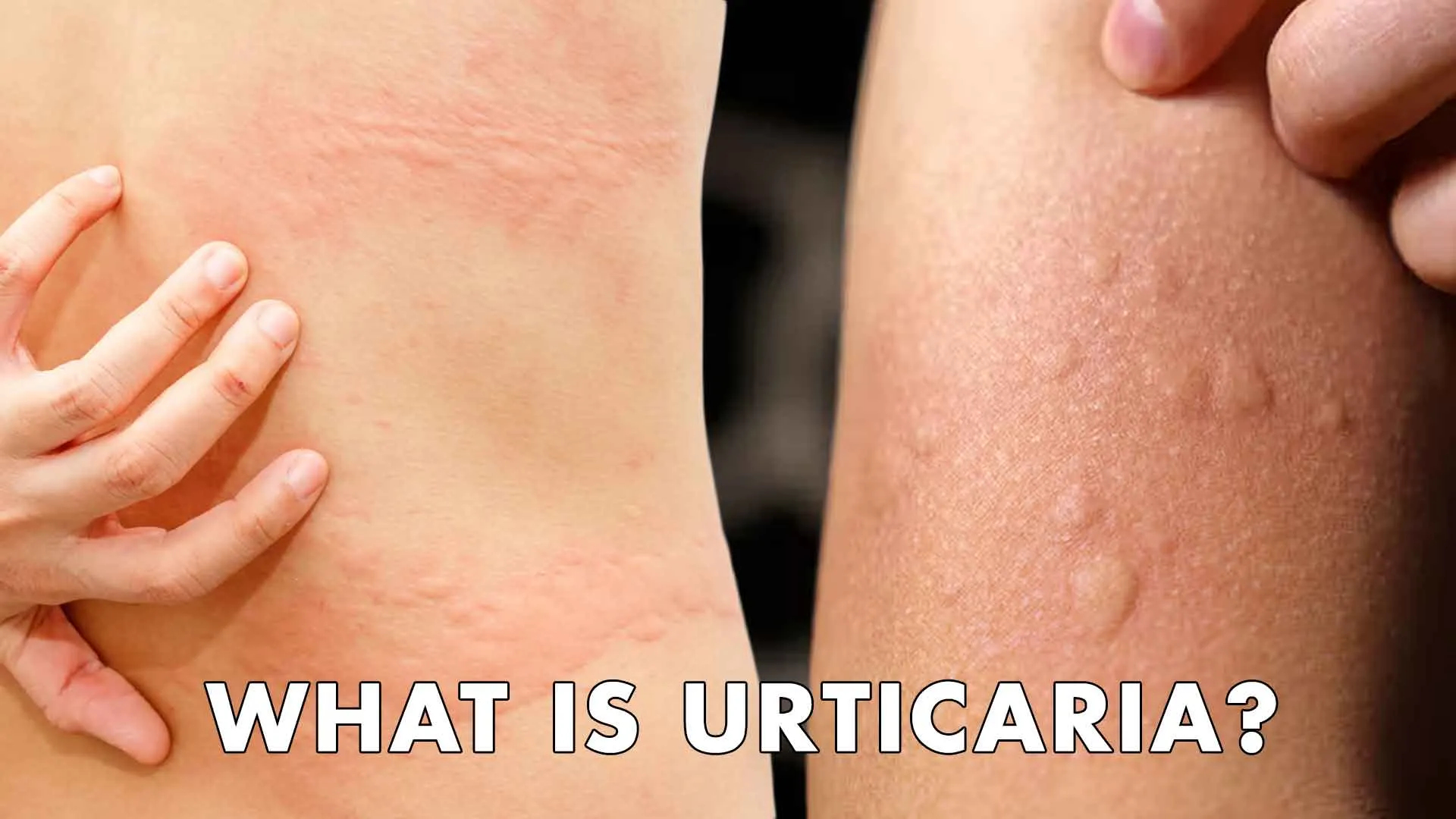
Skin conditions can often be a source of discomfort and concern for many individuals. Among these, one condition that frequently draws attention is characterised by raised, itchy welts on the skin. This phenomenon can arise due to a variety of triggers and may affect people in different ways, leading to varying degrees of severity and duration.
Table of Content:-
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that manifests as itchy welts or raised patches on the skin. These welts can vary in size and often change shape or location, making the experience somewhat unpredictable. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and why urticaria may worsen at night is essential for effective management.
What Is Urticaria?
Urticaria is an inflammatory skin disorder. According to the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology (IJDVL), it is defined as a temporary outbreak of localised, swollen, and typically itchy areas in the dermis. It is also known by other names such as nettle rash, hives, or wheals. These lesions usually last for a few hours but do not exceed 48 hours. It affects people at some point in their lives and can be classified as acute, lasting less than six weeks, or chronic, persisting for longer periods.
Symptoms Of Urticaria
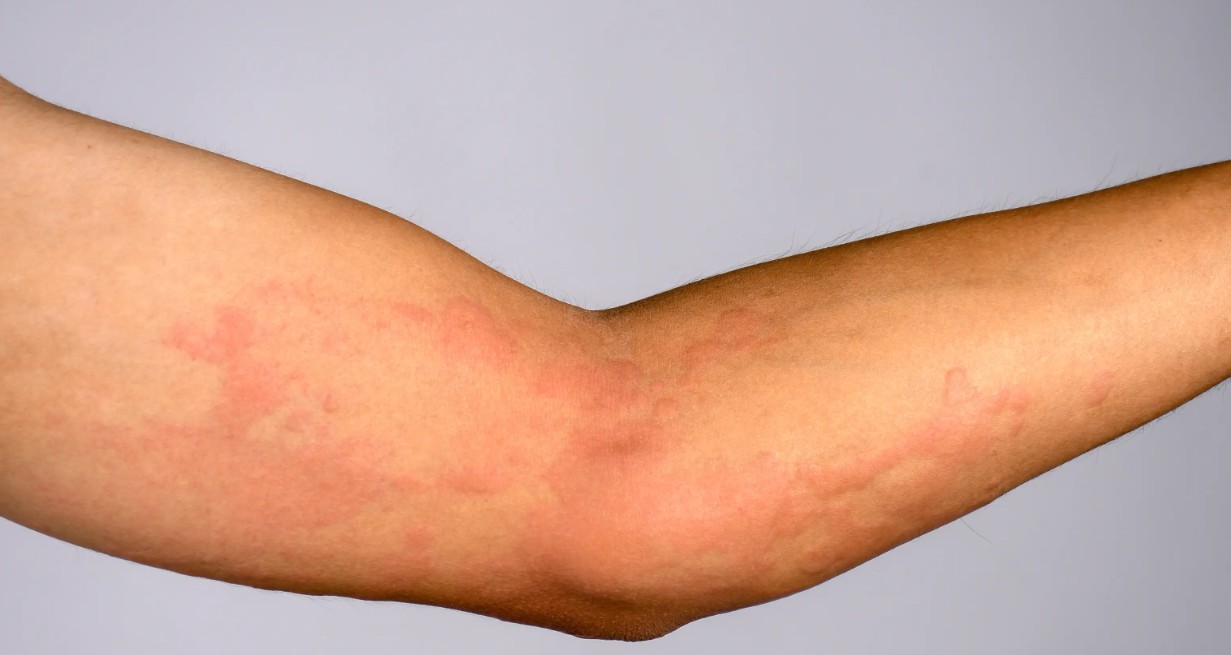
While Urticaria may seem straightforward, its symptoms can manifest in various ways and may be triggered by a range of factors. Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with this condition.
- Raised, itchy welts: These can vary in size and shape, appearing as red or skin-coloured bumps on the skin.
- Rapid appearance and disappearance: The welts may come and go quickly, often within 24 hours, although new ones can form.
- Intense itching: This is a hallmark symptom that can cause significant discomfort.
- Angioedema: Some individuals may experience swelling in deeper layers of the skin, particularly around the eyes, lips, and throat.
- Variability: Symptoms can be triggered by factors such as heat, cold, stress, or exposure to allergens.
- Severe reactions: In some cases, urticaria can lead to anaphylaxis, which includes symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness.
Treatment of Urticaria
As per a study on PubMed, the treatment for urticaria involves several strategies aimed at controlling symptoms and preventing exacerbations. Some of them are mentioned below.
- Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers is essential for managing urticaria.
- First-line Treatment: Second-generation H1-antihistamines are considered the first-line pharmacotherapy. They are effective and have a favourable side effect profile.
- Increased Dosage: If symptoms are not adequately controlled, the dosage of antihistamines can be increased to two to four times the standard dose.
- Corticosteroids: A short course of systemic corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases to help control symptoms.
- Second-line Medications: If antihistamines do not provide relief, medications like doxepin or leukotriene receptor antagonists may be considered.
- Third-line Options: For chronic cases that do not respond to antihistamines, immunomodulatory drugs may be effective.
- Supportive Treatments: Soothing creams or lotions can help alleviate itching, and in cases of severe allergic reactions, an epinephrine auto-injector may be necessary.
How Does Urticaria Get Worse At Night?
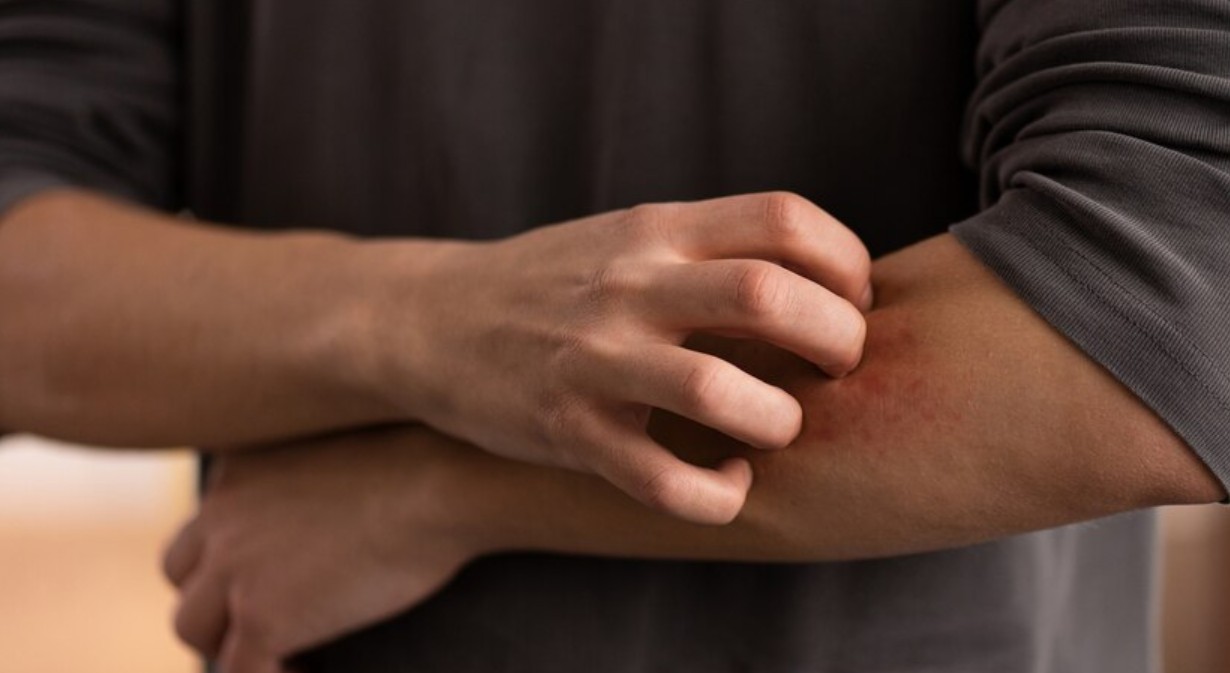

Research claims that symptoms often worsen at night due to several factors. One significant reason is that the body's natural anti-itch chemicals tend to be at their lowest during nighttime, leading to increased itching and discomfort. Additionally, allergens present in bedding or nighttime clothing can trigger flare-ups. Changes in body temperature, such as overheating while sleeping, may also exacerbate symptoms.
Additionally, the body's natural clock, known as the circadian rhythm, can affect how active mast cells are. This means that more histamine is released at night, which can make hives worse during this time. As a result, people with urticaria may have trouble sleeping and feel more frustrated because of their symptoms.
Conclusion
Urticaria is a common but often distressing condition that can significantly impact the quality of life. Understanding its causes and symptoms allows for better management strategies. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a dermatologist or a healthcare professional is recommended for tailored treatment options.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version