Blood circulation is an important function that helps supply oxygen and nutrients to various vital organs and body parts, including your fingers and toes.
In general, blood flow is described as the movement of blood through the vessels from the arteries to the capillaries and then into the veins of your heart, lungs, and overall body.
Table of Content:-
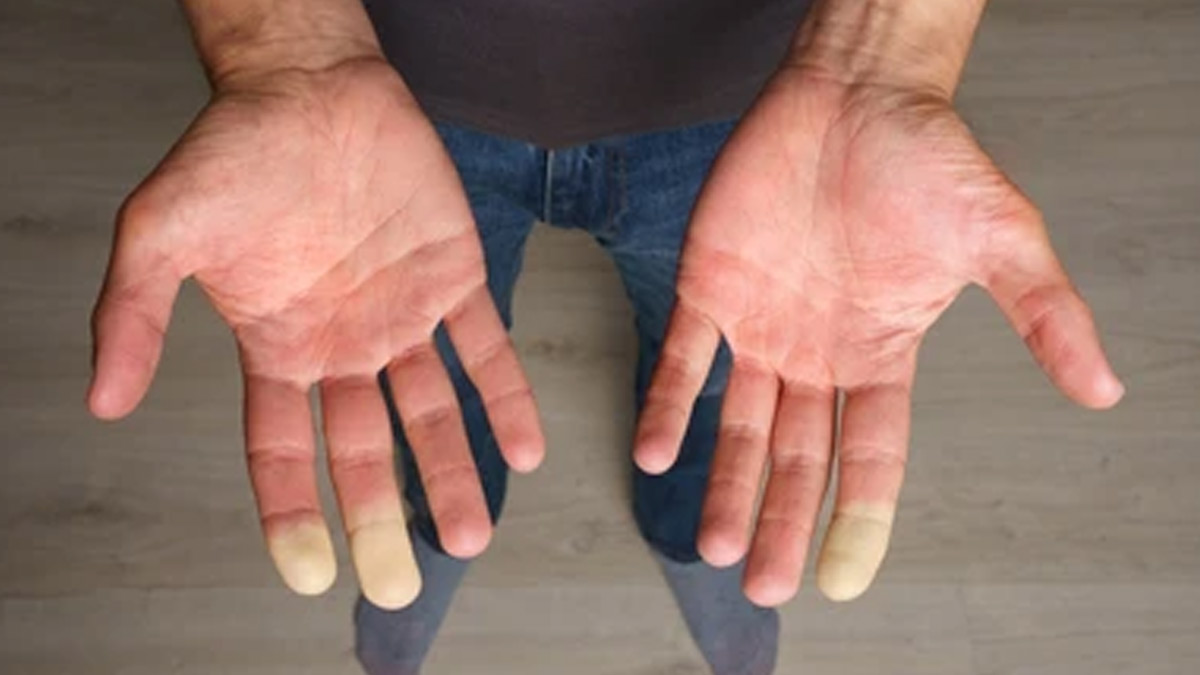
Raynaud's phenomenon is a condition that results from decreased blood flow to the fingers and toes in response to cold weather or stress. If you have experienced something of this nature but aren't aware of the condition, here's all you need to know.
Also Read: How To Know If You Have A Poor Blood Circulation: What To Do About It
What Is Raynaud's Phenomenon?

Speaking with the OnlyMyHealth team, Dr Harman Singh, Consultant Rheumatologist, Fortis Hospital, Kalyan, explains, "Raynaud's phenomenon is a condition that causes the blood vessels in extremities to narrow, restricting blood flow."
According to him, this happens due to spasms of the blood vessels in response to stress, a cold, or when a person is emotionally upset.
In general, there are two types of Raynaud's phenomenon:
- Primary, where the cause is unknown
- Secondary, which is associated with another disease like autoimmune or connective tissue diseases (lupus, scleroderma)—this is less common but more serious.
As per StatPearls Publishing, secondary Raynaud's phenomenon can also be caused by drugs such as antimigraine medications, interferon alpha and beta, cyclosporine, and nonselective beta blockers. Additionally, in people older than 60 years, obstructive vascular disease is a frequent cause. Moreover, infections, such as parvovirus B19, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, or underlying conditions like fibromyalgia, polycythemia, arteriovenous fistula, myalgic encephalitis, or malignancy can also contribute to it.
How It Impacts The Fingers And Toes

Raynaud’s phenomenon can affect different parts of the body, but it mostly impacts your toes and fingers. Some of the common symptoms include:
- The skin of the affected part turns pale or white due to a lack of blood flow.
- The affected area turns blue and feels cold and numb as the blood that is left in the tissue loses its oxygen.
- As the body warms up and circulation returns, the area turns red and may swell, tingle, burn, or throb.
- Small, painful sores, especially at the tips of the fingers or toes, and gangrene.
Also Read: Signs In Your Legs You Shouldn't Ignore: High cholesterol and Peripheral Artery Disease
Who Is At Risk?
Research suggests women, particularly younger age groups in their teens and 20s, are nine times more likely to develop Raynaud's phenomenon.
People with a family history of Raynaud’s phenomenon also have a higher risk of developing the condition, according to Dr Singh.
Treatment Approach

The treatment for Raynaud's phenomenon consists of both lifestyle modifications and certain medications. The aim should be to reduce the number and severity of the attacks, prevent tissue damage, and treat the underlying condition, as per the Mayo Clinic.
Dr Singh says, "Since the triggers of the attack are cold and stress, treatment involves keeping oneself warm, smoking cessation, avoiding certain medications, and making sure to visit a rheumatologist for treatment with medications."
In more severe cases, people with Raynaud's may have to take medications, including alpha-1 blockers, which constrict blood vessels; dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, which relax the smaller blood vessels of the hands and feet; and other vasodilators, which help dilate the veins, according to Medical News Today.
Conclusion
While Raynaud’s phenomenon is not a frequently heard term, it is a common condition that primarily affects your toes and fingers. While there is no cure for the condition, certain measures can help keep various triggers at bay. This includes cladding yourself with warm clothes, avoiding emotional stress, limiting the consumption of caffeine and alcohol, and avoiding smoking. The best way to diagnose the condition and determine the correct course of treatment is to consult a doctor or a rheumatologist. Do not overlook the signs and address them immediately.
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
