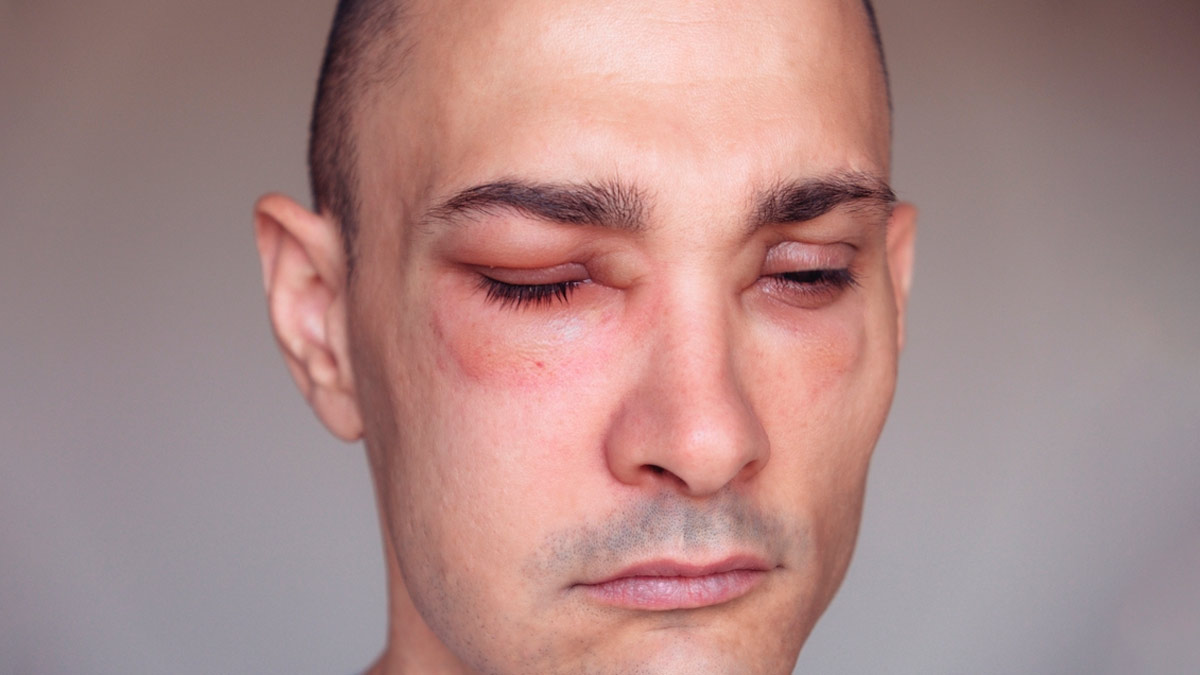
Angioedema is a sudden and alarming condition that can strike without warning, leading to swelling beneath the skin's surface. This swelling often affects areas like the face, eyes, lips, feet, hands, and genital regions. Unlike hives, which are limited to the skin, angioedema impacts deeper layers and can become a medical emergency if it involves the airways. To shed light on this condition, we spoke to Dr Atula Gupta, Dermatosurgeon, Paediatric Dermatologist MBBS, MD-Dermatology, Venerology and Leprosy, who explained the causes, symptoms, and treatments of angioedema.
Table of Content:-

According to StatPearls, angioedema is a condition characterised by rapid swelling beneath the skin and mucous membranes, often affecting the face, lips, tongue, and extremities. While typically harmless, angioedema can become life-threatening when it obstructs the airways. Additionally, swelling in the intestines can cause severe abdominal pain, mimicking other serious conditions.
Causes And Types of Angioedema
Angioedema can be classified into four main categories: allergic, non-allergic, hereditary, and acquired. Dr Gupta described each one in the following ways:

Allergic Angioedema
This is the most common form of angioedema mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE) and can be triggered by:
- Insect stings: Venom from wasps, bees, and other insects can trigger allergic angioedema.
- Food allergens: Nuts, shellfish, eggs and certain other food items can trigger allergic angioedema.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics, such as penicillin, are common triggers for angioedema.
Non-Allergic Angioedema
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor-induced: This class of blood pressure medication can lead to angioedema in some patients.
- Idiopathic Angioedema: The cause is unknown. This type is diagnosed when no specific trigger can be identified and can be challenging to manage due to the unpredictability of attacks.
Also Read: Why Thyroid Issues Causes Facial Swelling In Some People
Hereditary Angioedema
This is a rare genetic condition caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of the C1 inhibitor, a protein that helps regulate blood vessel function. It is common for symptoms to appear in childhood or adolescence.
Acquired Angioedema
Acquired angioedema, similar to the hereditary one, occurs due to reduced C1 inhibitor levels It is often associated with autoimmune disorders, certain cancers and infections.
Symptoms of Angioedema
The primary symptom of angioedema is swelling of the skin and mucosa including face, lips, eyes, airways, tongue and genital areas. This is often accompanied by:

- Pain and warmth: The affected areas may be tender and warm to the touch.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: When internal organs are affected, angioedema can lead to abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea
- Respiratory symptoms: Critical symptoms of potential airway obstruction can present as difficulty in breathing, swallowing and hoarseness of voice. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Also Read: From Swelling To Limited Motions: Expert Lists Signs Of Stiff Joints You Should Be Aware Of
Treatment of Angioedema
Angioedema treatment varies based on the specific type and severity of the condition. Dr Gupta listed the treatment measures as follows:

- Antihistamines: This is the first line of treatment and helps in reducing itching and swelling
- Corticosteroids: In severe cases, oral steroids are vital in reducing inflammation and swelling
- Epinephrine: Administered where angioedema affects breathing. Epinephrine can quickly open airways and reduce swelling
- C1 Inhibitor Concentrate: Used specifically for treating hereditary angioedema. It replaces the deficient or dysfunctional protein in the blood.
- Bradykinin Inhibitors and Kallikrein Inhibitors: These are novel treatments for hereditary angioedema that target specific pathways involved in the reaction.
- Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers is vital, especially for those with allergic or idiopathic angioedema.
- Long-term prevention: Long-term medications like androgens (danazol), antifibrinolytics (tranexamic acid), or newer targeted therapies like lanadelumab can be implemented for patients with frequent or severe episodes
Bottomline
Dr Gupta concluded, “Angioedema is a complex condition with various triggers and manifestations. Early detection and proper treatment are essential for managing angioedema and preventing severe complications. If you experience recurrent or severe swelling, consulting a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and management is crucial.”
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your own professional if you are dealing with any health issues to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version