
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that is chronic in nature and tends to confuse us as laymen due to its multi-symptom approach. In contrast to bacterial or viral infections, lupus occurs when the immune system of our body becomes overactive and ends up attacking healthy tissues. This, in turn, results in inflammation, pain, and damage in various parts of the body, making lupus a disease that can affect almost every organ.
Table of Content:-
In an exclusive interaction with the editorial team of Onlymyhealth, our expert, Dr Bhumesh Tyagi, Consultant, General Medicine and Physician, Shardacare, Health City, Noida, explained to us in detail what lupus is, and how it affects our body. Read ahead to know.
What Is Lupus?
The scientific term for lupus is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), although other types exist, including cutaneous lupus (skin) and drug-induced lupus. Dr Tyagi highlighted that any individual can acquire lupus, but it occurs more frequently among women, especially women between 15 and 45 years old. The main causes include genetics, hormone levels, and environmental factors such as infections, stress, or exposure to sunlight.
Also Read: Why Do You Get So Many Headaches? Expert Has A Message For You
Common Symptoms of Lupus
Since lupus appears like numerous other ailments, it is sometimes challenging to make a diagnosis. Symptoms can appear and disappear, come in flares, or be minor for weeks or months. According to Dr Tyagi, some of the most popular symptoms are:
- Ongoing fatigue and weakness
- Joint pain, stiffness, or swelling
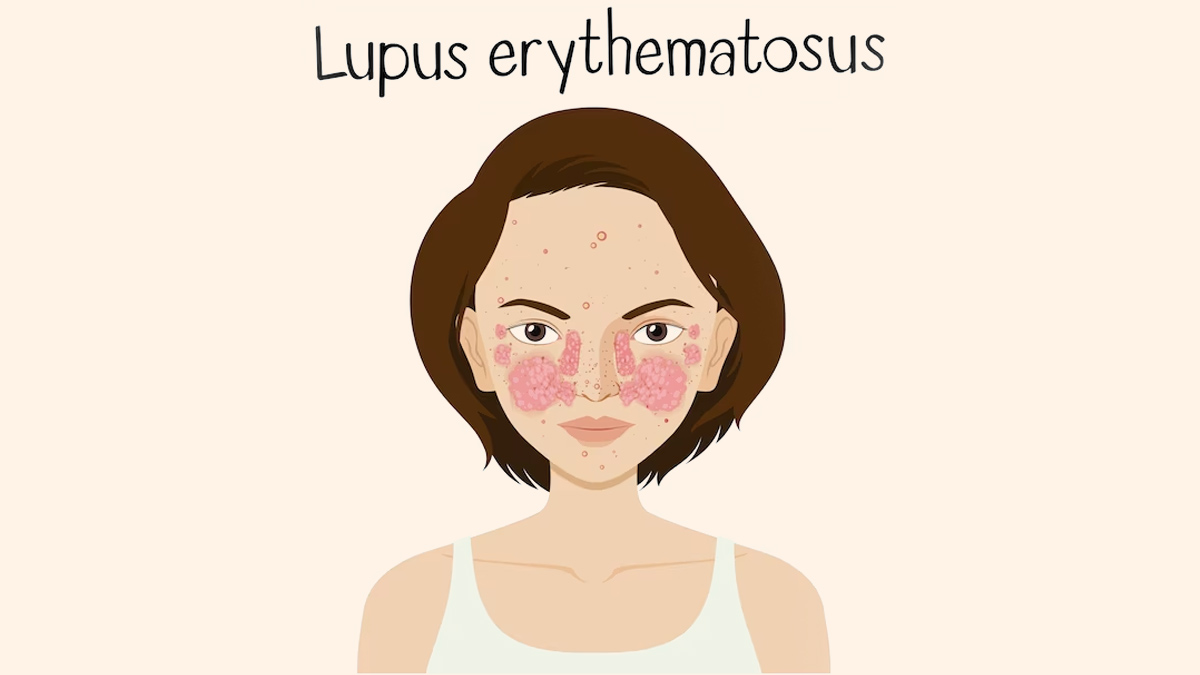
- Butterfly-shaped rash on cheeks and nose
- Sensitivity to the sun
- Hair loss and rashes
- Fever without a clear cause
- Mouth sores
How Lupus Affects the Body
Lupus is not organ-specific and can occur across several systems, causing severe complications if not treated. Such as:
- Joints and Muscles: Ongoing inflammation results in arthritis-like pain and swelling.
- Skin: Rashes, lesions, and severe sensitivity to sunlight are common.
- Kidneys: Lupus nephritis, a state wherein the kidneys get inflamed, can cause kidney failure if not treated.
- Heart and Lungs: The coating that surrounds these organs could become swollen, leading to pain in the chest, difficulty breathing, or an enhanced risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Brain and Nervous System: Certain individuals develop headaches, memory loss, seizures, or mood swings.
- Blood and Immune System: Lupus can lead to anaemia, problems with blood clotting, or reduced ability to combat infections.

Treatment for Lupus
While lupus cannot be cured, modern treatment enables most individuals to live full, active lives. Treatment usually involves:
- Medications like anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants are used to manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as proper rest, a balanced diet, and stress reduction.
- Protection from the sun, as UV radiation can cause flares.
- Careful monitoring by health professionals to avoid organ damage.
Bottomline
Lupus is a multifaceted condition that has differing effects on every individual, so awareness and an early diagnosis are crucial. By knowing the symptoms and their effects on the body, individuals can obtain timely medical attention and learn ways of managing flare-ups effectively. With proper care, lupus sufferers can keep thriving and enjoy their quality of life.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
Sep 03, 2025 15:40 IST
Published By : Tanya Srivastava