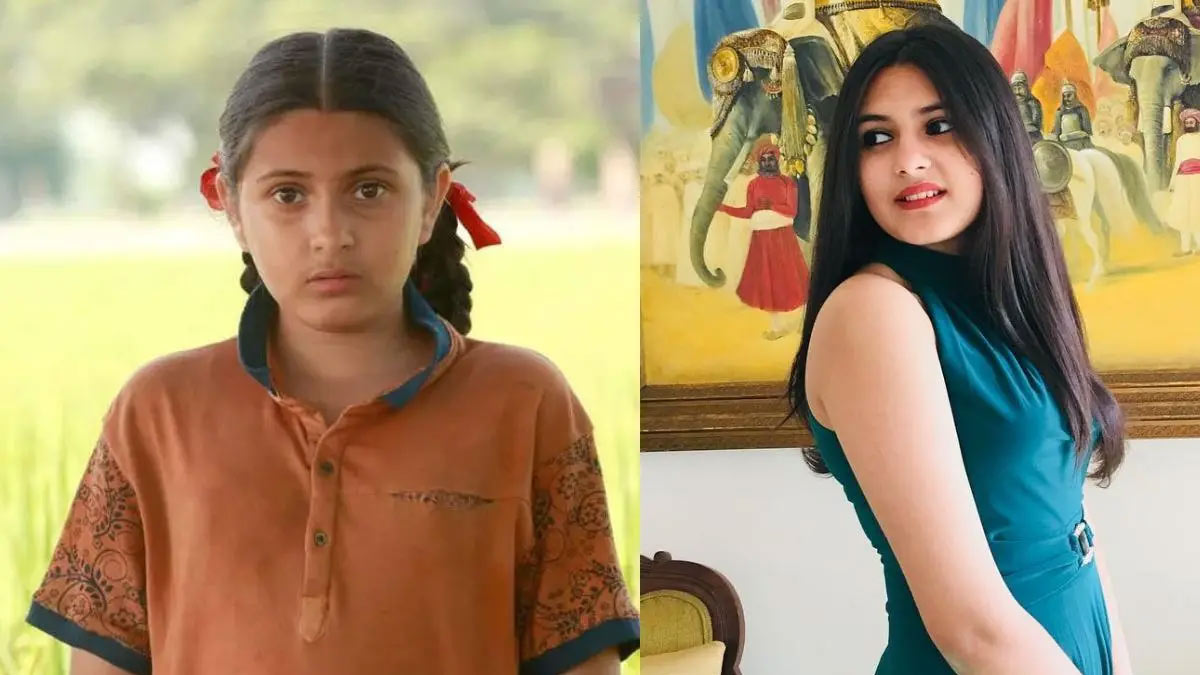
In a piece of shocking news reported earlier today, Suhani Bhatnagar, the actress who played the younger version of Babita Phogat in the Amir Khan starrer ‘Dangal’ passed away at the age of 19. Bhatnagar was admitted to the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi for a long time.
Table of Content:-
As per reports, she had suffered a leg fracture and was prescribed medicines for the same. Due to some side effects of the medicine, fluid had started building up in her body, causing her to seek hospital admittance. So far, the exact cause of death remains unknown, but fluid retention is one of the most common side effects of medications, and if it goes unchecked, it can cause severe health consequences and even death.
What Causes Fluid Retention?
According to Harvard Medical School, fluid retention, or oedema, is a common condition where excess fluid accumulates in the body's tissues, leading to swelling. Here are some common conditions that can cause fluid retention:
- Kidney Dysfunction: Kidneys play a crucial role in regulating fluid balance in the body. When they are unable to effectively filter and eliminate excess fluids, oedema can occur, leading to swelling in various parts of the body.
- Heart Failure: A weakened heart struggles to pump blood efficiently, causing fluid to accumulate in the lungs and other tissues. This condition is known as congestive heart failure.
- Liver Disorders: Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, can disrupt the production of proteins needed for maintaining fluid balance. This dysfunction can lead to fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity, a condition known as ascites, posing serious health risks.
- Malnutrition and Protein Deficiency: Inadequate protein levels in the blood can contribute to fluid retention. Proteins help regulate fluid balance, and a deficiency can disrupt this equilibrium, leading to swelling and compromising overall health.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can contribute to temporary fluid retention. However, persistent imbalances may indicate underlying health issues that require attention.
Also Read: What Causes Fluid Buildup In The Lungs? Here's Everything You Need To Know About Pulmonary Edema

Consequences of Extreme Fluid Retention
While often dismissed as a temporary inconvenience, persistent fluid retention can have severe consequences on health and even pose risks to mortality:
- Respiratory Complications: Severe fluid retention in the lungs can impede breathing, leading to respiratory distress and an increased risk of pneumonia. In extreme cases, it can be life-threatening.
- Cardiovascular Events: Fluid buildup puts additional strain on the heart, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Congestive heart failure, if left untreated, can significantly reduce life expectancy.
- Organ Failure: Persistent oedema can lead to organ failure, especially in the kidneys and liver. Once organs are compromised, the risk of mortality rises substantially.
- Infections: Edematous tissues are more susceptible to infections. Skin infections, cellulitis, and other complications can arise, posing further threats to overall health.
Also Read: How To Prevent Yourself From Heat Edema?
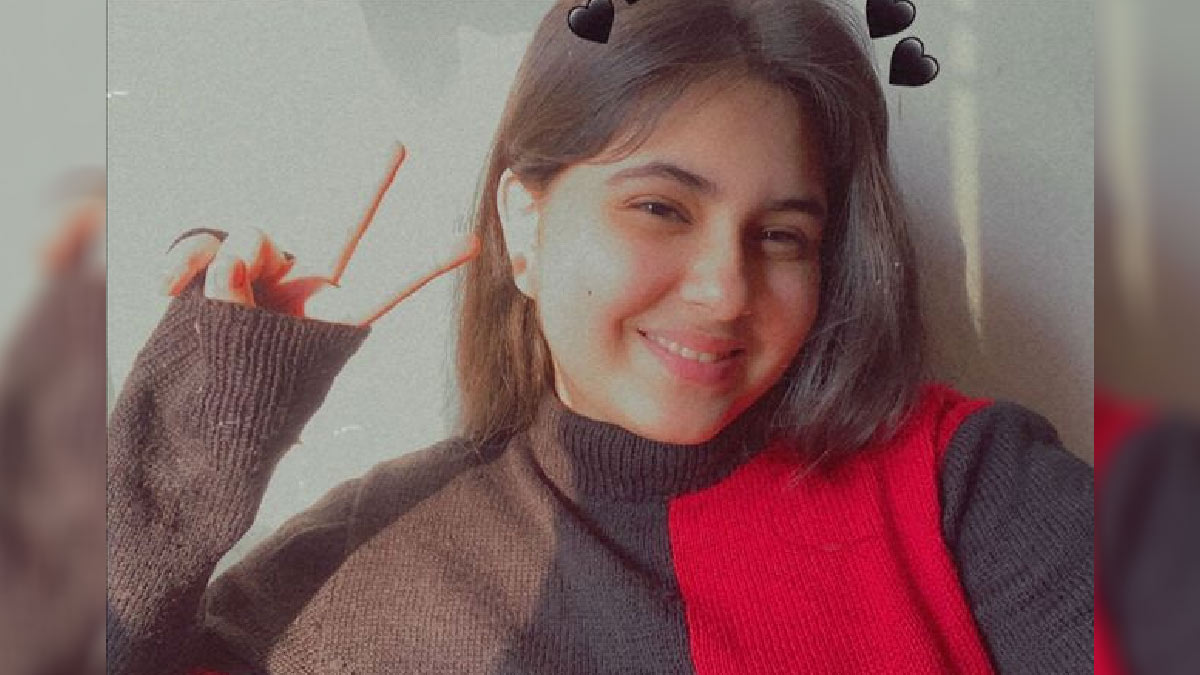

Suhani Bhatnagar’s tragic passing has sent shock waves throughout the country. While her cause remains unknown, the reports about her leg fracture and fluid retention do hold weightage as of now. If you or someone you know experiences persistent swelling, it's essential to seek medical attention to identify the underlying cause and implement appropriate measures to mitigate the risks associated with fluid retention. Early detection and management can make a significant difference in preserving both health and longevity.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version