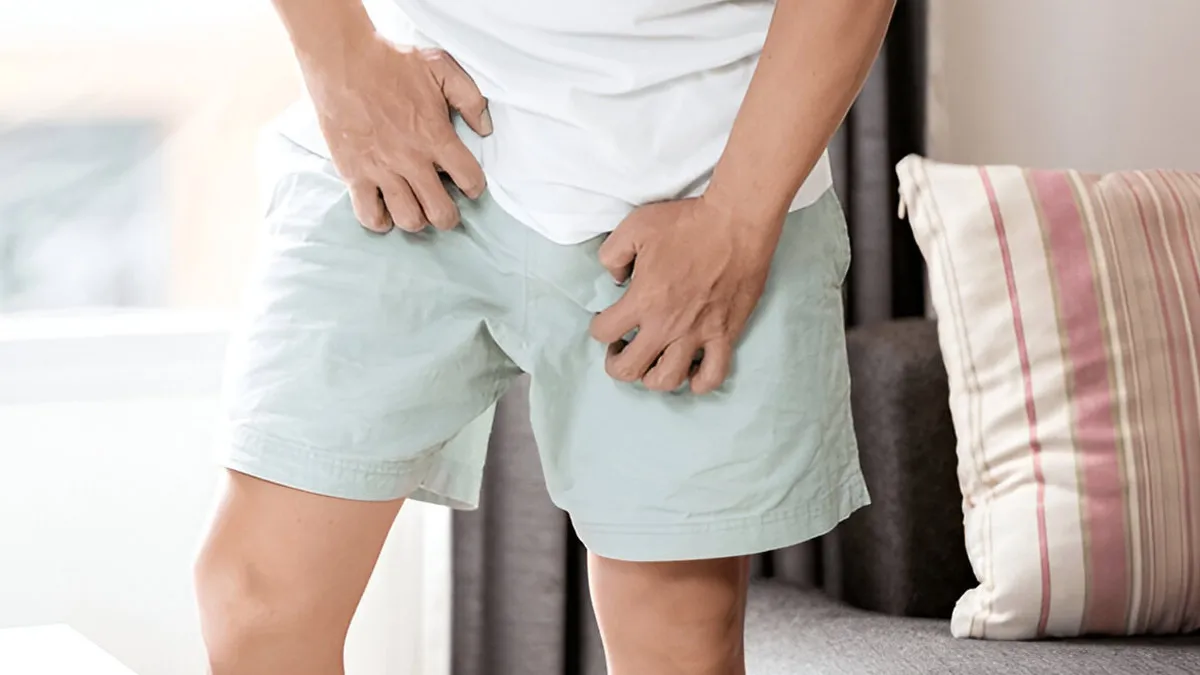

Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are infections that primarily spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 10 lakh curable STIs are acquired every day worldwide in people 15–49 years old, the majority of which are asymptomatic. The majority of the STIs are caused by bacteria or viruses; however, parasites and fungi can also lead to the infection.
Table of Content:-
In June 2024, the first sexually transmitted fungal infection in the US, caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII), was identified. The specific fungus was previously known to be transmitted sexually in other parts of the world, but this was the first time it was identified in the US as an STI.
Also Read: Why Shouldn't You Use Someone Else's Towel? Expert Shares Health Hazards
What Is Trichophyton Mentagrophytes Type VII?
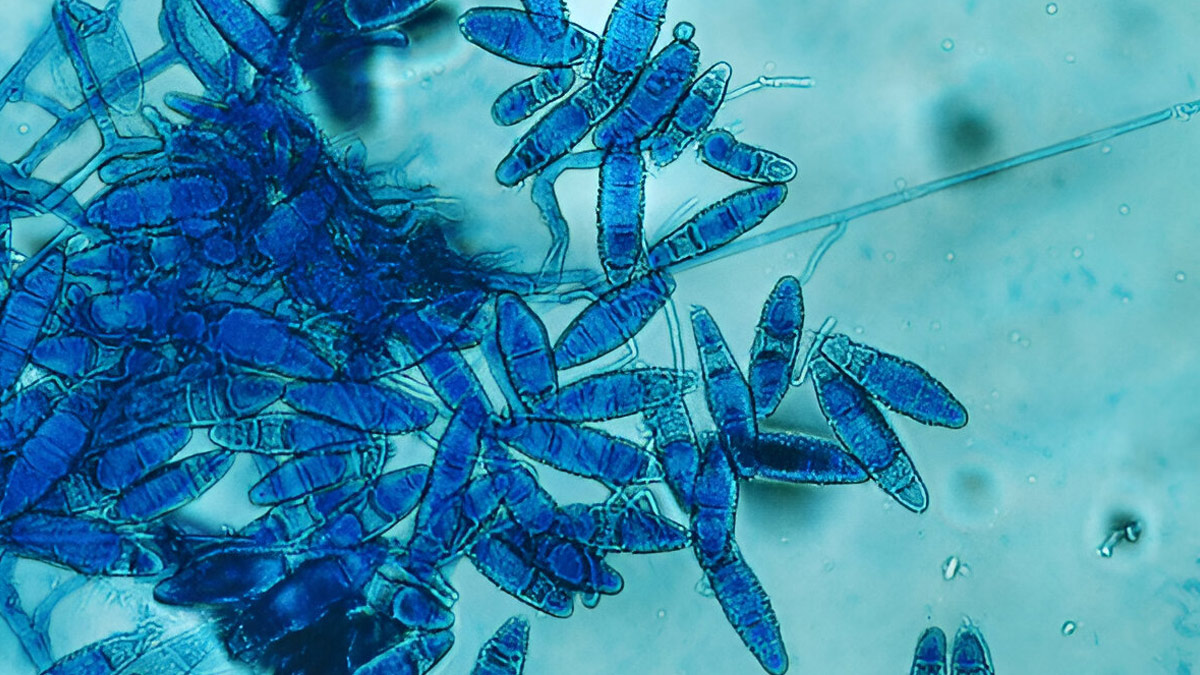
Trichophyton Mentagrophytes Genotype VII (TMVII) is an emerging dermatophyte fungus, a type of ringworm, that can be transmitted through sexual contact. It's closely related to T. indotineae and is known for causing inflamed, painful, and persistent skin lesions, often on the genitals, buttocks, or face.
"Unlike bacterial STIs, fungal STIs like TMVII cause a skin rash instead of a discharge. They are treated with antifungal pills, rather than antibiotics, so accurate diagnosis is critical to effective, targeted treatment and recovery," Dr Arpi Sagar Lodha, Consultant - Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Motherhood Hospitals, HRBR Layout, Bengaluru, tells the OnlyMyHealth team.
A recent study published in Mycoses Diagnosis, Therapy and Prophylaxis of Fungal Diseases reports that in 2019, TMVII was identified in Germany as a cause of sexually transmitted tinea. Since 2023, the fungal infection has been seen in men who have sex with men (MSM) in France, Italy, and the United States.
How Does Sexually Transmitted Fungal Infection Spread?
According to Dr Lodha, fungal STI spreads by sexual intercourse, resulting in ulcers on the genital area, leading to sexual transmission as the most common route for the infection. "It is transmitted via direct skin contact during intercourse, transmitting the spore or fungus from one person to another."
Other environmental conditions can also increase the risk of transmission, as tropical and humid environments are the most favourable for fungi to grow and survive.
Symptoms Of A Fungal STI To Watch Out For
Fungal STIs usually present as painful, inflamed skin plaques and are distinctly different in appearance compared to a bacterial or viral infection, shares Dr Lodha. Symptoms may include:
- Continuous or intermittent itching
- Itchy, scaly, and circular or annular lesions
- Burning sensitivity
- Localised swelling with or without treatment
- Rash on various body parts, particularly genitals, groin, and buttocks
- Pustules or pus-filled lesions
- Possible blistering and cracking of the skin
- Swollen lymph nodes
Also Read: Is That A Fungal Patch Or Just Hyperpigmentation? Simple Ways To Manage Both
Diagnosis And Treatment
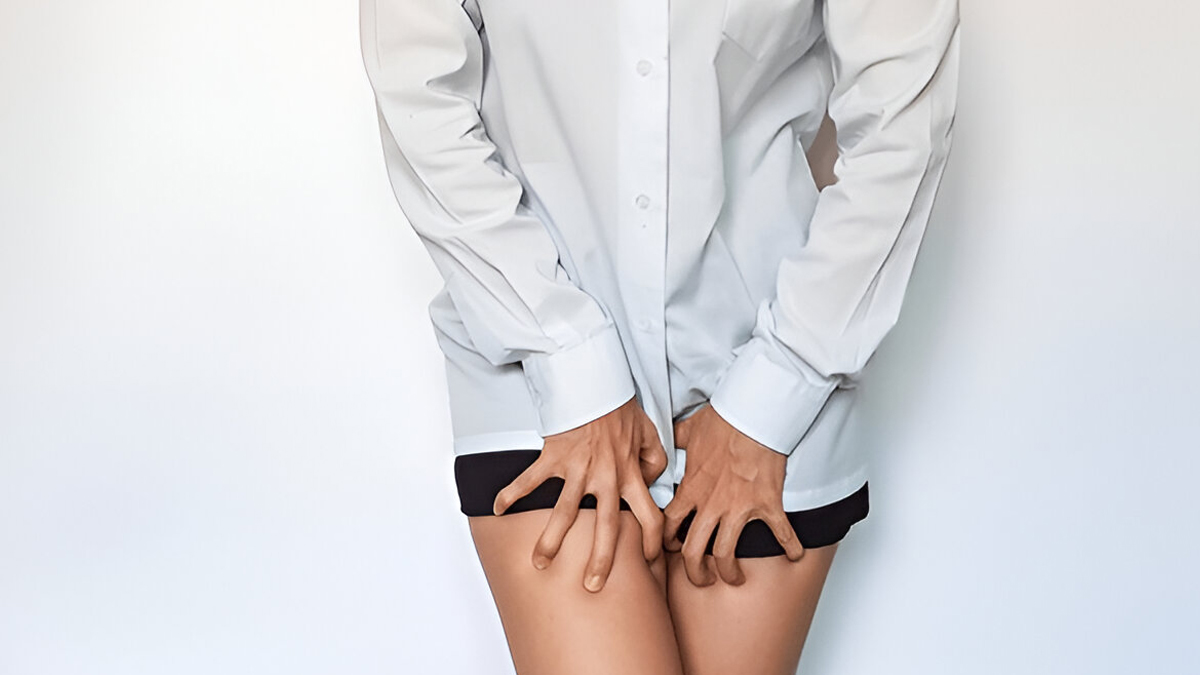

Diagnosing fungal STIs like TMVII requires clinical evaluation and fungal cultures from lesion edges. According to Dr Lodha, cultures are slow but essential for identifying the fungus and guiding treatment.
As far as treatment is concerned, oral antifungals like terbinafine or itraconazole are preferred over topical creams. Treatment usually lasts 2–6 weeks, depending on severity. Remember, self-medication with Over-The-Counter (OTC) antifungals is discouraged; proper prescription is key.
How To Prevent Fungal STIs
Some of the common ways to prevent the spread of fungal STIs include:
- Steering clear of infected partners, but this may not always be feasible.
- Having protected sex (condoms or dental dams)
- Regular STI testing and good hygiene practices
- Do not share personal items.
- Wear breathable, loose-fitting clothing to help stay dry and reduce fungus risk.
Conclusion
While most cases of sexually transmitted infections are caused by viruses or bacteria, fungal STIs have also become prevalent in recent years. Fungal infections such as TMVII were only recently identified as sexually transmitted infections, but it is crucial to still take them seriously. Diagnosing the condition is crucial for receiving appropriate and timely treatment. Consult a doctor if you notice symptoms.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
