
A whopping 13 million people suffer stroke each year, as per the World Stroke Association. Among them 5.5 million die. The disease prevalence is higher in low and middle-income countries, which includes India, as compared to the richer ones. The gap is so wide that two out of three individuals who suffer a stroke are from these countries, where preventive and stroke management facilities are inadequate. Lack of awareness around the disease and its signs and symptoms also play a role in making strokes among the biggest killers in the world. Then there are myths as well, which add fuel to the lack of awareness around stroke. And to bust some of such myths, Onlymyhealth spoke to Dr Shafeeq Mattumal, Senior Consultant and HOD - Cardiology, Aster MIMS, Calicut. But before that, let us understand the disease a bit better.
Table of Content:-
What Is Stroke?
A stroke occurs whenever the supply of blood to a certain part of the brain is disrupted. This blocks the supply of oxygen and vital nutrients, as a result of which the brain cells begin to die. Based on the cause, stroke is basically divided into two types:
- Ischemic Stroke: Due to a blocked artery
- Haemorrhagic Stroke: Due to a leak in a blood vessel
There is a third kind of stroke in which blood supply to the brain is temporarily disrupted. It doesn’t cause any lasting symptoms and is called transient ischemic attack.
Types Of Stroke
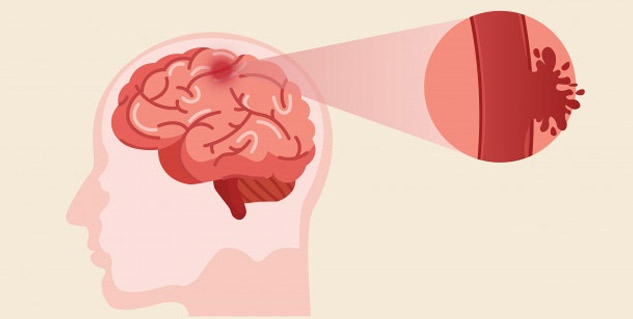
(Photo Credit: Freepik)
Let us now understand the types of stroke one by one:
Ischemic Stroke
This is the most common kind of stroke.
- It happens when blood vessels of the brain either get narrow or blocked, restricting the flow of blood.
- The blood vessels can get clogged due to fatty deposits. It can also happen if blood clots move into the blood vessels in the brain through the bloodstream.
Haemorrhagic Stroke
This is the second kind of stroke.
- Hemorrhagic stroke happens when the blood vessel in the brain either ruptures or leaks.
- The vessel rupture or leak can happen due to several health conditions such as uncontrollably high blood pressure, trauma, protein deposits in the walls of blood vessels, overuse of blood thinners, etc. Even ischemic stroke can lead to haemorrhage.
As you know transient ischemic attack is a third kind of stroke that lasts for a short duration of time. It happens when a clot or debris reduces blood flow to a part of the nervous system. This doesn’t last for a long time. No matter what kind, timely stroke management is crucial, the most important part of which is to reach the hospital on time.
Also read: Heart Attack, Cardiac Arrest, Stroke: What Is The Difference?
Stroke: Myths vs Facts

(Photo Credit: Freepik)
Now that you have a clear understanding about the disease, let us look at some of the myths and their corresponding facts about strokes.
Myth 1: Stroke Is More Prevalent Among The Elderly
Fact: Anyone, regardless of age or gender, can suffer from stroke.
Nowadays, many young people are dying of stroke. In fact, a study conducted at a hospital in Kolkata found that 31.38% of people who suffer stroke are the youth. This clearly shows that the disease burden is high among the young individuals in India.
Myth 2: Signs Of Stroke Are Difficult To Recognise
Fact: This is far from reality. In fact, the signs of stroke are easily recognisable.
BE-FAST (Balance, Eyes, Face, Arm, Speech, Time) is a test using which even a person from a non-medical background can recognise stroke. For more clarity, here are some of its symptoms:
- Headache
- Confusion
- Difficulty in understanding speech
- Paralysis or numbness of the arm, leg, or face
- Trouble walking
- Blurred vision in one or both the eyes
Myth 3: Sedentary Lifestyle & Co-Morbidities Are Not Major Contributors Of Stroke
Fact: The reality is quite the opposite. Both sedentary lifestyle and co-morbidities increase a person’s risk of suffering a stroke.
Although major technological strides have been made to cure this life-threatening condition. However, when it comes to diseases, prevention is always better than cure. Since stroke has associated risk factors that includes lifestyle and co-morbidities, it is crucial to manage these. Here are some tips that can help:
- Manage your blood pressure
- Lower your intake of saturated fat and bad cholesterol
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Quit smoking
- Manage diabetes
- Have a healthy weight
- Have a balanced diet, which includes lots of fruits and vegetables
- Exercise regularly
Also read: 1 In 4 Suffer From Stroke Globally: Know How To Prevent It
By following these, you can lower your chances of getting a stroke significantly. In case one suffers from it, stroke management is extremely crucial. The patient must reach the hospital as soon as possible, or at least within three hours since the onset of symptoms.
(With inputs from Dr Shafeeq Mattumal, Senior Consultant and HOD - Cardiology, Aster MIMS, Calicut)
Photo Credit: Pixabay
Also watch this video
Read Next
Stomach Bug Vs Food Poisoning: Know Difference Between Causes, Symptoms Of These Two Conditions
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version