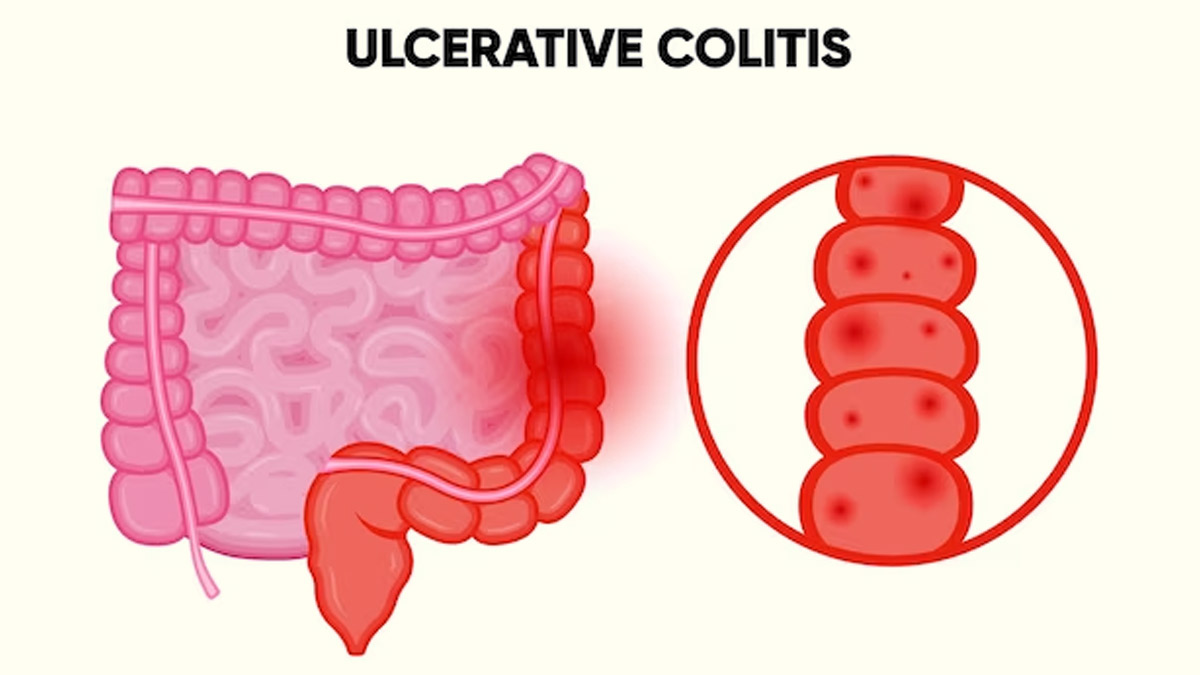
Do you experience abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or persistent urgency to have bowel movements? This may be a sign of a health condition called ulcerative colitis. It is a chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) characterised by inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum and is thought to result from an abnormal immune response. We spoke to our expert Nupuur Patil, Nutritionist, who explained ulcerative colitis and dietary tips to manage it.
Table of Content:-

According to HHS Public Access, ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown origin that primarily impacts the colon. This condition is characterised by recurring episodes of mucosal inflammation that begin in the rectum and extend into the upper parts of the colon. It frequently occurs in adults aged 30-40 and can lead to disability.
Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis

Patil shared symptoms of ulcerative colitis as follows:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea
- Rectal bleeding
- Persistent urgency to have a bowel movement
She added, “It can lead to complications, such as anaemia, malnutrition, and an increased risk of colon cancer.”
Risk Factors For Ulcerative Colitis
We asked our expert the risk factors for developing ulcerative colitis and she listed the following:
- Family History: A family history of IBD increases the risk
- Age: It often starts in early adulthood, but can develop at any age
- Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for UC but a protective factor for Crohn's disease, another type of IBD
- Environmental Factors: Diet, stress, and environmental factors may play a role
Als Read: World Inflammatory Bowel Disease Day: Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn's Disease
Dietary Tips To Follow

Patil listed the dietary tips for people dealing with ulcerative colitis as follows:
- Low-Residue Diet: Focus on easily digestible, low-fibre foods to reduce bowel movements and irritation
- Protein: Opt for lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and tofu
- Cooked Vegetables: Steamed or cooked vegetables are easier to digest than raw ones
- Fruits: Choose peeled, ripe fruits like bananas, melons, and applesauce
- Cereals: Select refined cereals like white rice and pasta for better tolerance
- Dairy Alternatives: Lactose-free or dairy-free options can help if you're lactose intolerant
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to prevent dehydration from diarrhoea
- Monitor Trigger Foods: Keep a food diary to identify personal trigger foods
Also Read: Can Probiotics Improve Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms? Read This To Find Out
Foods to Avoid In Ulcerative Colitis

In addition to the dietary tips mentioned above, Patil listed foods that you should be avoiding as follows:
- High-Fiber Foods: Foods high in fibre, such as nuts, seeds, and raw vegetables, should be avoided as they can potentially irritate the digestive tract, leading to discomfort and exacerbation of symptoms in individuals with ulcerative colitis.
- Dairy Products: Dairy products may be problematic, especially for those who are lactose intolerant. They can trigger discomfort and gastrointestinal issues, making it advisable to opt for lactose-free or dairy-free alternatives.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol consumption should be limited. These substances can stimulate the gut and may worsen symptoms or trigger discomfort.
- Spicy and High-Fat Foods: Spicy foods and high-fat meals can lead to inflammation and diarrhoea. It is advisable to steer clear of these foods, especially during active flare-ups of the condition.
- Carbonated Beverages: Carbonated beverages can contribute to gas and bloating, which are common symptoms of ulcerative colitis. Avoiding such drinks may help reduce discomfort.
- Artificial Sweeteners and Sugar Alcohols: Artificial sweeteners and certain sugar alcohols may worsen symptoms in individuals with ulcerative colitis. It's important to be cautious and check food labels for these ingredients.
- Regular Diet Monitoring: People with ulcerative colitis should consistently monitor their diet to identify specific trigger foods that may worsen their symptoms. Keeping a food diary can be a useful tool for this purpose.
Bottomline
Patil concluded, “Individual responses to specific foods can vary, so it's essential to work closely with healthcare professionals, including gastroenterologists and dietitians, to create a personalised dietary plan tailored to your specific needs. The goal is to manage symptoms, maintain nutrition, and improve overall quality of life while avoiding foods that exacerbate the condition.”
[Disclaimer: The information in this article is shared by a registered healthcare professional and is for informational purposes only. We advise you to not substitute this information with medical treatment and consult your expert for a treatment plan tailored to your needs.]
Also watch this video
Read Next
Risk Of Post-COVID Complications And Death Remains High Even After Two Years Of Getting COVID: Study
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version