When we discuss chronic illnesses, a chronic disease that often leaves experts perplexed is Crohn's Disease. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory illness of the digestive tract. It has the potential to affect any area of your digestive tract, from your mouth to your anus. However, it typically affects the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine.
According to Dr Adi Rakesh Kumar, Consultant Gastroenterologist, Therapeutic Endoscopist, and Endocrinologist at Yashoda Hospitals in Hyderabad, "Crohn's disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus." According to him, it involves inflammation that can penetrate the entire thickness of the intestinal wall and can occur in various segments of the digestive tract, with healthy portions of the gut in between the inflamed areas.
What is Crohn's Disease?
Crohn's Disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the digestive tract. Unlike its sibling condition, ulcerative colitis, which is localised in the colon, Crohn's can affect any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus. It is characterised by chronic inflammation that can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Certain factors, according to a 2012 study, can influence the severity of your symptoms. These are some examples:
- Whether you smoke
- Your age
- Whether the rectum is involved, and how long you've had the disease
Also read: Stop Sucking In Your Stomach, It Can Damage Your Organs!
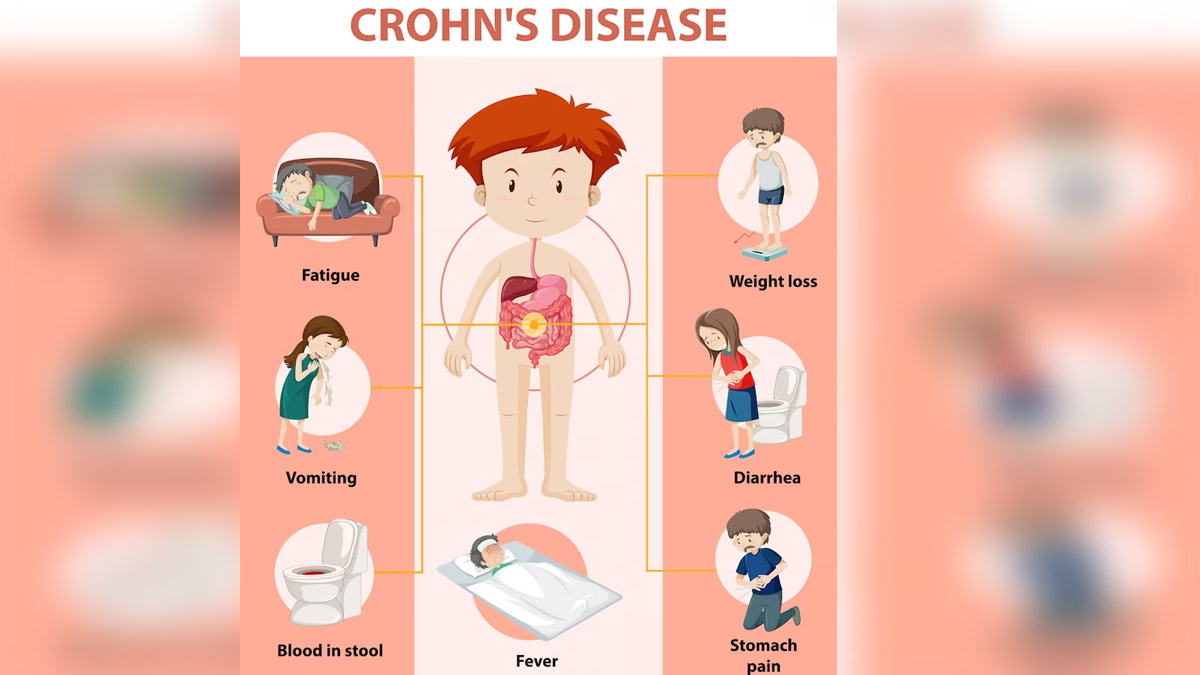
Symptoms of Crohn's Disease
- Abdominal Pain: One of the hallmark symptoms is abdominal pain, often severe and cramp-like, occurring in the lower right abdomen.
- Diarrhoea: Frequent, watery diarrhoea is common, sometimes accompanied by blood in the stool.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and nutrient malabsorption can lead to fatigue and weakness.
- Weight Loss: Reduced appetite, nutrient absorption issues, and diarrhoea can result in unintentional weight loss.
- Inflammation Beyond the Gut: Crohn's can cause inflammation in other parts of the body, such as the eyes, skin, and joints.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Crohn's Disease can be challenging because its symptoms often overlap with other gastrointestinal disorders. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Endoscopy and colonoscopy to visualise the digestive tract
- Imaging studies like CT scans and MRI
Treatment Options
While there is no known cure for Crohn's Disease, several treatment options can help manage its symptoms and induce periods of remission:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and control symptoms.
- Nutritional Therapy: Some individuals benefit from dietary modifications or exclusive enteral nutrition to manage symptoms and promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when complications arise, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove damaged sections of the digestive tract.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and avoiding trigger foods can help reduce symptom flare-ups.

Crohn's Disease is a complex and unpredictable condition that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing it, advances in medical research and treatment options continue to offer hope to those living with the condition. If you or a loved one suspect Crohn's Disease, seek medical attention promptly.
Also read: Stomach-Related Symptoms Triggered By A Fatty Liver
With the right medical care, support, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with Crohn's can lead fulfilling lives while managing their symptoms effectively.
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version