If you've noticed unexplained swelling, sharp pain, or even redness in your leg, it may indicate thrombosis. This condition, where blood clots form in the veins or arteries, can often go unnoticed until symptoms become severe. The impact of thrombosis can be far-reaching, ranging from swelling in the legs to more serious conditions like heart attacks or strokes. We spoke to our expert Dr Muralidaran C, Consultant Hematologist, Wockhardt Hospitals, Mira Road, who provided insights into this condition, its various types, symptoms, and the importance of early detection and treatment in protecting your health.
Table of Content:-
What Is Thrombosis?
"Thrombosis is a medical condition that results in the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels, which can occur in either the veins or arteries. These clots, known as thrombi, can disrupt normal blood flow," explained Dr Muralidaran.
Various factors can contribute to thrombosis. This can include reasons like being physically inactive for a longer duration, being diagnosed with certain medical conditions, or severe injuries that can damage your blood vessels.
"Multiple factors can lead to the formation of a thrombus (blood clot), such as drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes, genetic makeup, and being obese," added Dr Muralidaran.
Also Read: Feet Swelling While Travelling: When Should You Be Concerned?
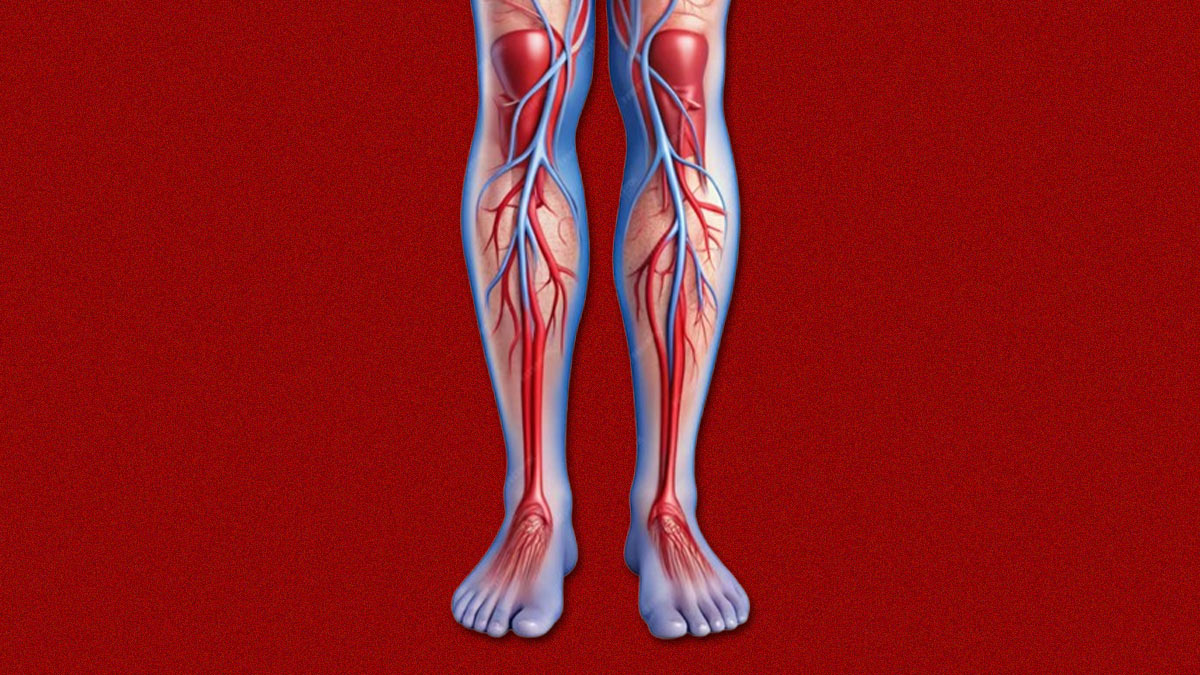
Types of Thrombosis

- Venous thrombosis: This particular type of thrombosis usually occurs in the veins. One of the common examples of venous thrombosis is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), which is more likely to develop in the legs. As time passes, individuals with DVT may develop swelling and intense pain in the affected leg.
- Arterial thrombosis: It mostly happens in the arteries. Arterial thrombosis can restrict the blood from flowing to the other parts of the body. A blood clot in the coronary artery can cause a heart attack, while one in the brain may trigger a stroke.
According to StatPearls, the incidence of thrombosis varies based on factors like whether it's venous or arterial, provoked or unprovoked, and whether it's the first or a recurring episode. For Venous Thromboembolism (VTE), the annual incidence is 1 per 100,000 in children, 1 per 10,000 in reproductive-age individuals, 1 per 1,000 in middle-aged adults, and 1 per 100 in older patients.
Also Read: Deep Vein Thrombosis Vs Pulmonary Embolism: Experts Share Key Differences
Symptoms of Thrombosis
"When the blood clots are formed one can experience a range of symptoms. The intensity and the severity of the symptoms can vary from person to person depending on their condition and the location of the clots," said Dr Muralidaran.
The symptoms can include:
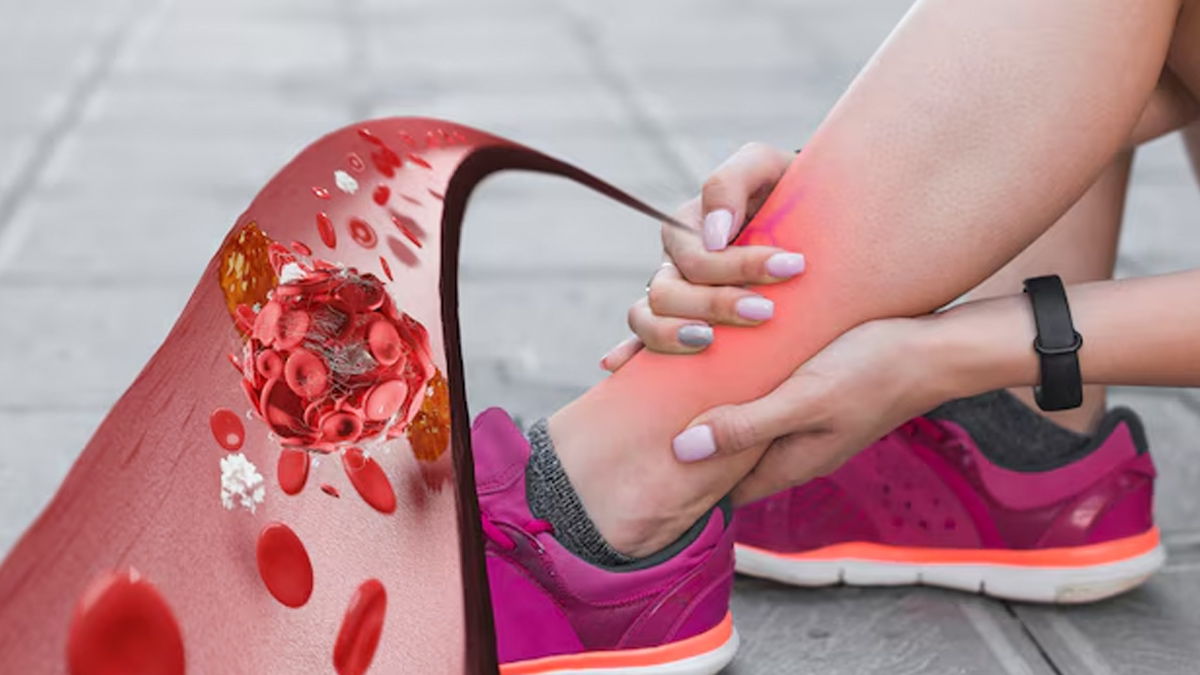

- Swelling
- Inflammation
- Unbearable pain
- Redness in the affected leg
- Chest pain
- Weakness
- Difficulty in speaking
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
It becomes crucial to address these symptoms promptly to detect the formation of blood clots early on.
Treatment for Thrombosis
- Consult a Doctor: Seek medical advice if you notice symptoms of thrombosis; early detection is crucial.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe anticoagulants or blood thinners to prevent existing clots from growing and to stop new ones from forming.
- Compression Stockings: For Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), wearing special stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling.
- Thrombectomy Surgery: In severe cases, thrombectomy may be performed to remove the blood clots.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Stay physically active
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet
- Maintain an optimal weight
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of thrombosis
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your own professional if you are dealing with any health issues to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version