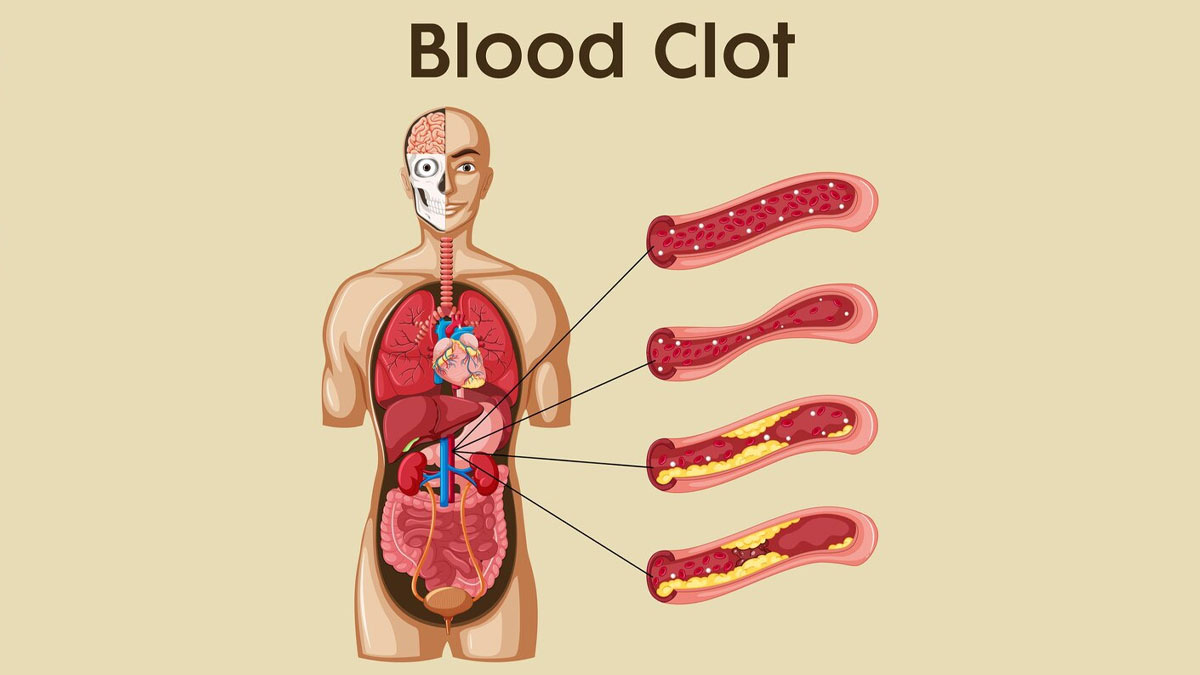
A blood clot is a gel-like clump of blood that forms in response to a cut or injury, acting to stop the bleeding by plugging the injured blood vessel. While this is a normal part of the healing process, clots can sometimes form unexpectedly and block blood vessels. This blockage can prevent blood from reaching vital organs, such as the lungs, resulting in serious health issues. We spoke to our expert Dr Mahadeva Swamy, Consultant Hematologist, Manipal Hospitals, Goa, who explained blood clots, symptoms, and their treatment.
Table of Content:-
What Is A Blood Clot?

“Blood clots can affect people of any age, gender, or race and typically form in one of the large veins. This includes areas, such as the lower leg, thigh, pelvis, or arm and is known as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT),” said Dr Swamy.
He said, “A blood clot can partially or completely block blood flow in a vein. If DVT is not treated, a portion of the clot may break loose and travel to the lungs, resulting in a blockage called Pulmonary Embolism (PE).”
According to NIH Medline Plus, PE is a condition where a blood clot in the lungs blocks blood flow to parts of the lung, which can make breathing difficult. It is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that can cause damage to the lungs and other organs, and may even lead to death.
Symptoms Of Blood Clot
Being aware of the symptoms of a DVT or PE can help you identify the need for medical treatment as soon as possible, even though they may sometimes be asymptomatic. If you have any of the symptoms mentioned below, alert your doctor as soon as possible:
Common Symptoms of a DVT
- Swelling of the affected area
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Redness of the skin
Common Symptoms of PE
- Difficulty breathing
- Faster than normal or irregular heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
- Low blood pressure
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
According to the American Society of Hematology, certain risk factors, such as obesity, can slow blood flow in the veins, while others, like age, can enhance the body's natural clotting ability. Also, some medications can influence how quickly your blood clots.
Treatment For Blood Clots
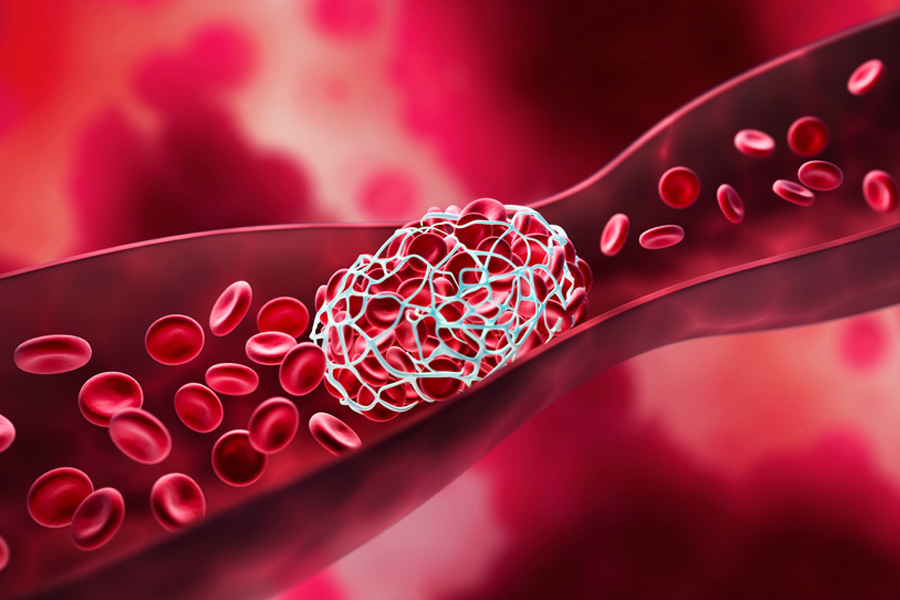
“Thrombolysis with blood thinners (oral medications or injections), and appropriate initiation of therapy can save life and limb complications. Re-assessment after blood thinners/thrombolysis to decide about interventional procedures to prevent complications,” highlighted Dr Swamy.
According to the National Institutes Of Health, US, in some cases, people with certain heart conditions are prescribed blood thinners to prevent blood clots. However, blood thinners can have side effects, including an increased risk of bleeding, so doctors do not prescribe them to everyone.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that DVT and PE impact up to 900,000 Americans each year. In the United States, these blood clots cause about 100,000 fatalities every year.
What You Should Know
Blood clots are often underdiagnosed. If left untreated, these clots can cause serious medical conditions that can lead to illness, disability, and even death.
“Blood clots can affect anyone, but certain risk factors, such as pregnancy, cancer and its treatment, and hospitalisation/long-term immobilisation can increase a person's risk for a blood clot. It's crucial to recognise the warning signs and symptoms of a blood clot to promptly seek medical attention,” said Dr Swamy.
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your own professional if you are dealing with any health issues to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version