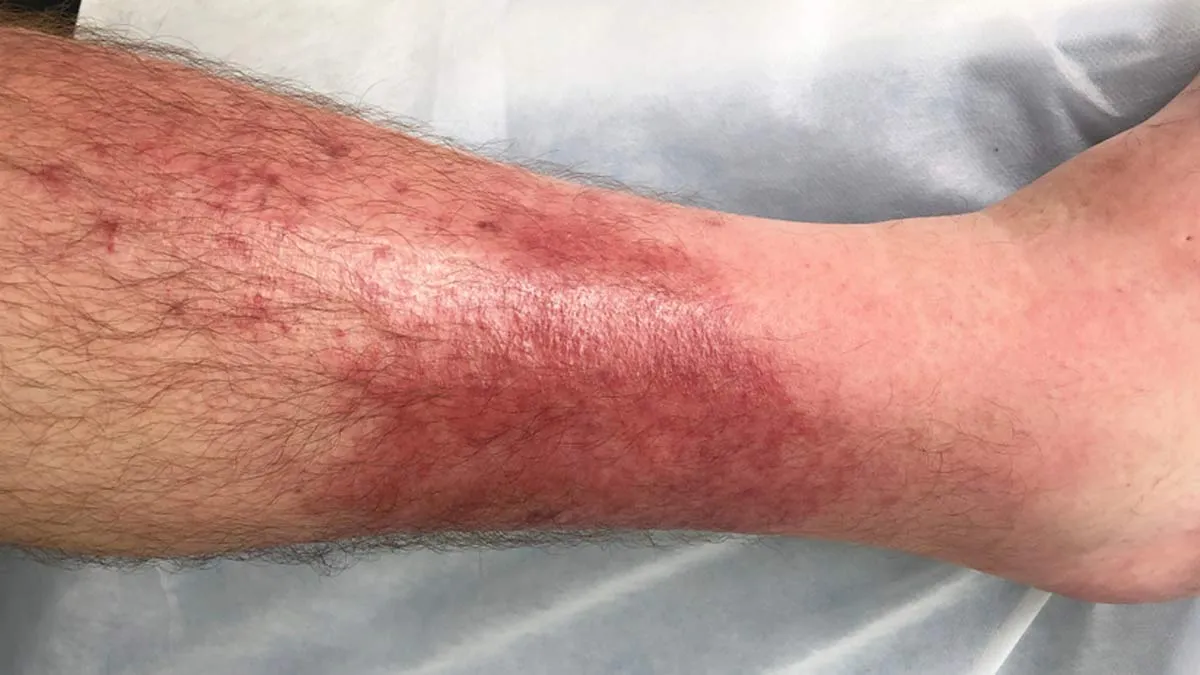
When it comes to our skin, we often overlook minor issues like redness, thinking they’re just part of daily life. However, ignoring these seemingly harmless signs can lead to serious health problems. For instance, conditions like cellulitis can cause an infection that spreads to deeper layers of the skin. Recognising early signs, such as swelling, warmth, and tenderness is essential. We spoke to our expert Dr Deepa Krishnamurthy, Consultant – Dermatologist, Manipal Hospital, Sarjapur Road, Bengaluru, who explained the complications of cellulitis and how to prevent it.
Table of Content:-
What Is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria penetrate the skin's barrier, leading to an infection that spreads to the deeper skin layer (dermis) and subcutaneous tissues. "Small cuts, insect bites, or cracks in the skin often provide these bacteria with entry points. Redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness are the hallmark signs of cellulitis," said Dr Krishnamurthy.
According to StatPearls, cellulitis is common and typically affects middle-aged and older adults. It shows no significant difference in the incidence of cellulitis between men and women and occurs in about 50 cases per 1,000 patient-years.
Leaving minor skin irritations untreated can lead to severe complications, such as abscesses, sepsis, and deep tissue infections. It is essential to pay attention to our skin's signals, as taking prompt action can prevent unnecessary health risks.
Also Read: Cellulitis: Causes Of The Skin Condition That Mostly Affects Your Legs
Complications of Cellulitis
Ignoring these early signs allows the infection to penetrate deeper into the tissues and increases the risk of severe complications. Here are some of the complications, as listed by Dr Krishnamurthy:
- Abscess Formation: The infection can lead to abscesses—pockets of pus that form under the skin. These require drainage and, if left untreated, can worsen and spread.
- Sepsis: This is one of the most dangerous complications of cellulitis. When bacteria spread into the bloodstream, they can trigger sepsis, a life-threatening condition that leads to widespread inflammation and organ failure.
- Lymphangitis: The infection may spread to the lymphatic system, resulting in inflamed lymph vessels. This condition can be recognised by red streaks radiating from the infected area.
- Deep Tissue Infections: Left untreated, cellulitis can spread to deeper tissues, including muscles, bones (osteomyelitis), and joints. Once the infection reaches these levels, treatment becomes more complicated, and surgery may be required.
Also Read: How Cellulitis Affects The Eye: Signs Of The Skin Infection To Watch Out For
Who Is At Risk?
While cellulitis can affect anyone, certain groups are at higher risk:
- Individuals with Compromised Immune Systems: People with diabetes, HIV, cancer, or those taking immunosuppressive medications are more vulnerable to bacterial infections, including cellulitis.
- People with Chronic Skin Conditions: Conditions, such as eczema or Athlete’s foot create cracks or openings in the skin, providing an entry point for bacteria.
- Obesity and Poor Circulation: Those who suffer from poor circulation due to obesity or conditions, such as chronic venous insufficiency are at increased risk of developing cellulitis, as these conditions weaken the body’s ability to fight off infection.
- Age and Skin Integrity: Older adults may have thinner skin, which is more susceptible to injury, increasing the risk of infection.
- Intravenous Drug Use: Sharing needles or using non-sterile techniques can introduce bacteria directly into the body.
How To Prevent Cellulitis
Prevention is key, especially for those with chronic skin conditions or weakened immune systems. Here are some measures listed by Dr Krishnamurthy that you should follow:
- Keeping Wounds Clean and Covered: Promptly clean and protect any breaks in the skin to minimise infection risk.
- Moisturising Skin Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated helps prevent cracking, which can lead to entry points for bacteria.
- Treating Any Skin Conditions Promptly: Conditions, such as Athlete’s foot, eczema, or psoriasis should be managed effectively to reduce infection risk.
- Using Proper Foot Care: Wearing protective footwear and inspecting feet regularly can help avoid injuries that may lead to cellulitis.
- Monitoring Surgical Wounds or Cuts: Especially for individuals with diabetes or poor circulation, vigilance in caring for any wounds is crucial to preventing infection.
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your own professional if you are dealing with any health issues to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
