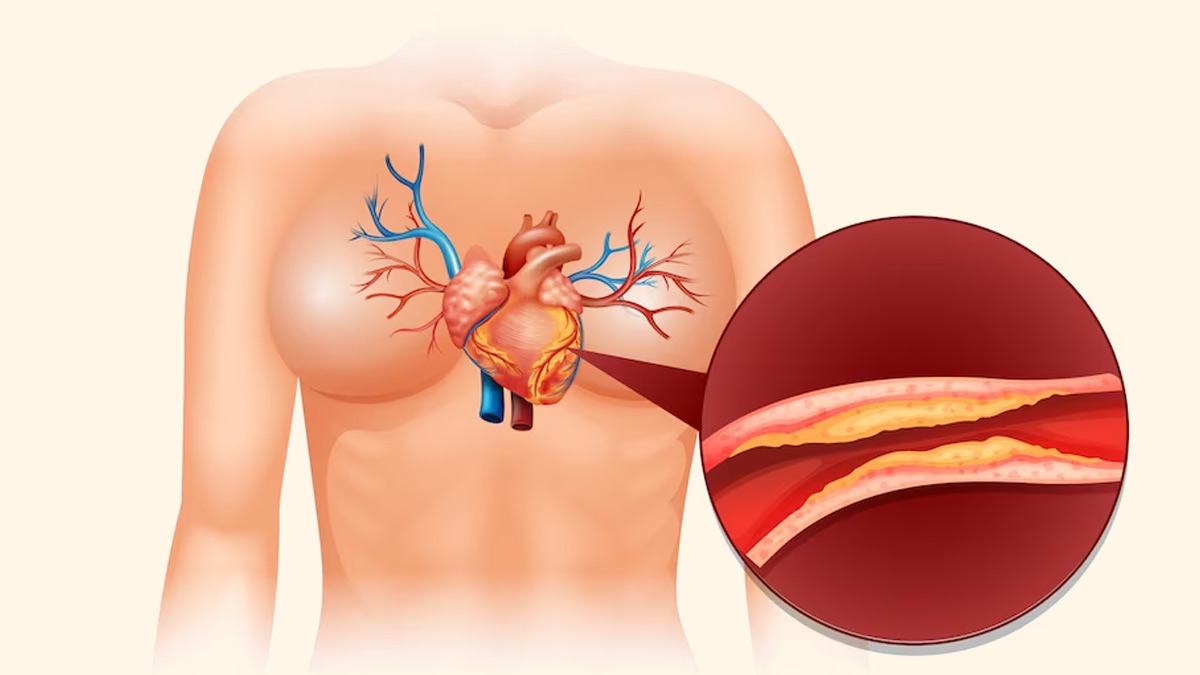
Our cardiovascular system is a network of arteries and veins that transport oxygen and nutrients to all parts of our bodies, including the heart. These important channels can become damaged due to a variety of circumstances, resulting in illnesses such as coronary artery disease (CAD).
Table of Content:-
Advancements in modern science have given rise to minimally invasive techniques such as angioplasty and stent implantation, providing patients with blocked arteries with hope and improved prognosis. In an interaction with Only My Health, Dr Shivanand S Patil, Senior Consultant Cardiology, Fortis Hospital, Bannerghatta Road, explained about the angioplasty and stent placement.
What Is Angioplasty and Stent Placement
Angioplasty, often combined with stent placement, is a medical process designed to restore blood flow in obstructed arteries. This innovative approach involves threading a thin, flexible tube known as a catheter through an artery in the groin or arm, guiding it to the site of the blockage.
According to the American Heart Association, angioplasty might take anything from 30 minutes to a few hours.
“Once positioned correctly, a small balloon attached to the catheter is inflated. The inflation of this balloon has a therapeutic purpose: it presses against the fatty deposits or plaques causing the artery to dilate, effectively widening the vessel and restoring normal blood flow,” Dr Patil said demonstrating the process.

“The procedure doesn't end with balloon angioplasty alone. To provide longer-lasting support and prevent the artery from recoiling , a stent is often implanted. A stent is a small, mesh-like tube made of metal that is inserted into the treated artery. Once in place, the stent acts as a scaffold, holding the artery open and ensuring that blood can flow freely,” said Dr Patil.
Also read: Angioplasty Or Bypass Surgery: When To Choose Which One, Explained By Expert
When are Angioplasty and Stent Placement Used?
Angioplasty and stent placement are versatile procedures used to address a range of arterial issues beyond just CAD:
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is one of the most common applications, where the procedures alleviate chest pain (angina) and improve overall heart function.
2. Peripheral Artery Disease: In this condition, arteries outside of the heart are affected, often leading to leg pain. Angioplasty and stent placement can help alleviate these symptoms and improve mobility.
3. Aneurysms: Weakening of artery walls can cause bulging or aneurysms. Stents can be used to reinforce the affected area and prevent further complications.
4. Stroke: In some cases, angioplasty and stent placement can be used to treat blocked arteries in the brain, reducing the risk of stroke.
5. Blood Clots: In specific situations, these procedures can be employed to remove or dissolve blood clots within arteries.
The Procedure and Recovery
According to Dr Patil, one of the remarkable aspects of angioplasty and stent placement is that they are minimally invasive, and patients can go home after 1 or 2 days after the procedure. But it's important to be aware of potential risks, including bleeding, blood clots, and damage to the artery.

“Recovery is generally swift, with patients often experiencing some discomfort, bruising, or tenderness at the insertion site. However, these side effects typically subside within a few days,” said Dr Patil, adding, strenuous activity should be avoided for a few weeks post-procedure.
Also read: 5 Empty Stomach Drinks To Consume For Better Heart Health
“Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. It is very important to continue all medications prescribed by your doctor, especially blood thinners. If blood thinners are skipped it can lead to clotting of blood inside the stent leading to massive heart attack,” Dr Patil added.
A Path to a Healthier Heart
Angioplasty and stent implantation have transformed the treatment of clogged arteries. They provide a less intrusive, more effective alternative to open-heart surgery, allowing patients to regain their quality of life with minimal disruption. It is critical to note, however, that these operations are not a solution for underlying diseases such as CAD. Long-term heart health requires lifestyle changes such as eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and stopping smoking.
“Angioplasty and stent placement represent remarkable achievements in the field of cardiovascular medicine. They provide a lifeline for individuals suffering from blocked arteries, offering renewed hope and a path to better cardiovascular health. By combining these procedures with a commitment to a healthier lifestyle, individuals can take charge of their heart health and reduce the risk of future complications,” Dr Patil concluded.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version