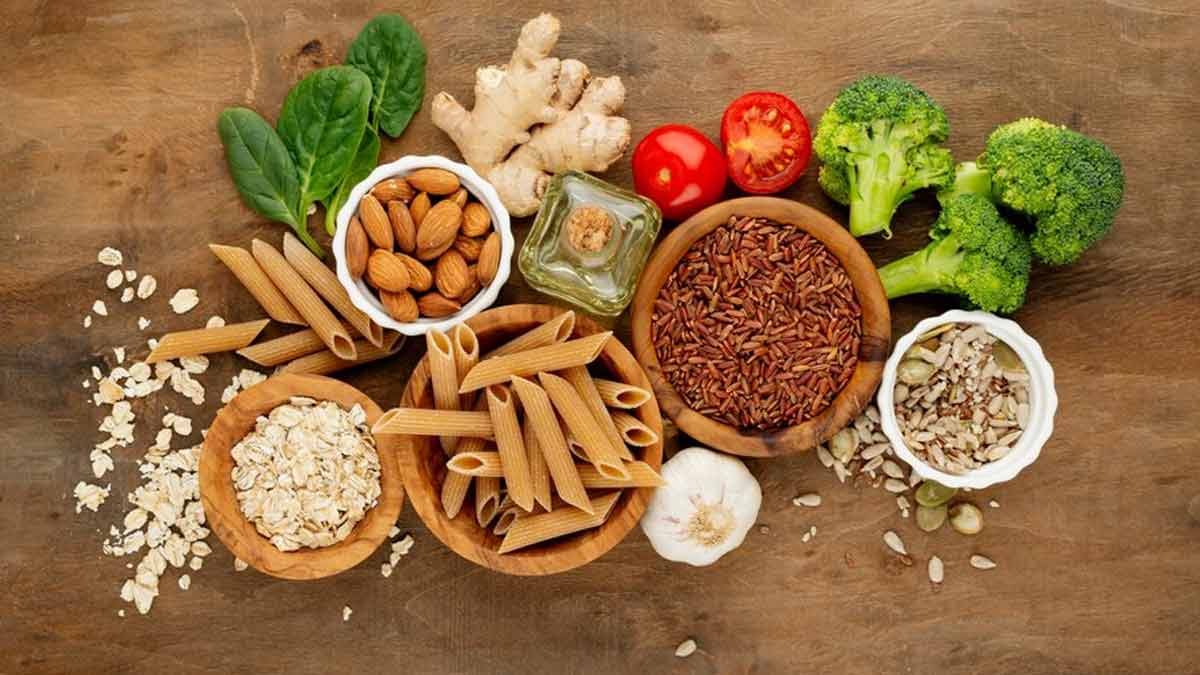

Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients, besides proteins and fats. Our body breaks it down into glucose (sugar), which in turn helps provide energy to our body's cells, tissues, and organs.
Table of Content:-
On the downside, all carbs raise blood sugar levels, which is why foods rich in carbohydrates are often considered unhealthy and unsafe for diabetes patients. But according to Dr Anurag Aggarwal, Consultant-Internal Medicine, Fortis Escorts Hospital, Faridabad, that is not entirely the case. In fact, carbohydrates are a combination of sugars, starches, and dietary fibre, which helps support several bodily functions.
So what is it that we may be doing wrong? Can we consume carbs without spiking blood sugar to alarming levels? Can diabetes patients also consume it? Here's all you need to know.
Also Read: How Diabetes Can Affect Different Parts Of The Body
Why Are Carbohydrates Considered Harmful For Diabetes Patients?
Diabetes occurs when the body does not produce or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that breaks down sugar in the blood for energy.
When people eat carb-rich foods, the digestive system turns them into sugar (glucose) that gets absorbed into the bloodstream. This in turn acts as a signal to your pancreas, which then releases insulin, causing the cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage.
As cells take up sugar, blood sugar levels drop, which then prompts the pancreas to produce glucagon, which instructs the liver to release its stored sugar back into the bloodstream.
Both insulin and glucagon help maintain a steady supply of sugar, especially for the brain.
However, in people with type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, causing blood sugar to stay high. Over time, the pancreas can't keep up with the demand for insulin, leading to complications. Therefore, with a faulty system, eating excessive carbs can spike blood sugar levels to alarming levels, especially in people with diabetes.
Tips To Eat Carbs Without Raising Blood Sugar Levels
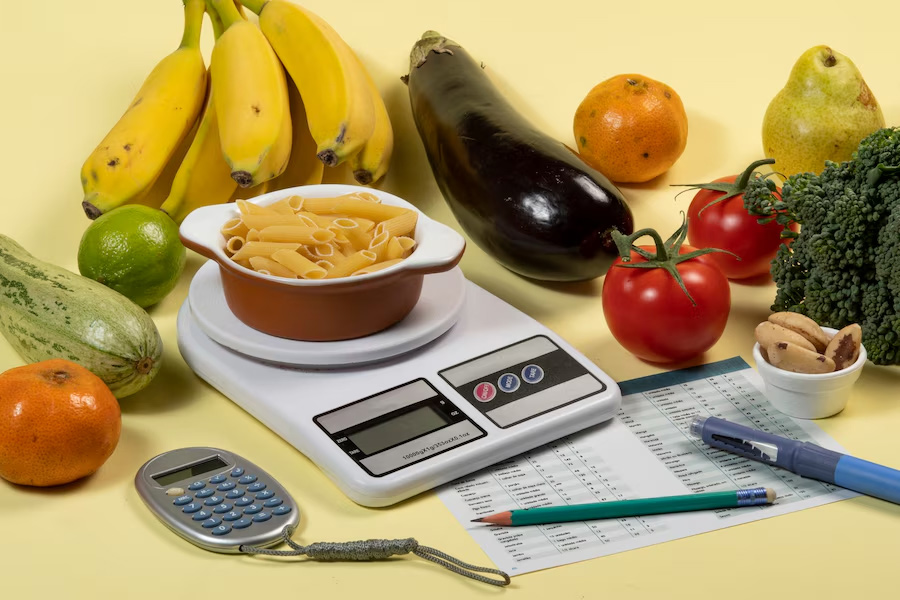

It is important to note that not all carbs are bad, and some amount is necessary to produce energy, even for diabetics. In fact, not only the amount but also the type of carbohydrates you consume can also make a significant difference to blood glucose levels and diabetes management. Let's look at some of the ways you can have carbs without spiking your blood sugar levels.
Moderate consumption is key
A study published in the Indian Journal of Medical Research suggests that excess consumption of sugary and processed carbs not only raises blood sugar too quickly but can also lead to type 2 diabetes. However, according to Dr Aggarwal, moderate consumption of complex carbohydrates is safe for diabetes patients.
Most people with diabetes report a moderate intake of carbohydrates, between 44 and 46 percent of total calories, according to research published in UpToDate.
However, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggest that there is no “one size fits all” answer to how much carbohydrate diabetics should consume. "The amount you can eat and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors," the health body says. It is best to consult a healthcare professional about the amount of carbs to consume, depending on your own individual needs and requirements.
Also Read: What Does An Ideal Breakfast Look Like For Diabetics: Foods To Eat And Avoid
Choose complex carbs
Not all carbs are bad for your health. In fact, diabetes patients need some carbs to support various functions in the body.
The key is to choose the right type of carbs. There are mainly two kinds: simple carbs and complex carbs.
Simple carbs are carbs that are made of sugars, such as fructose and glucose. They are mostly composed of only one sugar, monosaccharides, or two sugars, disaccharides. These are commonly found in candies, soda, syrups, white rice, and pasta and are easily utilised for energy by the body. Hence, they lead to a faster rise in blood sugar and insulin secretion from the pancreas, according to the US Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health.
On the other hand, complex carbs are made from three or more sugars, called oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, which makes it difficult for the body to break down and digest. These also contain fibre, vitamins, and minerals that do not have an immediate impact on blood sugar levels.
Fibre and starch are the two types of complex carbohydrates, of which fibre is more beneficial for digestive health and reduces the risk of various chronic conditions. These are found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains.
Distribute carbohydrate intake throughout the day
When it comes to consuming carbs, Dr Aggarwal also advises managing portion sizes and distributing carbohydrate intake throughout the day rather than consuming a large amount in a single meal. This may not only help maintain stable blood glucose levels but also provide a consistent source of energy.
Bottomline
To avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar levels, a balanced intake of carbohydrates is essential. This can be achieved by consuming complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Not only does it provide individuals with sustained energy, but it also helps them get the necessary vital nutrients. Additionally, mindful portion control and regular physical activity also play crucial roles in managing blood sugar levels effectively. However, consult your doctor to understand more about carbohydrate intake if you have diabetes.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
