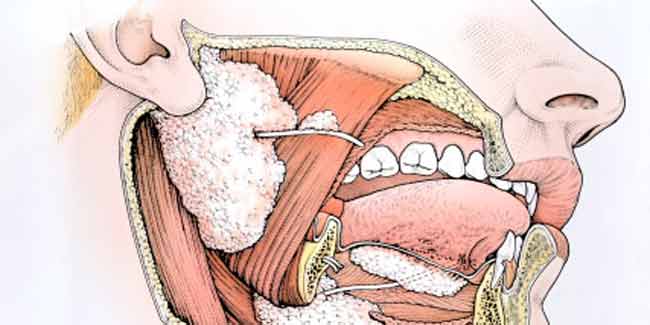
Bacterial infection of a salivary gland, which usually occurs due to obstructing stone or gland hyposecretion is known as sialadenitis. The symptoms of sialadenitis include swelling, pain, redness and tenderness. The diagnosis for sialadenitis is clinical and CT, ultrasonography and MRI help to diagnose the cause.
Table of Content:-

Risk Factors of Sialadenitis
The condition usually occurs in the parotid gland and typically occurs in:
- People who are in their 50s and 60s
- Chronically ill patients suffering from xerostomia
- Patients with Sjögren syndrome
- Patient who have had radiation therapy to the oral cavity
- Adolescents and young adults with anorexia
The most common organism that can cause sialadenitis is Staphylococcus aureus.
Symptoms of Sialadenitis
The most common symptom of sialadenitis are fever, chill and unilateral pain and swelling. The gland becomes firm and diffusely tender with erythema and edema of the overlying skin.

Treatment for Sialadenitis
The initial treatment for sialadenitis consists of antibiotics given against S. aureus. When the prevalence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus increases, especially among elderly living, vancomycin is given.
Diagnosis of Sialadenitis
CT scan, ultrasonography and MRI are used to diagnose sialadenitis or abscess which is not obvious clinically. MRI may miss an obstructing stone though. When pus can be expressed from the duct of the affected gland, it is sent for Gram stain and culture.
Image courtesy: Getty Images
Read more on Understand Sialadenitis.
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
