
Fatty liver disease, and specifically Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), has emerged as the most prevalent liver condition globally. According to stats, it impacts almost one in four individuals worldwide and is directly related to lifestyle factors, such as unhealthy diet, obesity, and insulin resistance. However, as awareness of the function of food in controlling chronic diseases has grown, superfoods such as quinoa have begun to get their due. While we all know that quinoa is healthy for weight loss and cardiovascular health, what about liver health?
Table of Content:-
In an exclusive interaction with the editorial team of Onlymyhealth, Dr Bhumesh Tyagi, Consultant, General Medicine and Physician, Shardacare, Health City, Noida, explained whether quinoa should save a spot on your plate when you're trying to reverse fatty liver. Here is what he shared with us.
What Is Fatty Liver Disease?
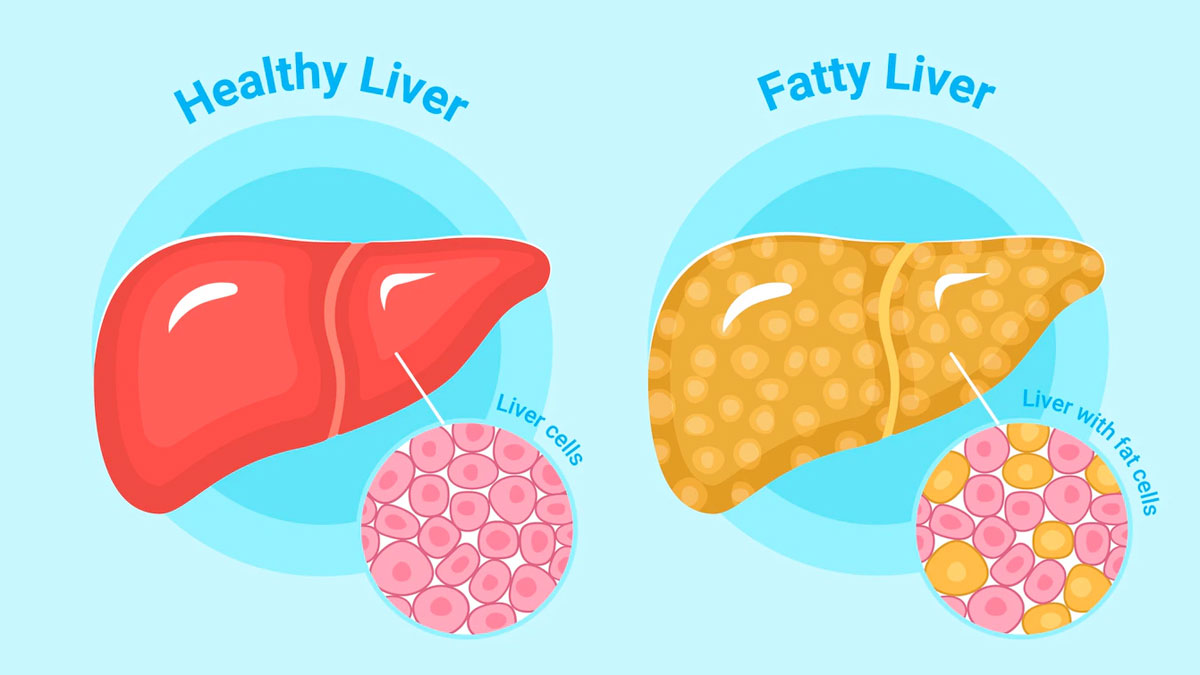
According to Mayo Clinic, fatty liver occurs when excessive fat builds up in the liver cells. The two most significant types:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and diet.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) results from excessive alcohol consumption.
If left untreated, fatty liver can develop into more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or liver cancer. However, Dr Tyagi highlighted that NAFLD may be reversed or greatly improved through lifestyle modifications, most notably diet.
Why Diet Plays a Role in Reversing Fatty Liver
Some dietary habits have been proven to lower liver fat and inflammation. Specifically, diets that:
- Are low in refined carbohydrates and added sugars
- Contain high-fibre, nutrient-dense foods
- Emphasise plant-based protein and healthy fats
- Are linked to improved liver outcomes.
Also Read: Should You Eat Beetroots Boiled Or Raw? Six Ways To Consume Beets
What Is So Great About Quinoa for Liver Health?
Quinoa is a seed, but it acts as a grain. It's been farmed for thousands of years and is generally lauded for its superior nutritional profile. Here's why quinoa could help promote liver health:
1. High in Fibre
Quinoa contains high levels of both soluble and insoluble fibre, and a high-fibre diet is a mainstay of NAFLD reversal. Here is how fibre helps:
- Lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels
- Decrease fat deposition in the liver
- Enhance gut microbiome, which is associated with liver health
2. Low Glycemic Index (GI)
In contrast to processed grains such as white bread or white rice, quinoa is a low glycemic index food. This implies that it:
- Does a less strenuous job on blood sugar
- Reduces insulin resistance, one of the main causes of fatty liver
3. Plant-Based Complete Protein
Quinoa is one of the rare plant foods that is rich in all nine essential amino acids. Adequate quality protein intake can:
- Enhance satiety and prevent overeating
- Contribute to muscle mass, which aids in metabolic health
- Decrease the accumulation of fat in the liver, particularly in place of red or processed meat
4. High in Antioxidants
Quinoa is rich in antioxidants like quercetin and kaempferol that could suppress inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver, two major drivers of fatty liver disease progression.
Dr Tyagi suggested swapping refined grains with whole grains such as quinoa as part of a diet plan that is beneficial for the liver.

Incorporating Quinoa into a Liver-Friendly Diet
Try these simple expert-approved ideas:
- Quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables and avocado
- Quinoa salad with leafy greens, chickpeas, and lemon-tahini dressing
- Replace white rice or pasta as a side dish with cooked quinoa
- Mix cooked quinoa with soups, stews, or even smoothies for added nutrition
Bottomline
Concluding his insights, Dr Tyagi affirmed that yes, quinoa may be a useful component of a diet to reverse or control fatty liver disease. It is high in fibre, low in sugar, and rich in plant protein and antioxidants. Although it is not a silver bullet, adding quinoa consistently to a balanced whole-foods-based diet may be helpful for both liver and metabolic health.
As always, talk to your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making major dietary changes, especially if you’ve been diagnosed with liver disease.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
Aug 04, 2025 11:42 IST
Published By : Chanchal Sengar