Fungal infections, or mycosis, are common diseases caused by fungi, tiny, microscopic organisms that thrive in the air, soil, water, plants, and even the human body, in areas like the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and on the skin. While fungal infections are usually not contagious, there are certain types that can spread from one person to another or from one area in the body to another. The OnlyMyHealth team spoke with leading experts to understand how these infections are transmitted and to discuss effective strategies for preventing their spread.
Table of Content:-
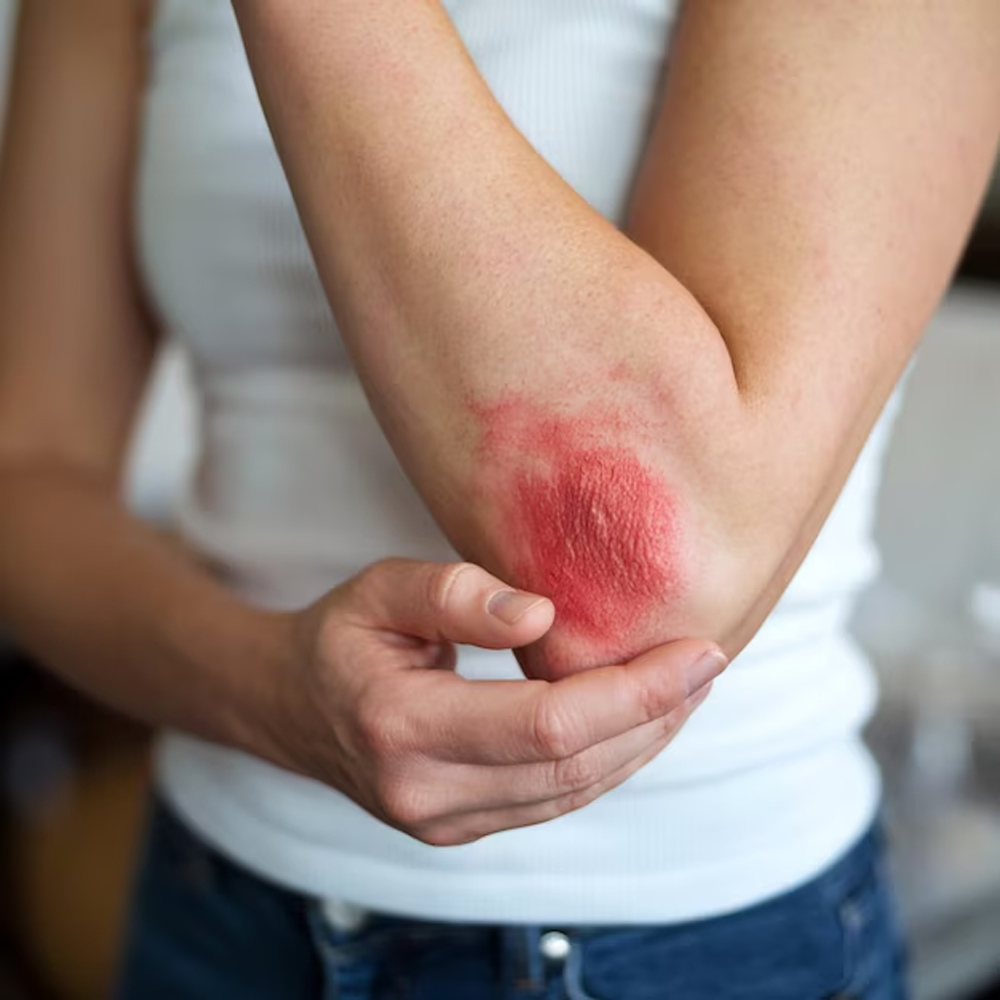
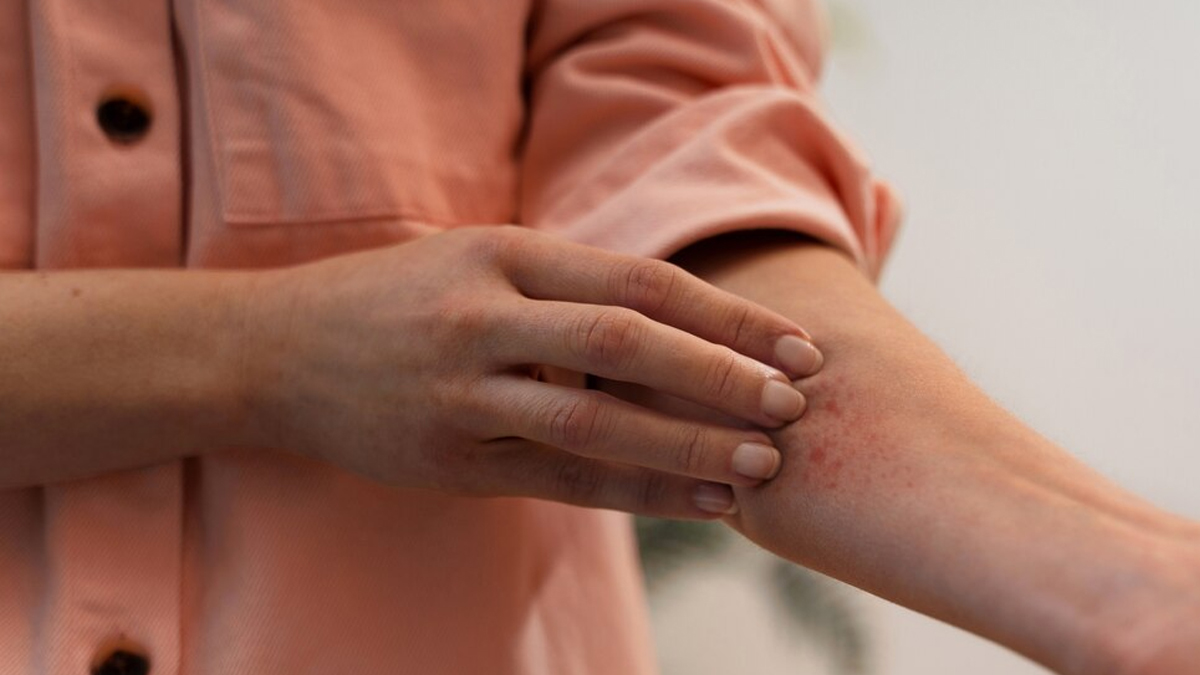
What Types Of Fungal Infections Can Be Contagious?![]()
According to Dr Shireen Furtado, Senior Consultant - Medical and Cosmetic Dermatology, Aster CMI Hospital, Bengaluru, fungal infections can be transmitted from one individual to another, although it varies depending on the specific type of fungus involved.
"Certain fungal infections, such as those caused by dermatophytes, which lead to conditions like athlete's foot or ringworm, are known to spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly via contaminated surfaces, such as floors, towels, or clothing," she said, adding that other types of fungal infections, particularly those that affect the respiratory system, may be contracted through inhalation of airborne spores, which can be released into the environment from decaying organic matter or infected individuals.
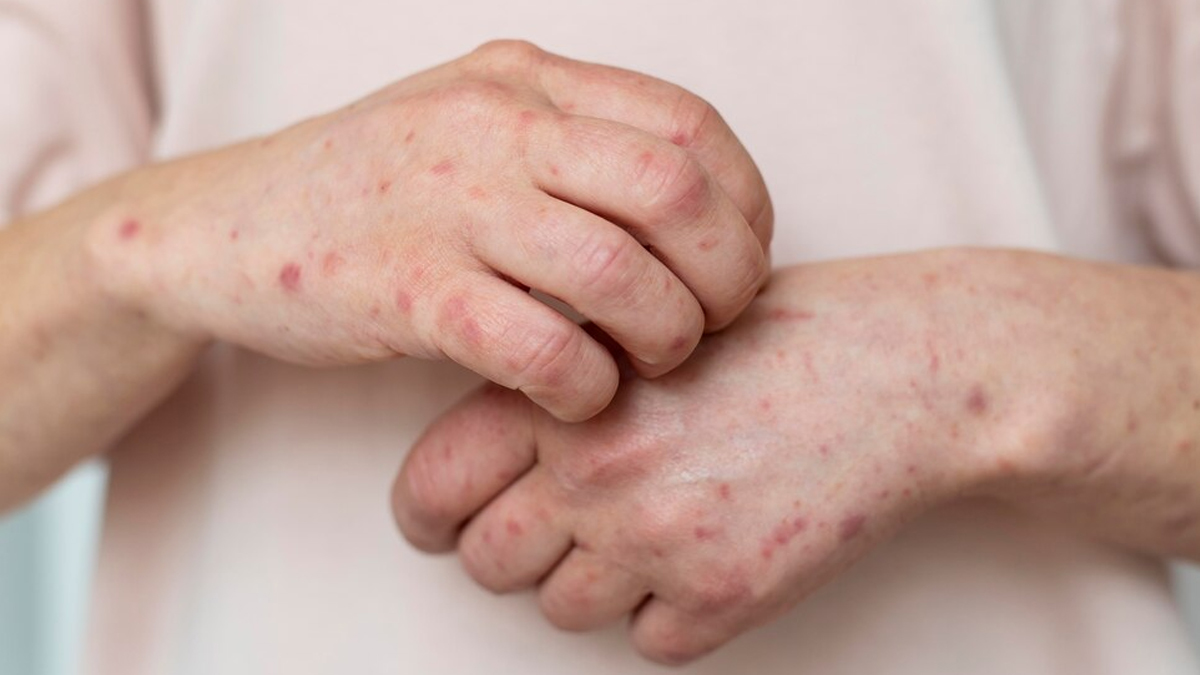
An athlete's foot, which is caused by dermatophytes, primarily affects the skin between the toes and can be transmitted through direct contact or via contaminated surfaces.
On the other hand, ringworm, despite its misleading name, is a fungal infection that manifests on various body areas, typically featuring a circular, red, and itchy rash.
Lastly, candidiasis, often resulting from the Candida species, can take several forms, such as oral thrush and vaginal yeast infections, and is particularly adept at thriving in warm, moist environments.
Adding to it, Dr Smitha Prabhu, MD, FRCP (Edin), Professor and Head - Department of Dermatology and Venereology, KMC, Manipal, MAHE, highlighted that while most fungal infections are contagious, there are some that are less contagious than the others.
For instance, pityriasis versicolour, while caused by a fungal overgrowth, is significantly less contagious compared to infections like ringworm or candidiasis.
Pityriasis versicolour presents as hypopigmented (lighter) or sometimes darker patches on the skin, rather than the reddish, scaly appearance seen in ringworm, the doctor explained. Additionally, it is usually less itchy and has a flat, smooth texture, unlike the raised, irritated lesions of other fungal infections.
How Do They Transmit?![]()
Dr Furtado shared common modes of transmission for contagious fungal infections. These include:
- Direct contact with infected individuals, surfaces, or contaminated objects.
- Skin-to-skin contact, particularly in communal settings such as gyms, swimming pools, and locker rooms where the fungus can thrive in warm, moist environments.
- Airborne transmission, in which the spores of certain fungi can spread through inhalation or contact with contaminated dust.
- Sharing of personal items, such as towels, shoes, or nail clippers, which can harbour fungal spores and facilitate infection.
Difference Between Contagious And Non-Contagious Fungal Infections
Unlike contagious fungal infections that spread between individuals, non-contagious fungal infections, such as those caused by fungi that are part of the normal skin flora, may arise from factors like a weakened immune system or environmental conditions.
To differentiate between the two, individuals should be aware of the symptoms, the mode of transmission, and the specific fungi involved, as well as consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and guidance on management, Dr Furtado advised.
Also Read: Monsoon Health: Expert Lists Ways to Prevent Fungal Infections At Home
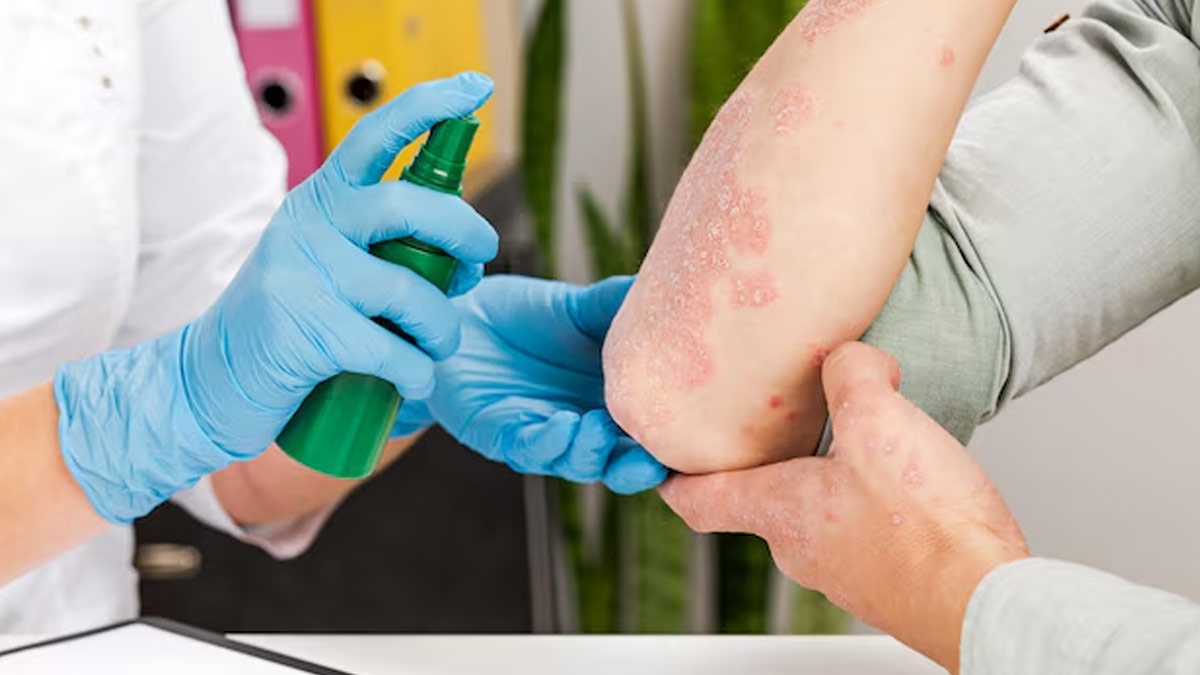
Ways To Prevent Transmission Of Fungal Infections![]()
There are various effective ways to minimise the risk of contracting or transmitting fungal infections. These include:
- Maintaining good personal hygiene, like regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after touching potentially contaminated surfaces or handling animals.
- Wearing breathable footwear and moisture-wicking socks to keep feet dry reduces the likelihood of fungal growth.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, shoes, or nail clippers.
- Being cautious in communal areas like swimming pools, gyms, and locker rooms, where the risk of exposure to fungi is heightened.
- Keeping living spaces clean and well ventilated.
- Promptly addressing any signs of mould or dampness.
Conclusion
Interestingly, there are nearly 10–50 lakh species of fungi, of which only a few can make people skin. Fungal infections can range from mild to life-threatening cases, and therefore it is crucial to prevent them in the first place. Contagious fungal infections are more concerning as they can spread from one person to another, posing widespread risk. Therefore, it is not only important to maintain proper hygiene but also crucial to take necessary steps to prevent transmission.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Combating Mosquitoes Naturally: Effective Ways to Use Neem To Fight Mosquito-Borne Diseases
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version