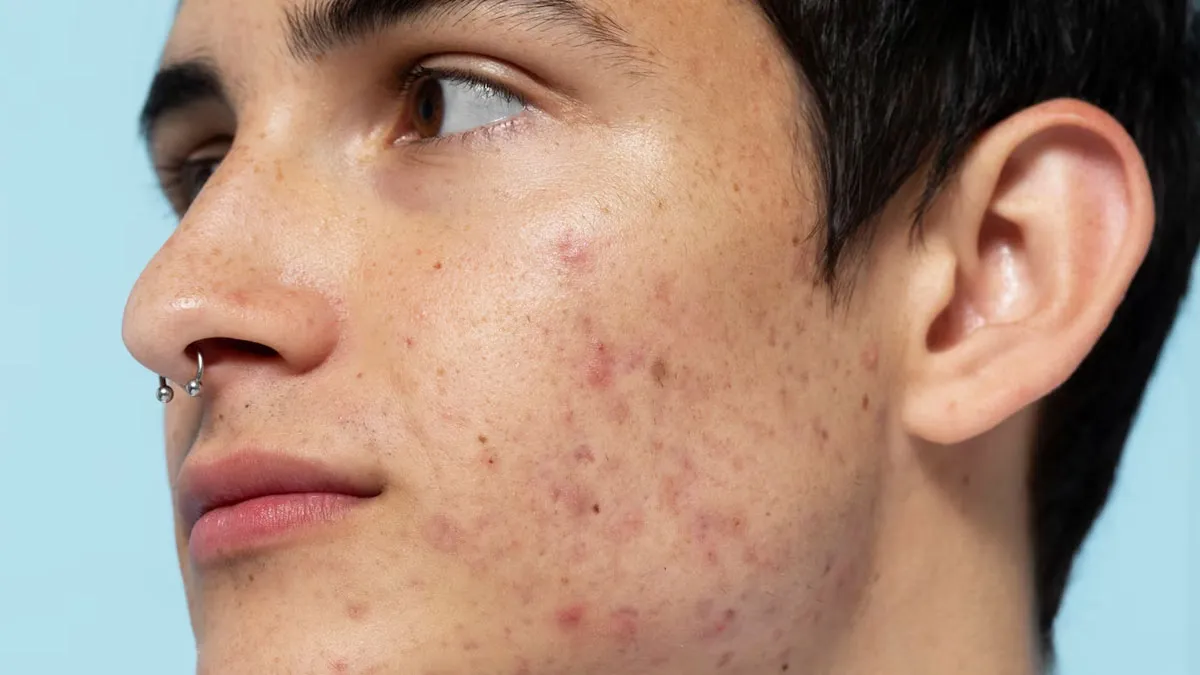
Anyone can have acne - men, women, young or old. But the cause behind acne can vary from person to person.
Acne is a common skin condition that is caused by clogged hair follicles in the skin. From oil, dead skin cells, to bacteria, many factors can contribute to it. However, not all acne is a pimple. Acne is a broader skin condition that can lead to various types of blemishes.
Table of Content:-
Fungal and bacterial acne are two different types of acne, which may seem or appear similar, but are two different conditions. Speaking with the OnlyMyHealth team, Dr Shefali Mahlawat, MBBS, MD Dermatology, Senior Resident, NIIMS Medical College and Hospital, Noida, helps distinguish between the two.
Also Read: Early Signs of Hormonal Imbalance You Shouldn’t Ignore
What Is Fungal Acne?
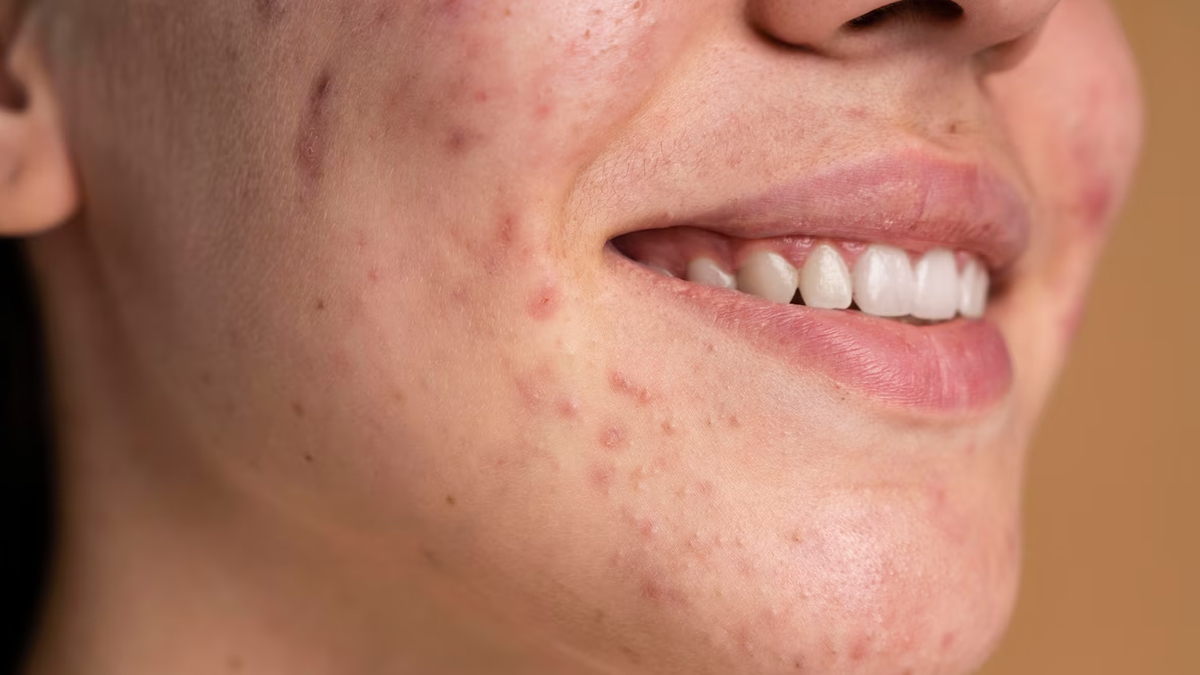
Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is a skin condition caused by an overgrowth of yeast in hair follicles. It's characterised by small, itchy, red bumps, often appearing in groups, and can be mistaken for regular acne. However, unlike typical acne, fungal acne is mostly itchy and lacks comedones, such as blackheads and whiteheads.
According to StatPearls Publishing, fungal acne more commonly occurs in hot and humid environments. People with a weakened immune system are more at risk of developing the condition, and those with other Malassezia conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis, can experience the fungal acne simultaneously.
What Is Bacterial Acne?
Bacterial acne, also known as inflammatory acne, is a skin condition caused by the overgrowth of bacteria called Cutibacterium acnes. These bacteria are naturally found on the skin, but when they multiply due to clogged pores, they can cause inflammation and breakouts.
Research suggests that it is prevalent in an estimated 35-90% of adolescents.
Fungal Vs Bacterial Acne: What Is The Difference?
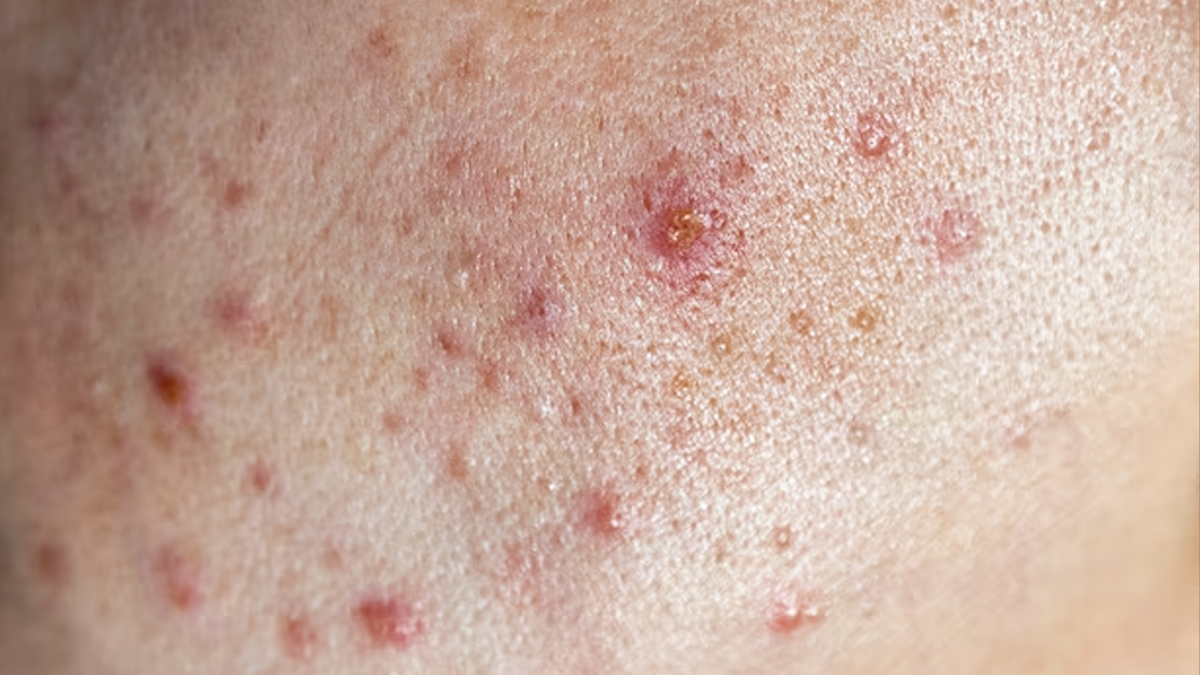
Sharing the key differences between fungal and bacterial acne, Dr Mahlawat says that bacterial acne typically presents as red, inflamed bumps containing pus, and is often sensitive to the touch.
Fungal acne is typically of the same size. Small red or skin-coloured bumps which are usually itchy. Fungal acne does not normally react to conventional treatments for acne.
She adds that bacterial acne is commonly found on the face, especially the T-zone, shoulders, and upper back. Fungal acne, on the other hand, prefers oilier, sweatier areas like the chest, upper back, shoulders, and sometimes even the forehead, especially in hot and humid environments.
What Triggers Fungal And Bacterial Acne?
Bacterial acne is often triggered by hormonal changes, excess oil production, clogged pores, and bacteria.
Fungal acne, however, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia) and is often triggered by excessive sweating, humid weather, or wearing tight, sweaty clothing for long periods.
Are Treatments Different For Fungal And Bacterial Acne?
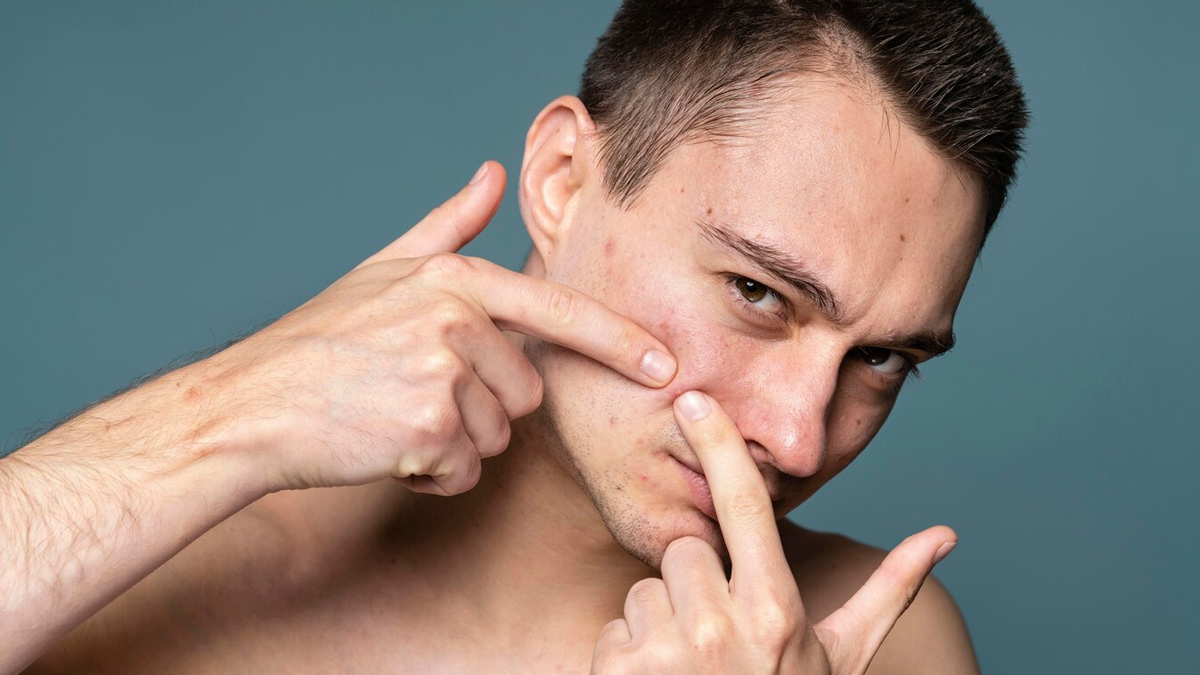

According to Dr Mahlawat, many people mistakenly treat fungal acne with antibiotics or benzoyl peroxide, which can worsen it by disrupting the skin’s microbiome and encouraging yeast growth. That's why an accurate diagnosis is key.
“Bacterial acne is usually treated with topical antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids. Fungal acne typically requires antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole creams or oral antifungals, in persistent cases,” the doctor shares, adding that lifestyle changes, like wearing breathable fabrics and showering after sweating, also help manage fungal acne effectively.
Conclusion
Different types of acne can affect your skin, including fungal and bacterial acne. While bacterial acne is caused by a buildup of bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells in hair follicles, fungal acne can be caused by an overgrowth of yeast. Both conditions can lead to similar symptoms, but they are caused by different microorganisms and have distinct treatments. Dr Mahlawat highlights the need to differentiate between the two so as it ensure appropriate treatment.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Sun-Deprived And Sedentary Lifestyle: Expert Explains The New Threat To India’s Bone Health
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version