
Monsoon can bring you relief from heat, but to your skin, it's usually a troublesome season. The humidity, sweat, and oil create a perfect breeding ground for breakouts. But not all acne is the same—what you think is regular acne might be fungal acne, a skin condition that needs different care. Understanding the difference is the first step to treating it properly and not ending up with months of frustration.
Table of Content:-
Why Monsoon Is a Breeding Ground for Skin Issues
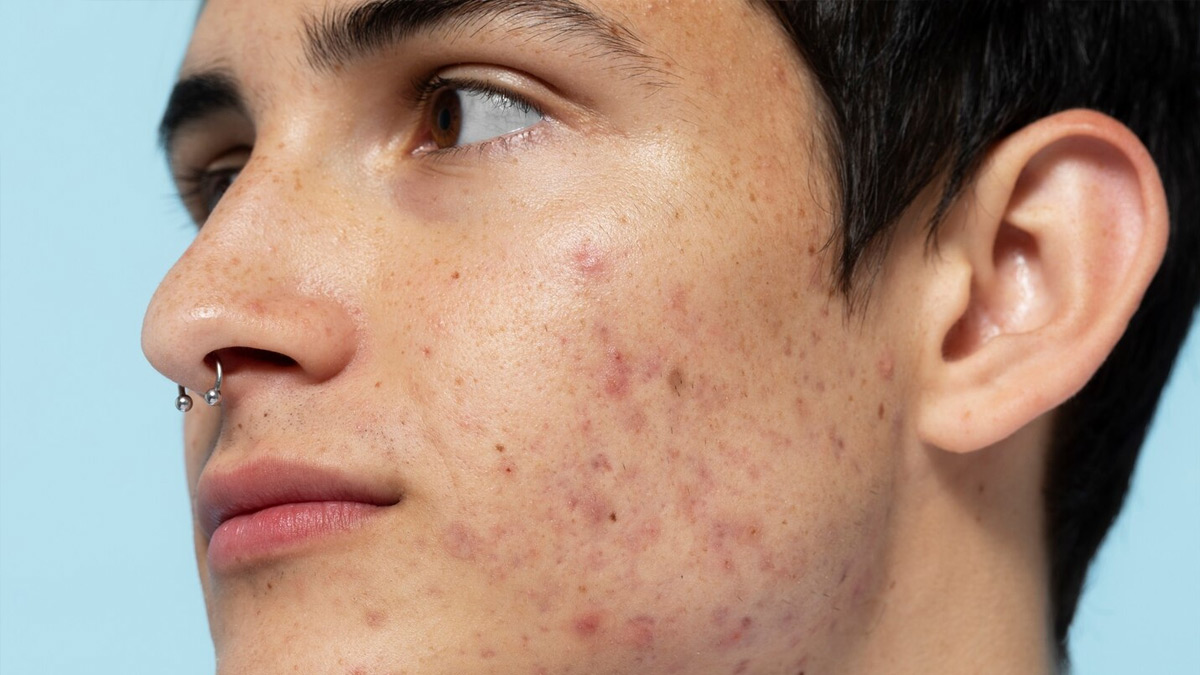
The monsoon brings with it extra moisture in the air, so your skin remains damp for longer. Combine that with sweat, clogged pores, and friction from clothes, and you have an ideal setup for both bacterial and fungal skin problems.
And while normal acne is more often due to blocked pores and bacteria, fungal acne is due to an excess growth of yeast (Malassezia) that already exists on the skin. Humid weather and sweaty skin give this yeast the perfect opportunity to multiply, causing itchy, pimple-like bumps.
Also Read: How To Distinguish Between PCOS Acne Vs. Normal Acne
What Is Fungal Acne?

Regardless of its name, fungal acne isn't technically ‘acne’ at all. It's a condition known as Malassezia folliculitis, where yeast infects the hair follicles, resulting in uniform, itchy bumps.
Key Causes in Monsoon
- Wearing sweaty clothes for too long
- Not showering soon after workouts or getting drenched
- Using oily skincare products that feed yeast
- Weakened skin barrier from excessive humidity
Fungal Acne vs Regular Acne: Spotting the Differences
Here’s how to tell them apart:
Feature
- Fungal Acne: Yeast overgrowth in hair follicles
- Regular Acne: Clogged pores + bacteria
Cause
- Fungal Acne: Small, uniform, red or skin-colored bumps
- Regular Acne: Mixed types—whiteheads, blackheads, pustules
Appearance
- Fungal Acne: Small, uniform, red or skin-colored bumps
- Regular Acne: Mixed types—whiteheads, blackheads, pustules
Itchiness
- Fungal Acne: Often itchy
- Regular Acne: Usually not itchy
Location
- Fungal Acne: Common on forehead, chest, back, upper arms
- Regular Acne: Mostly on face (especially T-zone)
Triggers
- Fungal Acne: Humidity, sweating, tight clothes, oily products
- Regular Acne: Hormonal changes, excess oil, poor skincare
Treatment
- Fungal Acne: Antifungal products
- Regular Acne: Acne treatments like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide
Why They’re Often Confused
Both ailments might appear the same in their beginning stages. Fungal acne is commonly treated with regular acne treatments, which will make it worse, particularly if they are oil-based or excessively harsh, as they have the ability to break the skin's barrier and provide yeast with a habitat to grow.
A clinical review of Pityrosporum folliculitis (PF) found that most patients are young adults (average age ~24), primarily male, and commonly have itchy outbreaks on the chest and back. Remarkably, 92% responded to oral antifungals and 81.6% to topical ones.
Also Read: Fungal Vs. Bacterial Acne: How To Differentiate Between The Two
Treating Fungal Acne in Monsoon
If you suspect fungal acne, a few targeted changes can help:

- Use antifungal cleanser or shampoo: Products containing ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, or selenium sulfide help balance yeast overgrowth.
- Wear loose, natural clothing: Do not wear tight, non-breathable clothes, which hold sweat.
- Shower immediately after perspiring: Do not let yeast start multiplying.
- Avoid heavy, oily creams: Opt for lightweight, non-comedogenic, water-based moisturisers.
- See a dermatologist: Severe cases may require oral antifungal medication.
Prevention Tips That Work for Both
- Keep your skin dry when possible. Dab away sweat instead of rubbing.
- Wash pillowcases, towels, and workout clothes frequently.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels or face cloths.
- Maintain a balanced diet; limit high-sugar foods, which can worsen both conditions.
When to Seek Help
If your skin isn't getting better after 2–3 weeks of routine care or the bumps are getting more widespread, it's time to see a dermatologist. They can make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the appropriate treatment, avoiding months of trial and error.
[Disclaimer: This article contains information for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your professional if you are dealing with any health issue to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version