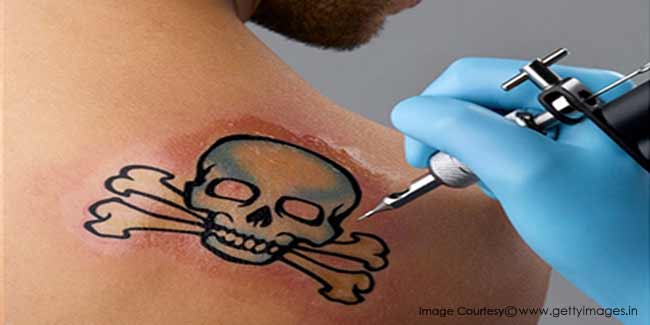
A tattoo is a permanent mark or design made on your skin with pigments inserted through pricks into the skin's top layer.  Typically, the tattoo artist uses a hand-held machine that acts much like a sewing machine, with one or more needles piercing the skin repeatedly. With every puncture, the needles insert tiny ink droplets.
Typically, the tattoo artist uses a hand-held machine that acts much like a sewing machine, with one or more needles piercing the skin repeatedly. With every puncture, the needles insert tiny ink droplets.
The process — which is done without anaesthetics — causes a small amount of bleeding and slight to potentially significant pain.
Table of Content:-
Allergic reactions
Tattoo dyes — especially red, green, yellow and blue dyes — can cause allergic skin reactions, such as an itchy rash at the tattoo site. This can occur even years after you get the tattoo.
Skin infections
A skin infection — which might cause redness, swelling, pain and a pus-like drainage — is possible after tattooing.
Other skin problems
Sometimes bumps called granulomas form around tattoo ink. Tattooing can also lead to keloids — raised areas caused by an overgrowth of scar tissue.
Blood-borne diseases
If the equipment used to create your tattoo is contaminated with infected blood, you can contract various blood-borne diseases — including tetanus, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
MRI complications
Rarely, tattoos or permanent makeup might cause swelling or burning in the affected areas during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams. In some cases, tattoo pigments can interfere with the quality of the image — such as when a person who has permanent eyeliner has an MRI of the eye.
Precautions
In the majority of cases, a tattoo that has been correctly applied will heal without problems. While some people may experience an allergic reaction or infection, this can usually be avoided by taking the correct precautions before getting a tattoo and following some simple procedures after.
Each tattoo artist may suggest a slightly different tattoo aftercare process, but in most cases the purpose of the process is to speed up healing and avoid infection.
When a tattoo is first completed, the tattoo artist should cover it with a bandage. This bandage can be removed after about an hour. As soon as the bandage is removed, the tattoo area should be washed gently with antibacterial soap and rinsed with warm water.
For the next few days, most tattoo artists recommend coating the tattoo area with a fragrance-free and colourless ointment like Aquaphor. Fragrance can irritate the tattoo area or even cause a rash, so it’s important to avoid ointments and lotions that have fragrance. All that’s needed is a thin layer of ointment – many people make the mistake of applying too much ointment.
As part of the normal healing process, a tattoo will start to peel after a few days. When this happens, a fragrance-free and colourless skin lotion should be applied instead of ointment. Lubriderm, Curel and Vasoline Intensive Care lotion can all be used for tattoo aftercare. During the peeling stage, the tattoo may appear to be blurry. This is caused by the formation of a new upper layer of skin. As healing continues, the tattoo will become more distinct and clear.
While the tattoo heals, it’s important to keep it clean. Avoid immersing it in water or scrubbing it. Instead, continue to wash it gently with mild soap.
Avoid exposure to harsh chemicals and bacteria. People who handle hazardous materials, such as animal waste or medical waste, should take extra precautions during tattoo aftercare to limit the risk of exposure to hazardous materials.
Next to keeping the tattoo clean, one of the most important rules of tattoo aftercare is avoiding sun exposure.
Getting too much sun during the healing process can permanently damage the tattoo. A new tattoo should be protected from direct sunlight. Most tattoo experts suggest avoiding overexposure to the sun even after a tattoo is healed, since the sun can ruin a tattoo’s look by damaging the skin and fading the tattoo’s pigment.
Indications of a bad reaction to a new tattoo include heavy scabbing, seeping, inflammation or the appearance of a rash.
It’s important to see a medical professional if any of these symptoms occur during tattoo aftercare. Individuals who have immune system problems, diabetes or other blood disorders or who are taking blood thinners may develop problems after receiving a tattoo and should consult with a doctor before undergoing the tattoo process.
Some people should take a few precautionary measures before they have a tattoo applied. Individuals who are allergic to latex should let the tattoo artist know so that a different type of gloves can be used. People who suspect they may be allergic to tattoo inks should have a small area of skin tested before undergoing the full tattoo procedure. This precaution will eliminate the chance of an allergic reaction during tattoo aftercare.
The most important precaution for tattoo aftercare is to make sure your tattoo is applied under sanitary and sterile conditions.
A clean environment will go a long way towards easy tattoo healing. Make sure the tattoo artist that you use follows sanitary procedures, and then do your part by keeping your tattoo clean while it’s healing. By following these simple rules of tattoo aftercare, you will soon have a beautiful finished piece of body art that you can enjoy for a lifetime.
Read more articles on Body Art.
Read Next
Health Risks of Tattoos
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version