
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes a lot of pain and swelling in the joints. The symptoms usually last a week or two and then resolve on their own or with medical assistance.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, gout mostly occurs in people who have high levels of uric acid from the breakdown of purines, which are chemical compounds found in the body's cells and in many foods. This is why some experts advise against consuming certain foods that contain high levels of purines, which can lead to gout attacks.
Table of Content:-
In an interaction with the OnlyMyHealth team, Veena V, Dietitian, Aster Women and Children Hospital, Whitefield, Bengaluru, sheds light on the same.
Also Read: Dealing With Gout? Expert Explains Its Causes, Symptoms, And Tips For Management
How Gout Impacts The Body
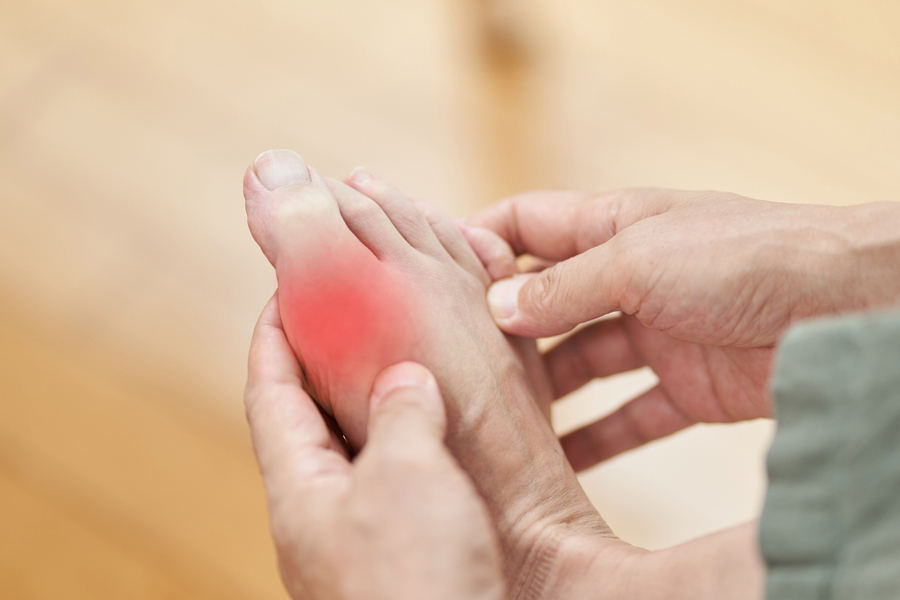
Gout occurs when urate/uric acid, a substance in your body, builds up and forms needle-shaped crystals in your joints, explains Veena.
“This leads to pain, swelling, redness, and changes in the movement and use of the affected joint,” she shares.
However, according to the dietitian, not everyone with high urate levels develops gout.
She notes that urate comes from purines, which are found in your body’s tissues and many foods.
When purines break down, they become urate.
Normally, urate passes out of your body in urine. However, when too much is made or too little is removed, urate builds up in your blood, forming crystals in your joints and causing inflammation.
Research suggests the prevalence of gout can vary by age, sex, and country of origin. Generally, about 1–4% of people are affected by gout. Men have a 2–6-fold higher risk of developing gout than women. This increases with age but plateaus after 70 years of age, according to StatPearls Publishing.
Veena says, “Gout is frequently associated with specific food intake, alcohol consumption, being overweight, and other medical conditions like kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), myocardial infarction (heart attack), and congestive heart failure.”
Should People With Gout Avoid Eating Fish?

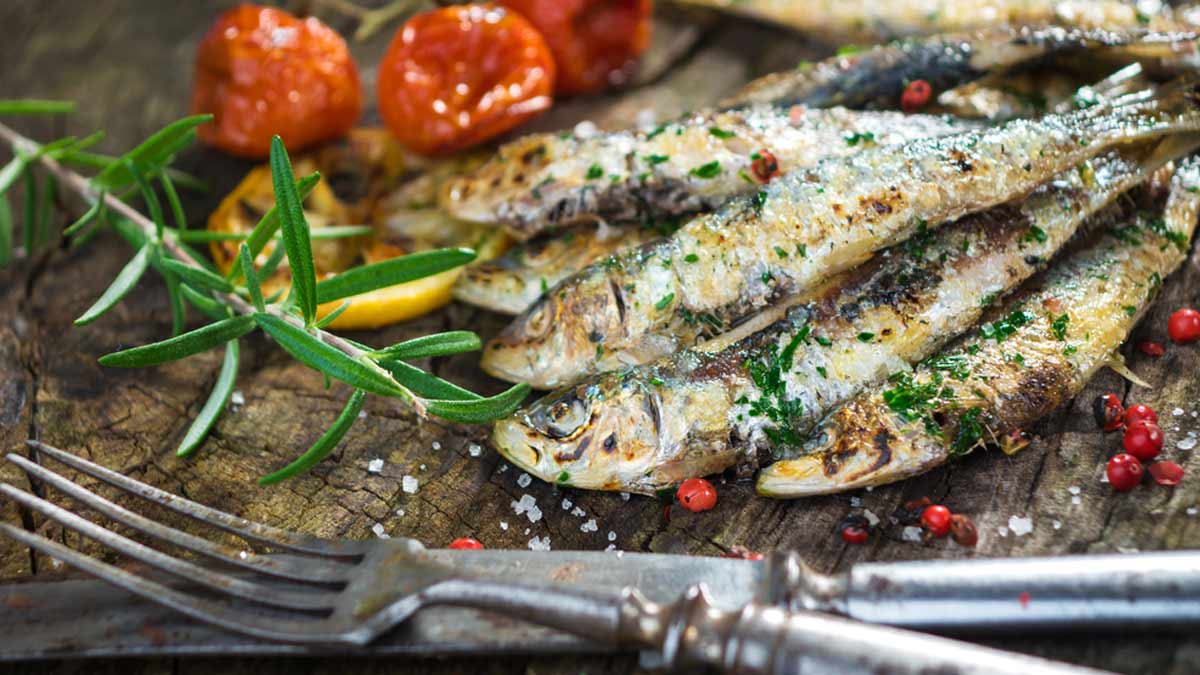
According to Veena, certain fish, like shellfish (shrimp and lobster), sardines, and anchovies, are high in purines, which can trigger gout attacks.
A 2014 study published in the journal Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin found that a high intake of purines can increase the risk of recurrent gout attacks by almost fivefold.
Researchers also noted that purine-rich foods are often high in calories as well, including meats, organ meats, and yeast.
However, while people with gout should be cautious about fish consumption, it's not entirely forbidden, says Veena, recommending that people go for low-purine fish like flounder or sole and enjoy moderate-purine fish like salmon in limited quantities.
Also Read: Expert Explains How To Safely Eat Fish And Avoid Health Risks Associated With Mercury
Fish That Are Safe To Eat

Not all fish contain high levels of purine or worsen gout symptoms. There are certain fish types that can be consumed by everyone, including gout patients. These include:
- Flounder
- Sole
- Salmon
- Trout
- Tuna
However, it is important to consume them in moderation and consult a doctor for personalised serving sizes.
Additionally, boiling or poaching fish can lower the purine content, which is responsible for gout attacks, says Veena. These cooking methods help in removing some purines from the cooking water, which you can then throw away, she adds.
Conclusion
Gout was once referred to as the ‘disease of kings’ or the ‘rich man’s disease.’ This was mainly because the condition was associated with overindulgence in lavish foods and alcohol consumption by the wealthy, like King Henry VIII, who suffered from it. This includes purine-rich foods such as sardines, anchovies, and shellfish, which can increase uric acid levels in the body and lead to gout flare-ups. Experts recommend consuming such foods in moderation or not eating them at all. Choose healthier and more appropriate alternatives, and consult a doctor to better understand your situation.
Also watch this video
Read Next
How To Recover From A Traumatic Brain Injury? Expert Recommends Tips To Avoid Long-Lasting Effects
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version