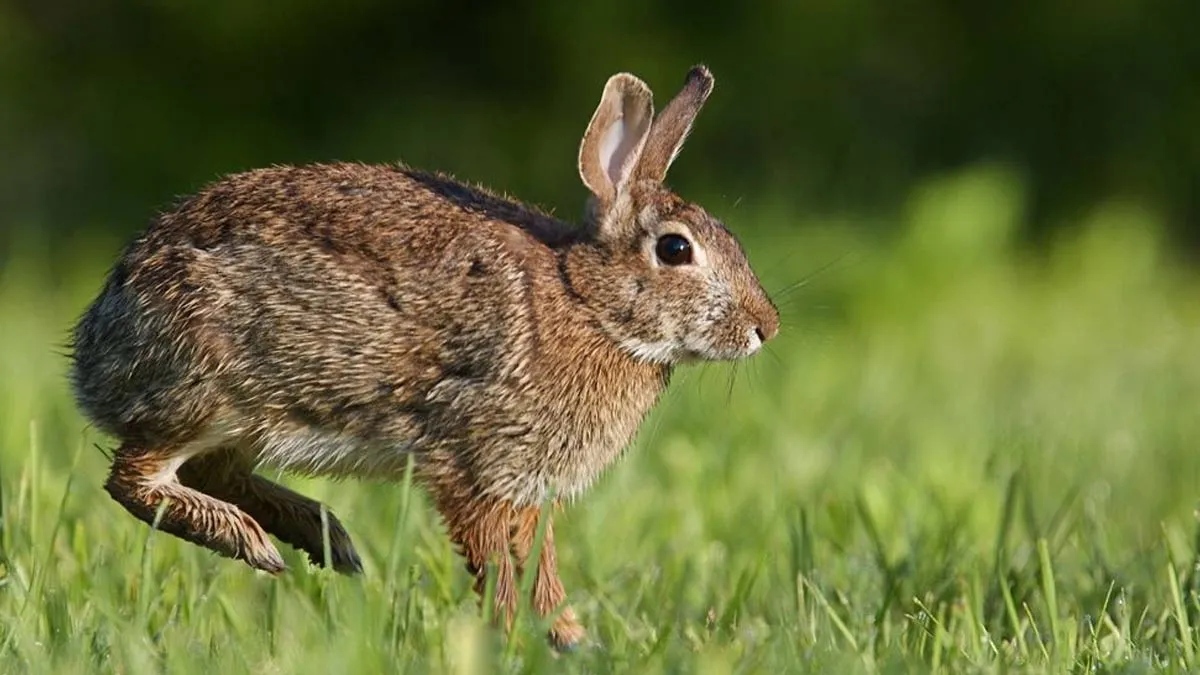

Tularemia, a rare but potentially severe bacterial infection, has been making a resurgence in the United States. Often referred to as “rabbit fever,” the disease saw a staggering 56% increase in reported cases during the 2010s compared to the previous decade, according to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Nearly 2,500 cases were reported between 2011 and 2022, with half originating from Arkansas, Missouri, Kansas, and Oklahoma. Alarmingly, cases have been recorded in 47 states, underscoring the disease's growing geographic reach.
Table of Content:-
What Is Tularemia and How Does It Spread?
Tularemia is caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis, which has been classified as a Tier-1 select agent due to its potential use as a bioweapon. The disease is zoonotic, meaning it spreads between animals and humans. Humans can become infected in several ways, including:
- Tick and Deer Fly Bites: Infected insects are a common vector.
- Contact with Infected Animals: Handling rabbits, rodents, or other wildlife carrying the bacteria can lead to infection.
- Contaminated Water or Food: Drinking or consuming bacteria-laden water and food can also spread the disease.
Depending on how the bacteria enter the body, tularemia can infect various parts, including the lungs, throat, eyes, or intestines.
Symptoms of Tularemia: What to Watch For
Tularemia symptoms vary based on the infection site but often include:
- Swollen and painful lymph nodes, sometimes resembling large bumps.
- Skin ulcers or lesions where the bacteria entered.
- Eye pain, sensitivity to light, and watery or red eyes.
- Swollen throat, white patches, and chest discomfort.
General symptoms such as fever, chills, muscle aches, headaches, and fatigue.
In severe cases, symptoms like confusion, loss of appetite, and breathing difficulties may occur.
Also Read: 40 Years After Bhopal Gas Tragedy: Toxic Waste Cleared, but Health Scars Remain
Who Is at Risk?
While tularemia can affect anyone, certain groups face higher risks:
- Outdoor Workers and Hobbyists: Hunters, veterinarians, farmers, and animal control officers are at elevated risk due to frequent contact with wildlife and animals.
- Residents of High-Prevalence Areas: Those living in the central U.S., particularly Arkansas, Missouri, Kansas, and Oklahoma.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: People with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable to severe infections.

Is Tularemia Contagious?
Fortunately, tularemia is not contagious and cannot spread from person to person. However, it is highly infectious, meaning even small amounts of the bacterium can cause illness. This makes precautions crucial, particularly in high-risk environments.
Also Read: Health Ministry Seizes Rs 6.6 Crore Worth of Fake Cancer and Diabetes Drugs in Kolkata Crackdown
Treatment and Prevention
The good news is that tularemia is treatable, especially when diagnosed early. Physicians typically prescribe high-spectrum antibiotics, administered either orally or via injection. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications, which can be life-threatening. To minimize your risk of infection:
- Avoid direct contact with wildlife, especially rabbits and rodents.
- Use insect repellent to ward off ticks and deer flies.
- Ensure food and water are sourced from safe, uncontaminated sources.
- Wear gloves and protective clothing when handling animals or working outdoors.
Bottomline
As tularemia cases continue to rise across the U.S., understanding the disease and its risks is more critical than ever. Increased awareness, vigilance, and prompt medical attention can help reduce its impact, safeguarding public health against this highly infectious disease.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Health Ministry Seizes Rs 6.6 Crore Worth of Fake Cancer and Diabetes Drugs in Kolkata Crackdown
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
