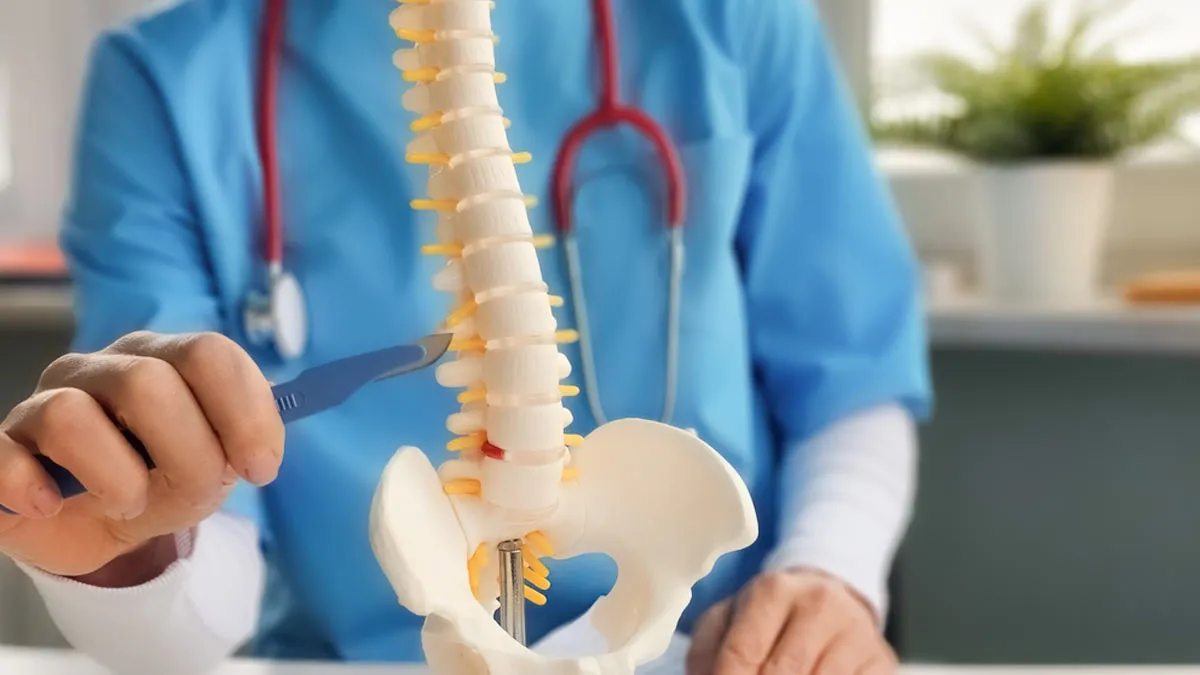
Back pain can be a silent disruptor. It is not only painful but also disturbs sleep, saps your energy, and slowly erodes your quality of life. The pain can become so constant and debilitating for some individuals that mundane activities, such as bending to lace up a shoelace or standing to be able to have a conversation feel like challenges. When physiotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes don't offer relief, spinal fusion surgery might come into the picture as a last but hopeful resort.
Table of Content:-
We spoke to Dr Arpit Bansal, Laparoscopic Cancer Surgeon and Health Advocate, Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, who explained spinal fusion surgery, its process, benefits, and potential side effects.
What Is Spinal Fusion Surgery?
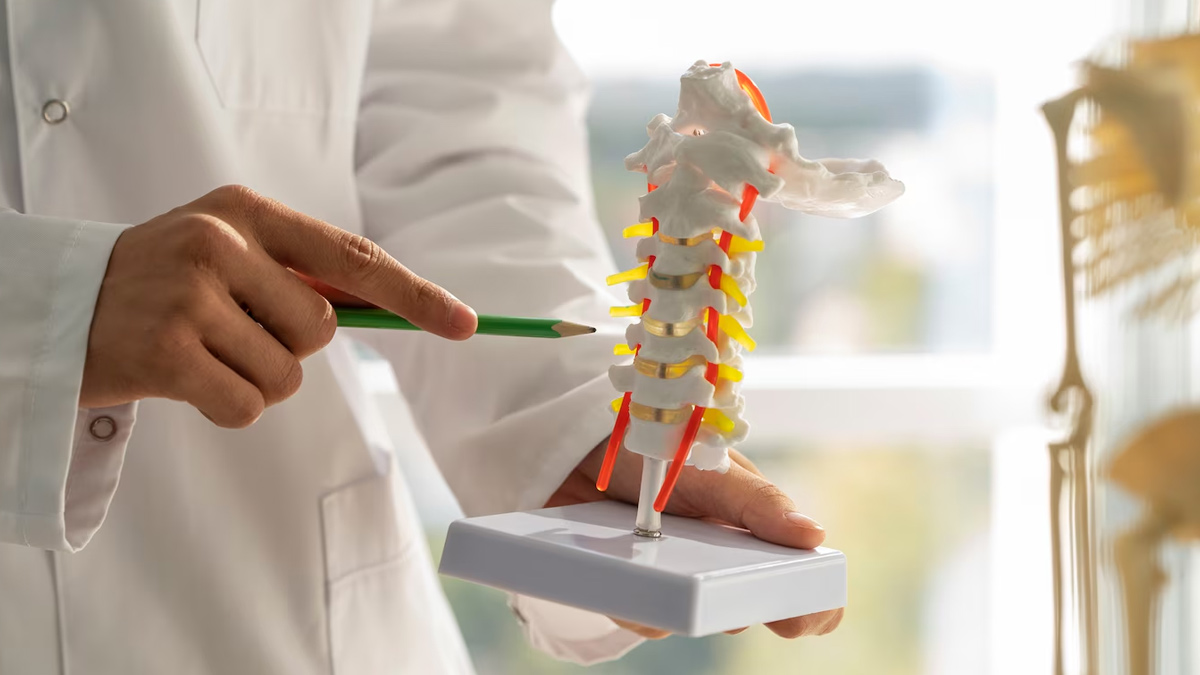
"Spinal fusion is a surgery aimed at joining two or more bones in the spinal cord. It is generally taken into account when a person suffers from extreme backaches, instability or spinal abnormalities and other courses of treatment, such as physiotherapy and meditation have failed," explained Dr Bansal.
During the operation, the surgeon places a piece of bone from the patient's body or a substitute between the affected vertebrae. "Special hardware and rods may hold everything steady while the bone gradually fuses into one solid unit. Today many spinal fusions are done using advanced techniques, making recovery easier and faster than before," he added.
Also Read: Metastatic Spine Cancer: Recognising Risks, Symptoms, and Life-Saving Treatments
When Is Spinal Fusion Recommended?
Spinal fusion isn’t a first step. It’s more like a backup plan when nothing else works. It’s commonly recommended for:

- Chronic back pain that has not improved with non-surgical treatments.
- Spinal instability is caused by conditions, such as degenerative disc disease or trauma.
- Spinal deformities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis.
- Fractures or injuries that weaken spinal strength.
- Nerve compression is caused by slipping vertebrae (spondylolisthesis).
- In such situations, fusion can restore stability, alleviate pain, and avoid further nerve or spinal cord damage.
Benefits of Spinal Fusion
For patients selected carefully, spinal fusion can be a life-changing surgery. Key benefits include:
- Pain relief: By eliminating the painful movement between vertebrae, most patients get a substantial or complete alleviation of chronic back pain.
- Stability: Fusion stabilises the spinal part that is weak or unstable.
- Improved function: Many individuals regain the ability to perform daily activities with far less discomfort.
- Correction of deformity: In cases like scoliosis, spinal fusion can straighten and realign the spine.
- Prevention of further damage: Stabilising the spine can stop progressive degeneration or nerve injury.
- Many patients return to active, fulfilling lives post-surgery with proper rehabilitation and guidance.

Also Read: Do I Need Spine Surgery? Expert Helps You Find Out
Possible Risks and Downsides
Similar to any surgery, there are risks to spinal fusion. These include:
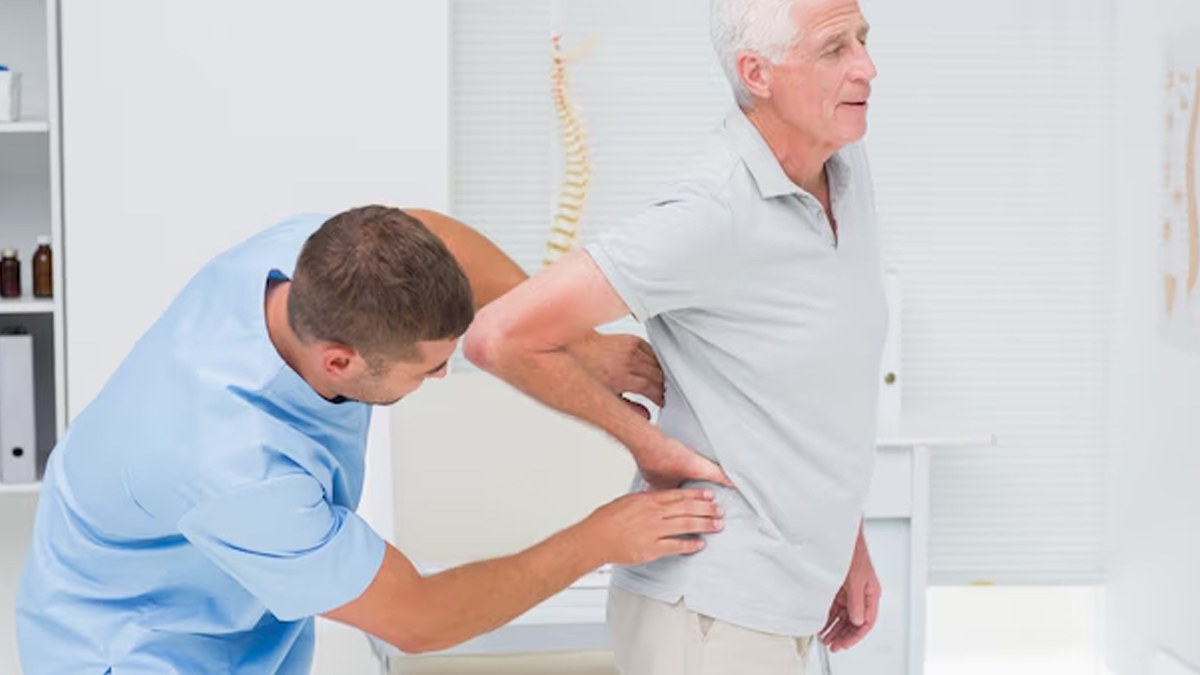
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Blood clots, especially if mobility is reduced during recovery.
- Limited flexibility in the fused portion of the spine.
- Increased stress on nearby vertebrae may cause wear and tear or pain over time.
- No improvement in symptoms if the source of pain isn’t accurately identified.
Conspicuous risk factors affecting spinal fusion include three patient-related risk factors (smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and diabetes) and four surgery-related risk factors (without BMP-2, allograft, CPS fixation, and posterolateral fusion). These results will enable clinicians to improve alertness for treatment in the early stages of high-risk patients developing fusion failure.
Noticeable risk factors influencing spinal fusion include three patient-related factors (smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and diabetes) and four surgery-related factors (the absence of BMP-2, allograft, CPS fixation, and posterolateral fusion). These insights could assist clinicians in enhancing their vigilance for early intervention in patients at a higher risk of experiencing fusion failure.
Hence, spinal fusion should never be a rushed decision. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) states that spine surgery is generally suggested only when a doctor can identify the exact source of your pain. To achieve this, your doctor might utilise imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans. A thorough evaluation, including scans, physical exams, and trials of other treatments, is crucial before moving forward.
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your professional if you are dealing with any health issue to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version