Have you ever thought a bruise could change the course of your life? For people with haemophilia, that’s often the case. While most of us know that this condition makes it hard for blood to clot, what’s less known is how dangerous microbleeds can be. These are tiny bleeds inside the body that don’t cause pain or show any visible signs, but over time, they can damage joints, affect the brain, and lead to serious health problems.
Table of Content:-
We spoke to Dr Rajeev Vijayakumar, Senior Consultant, Gleneagles BGS Hospital, Bengaluru, to learn why it is essential to identify and treat these silent bleeds early.
Understanding Microbleeds in Haemophilia
"Microbleeds are tiny, spontaneous bleeds within soft tissues, joints, and the brain. Large bleeds are noticeable right away; however, minor bleeds are hard to notice initially, as they don't cause pain or leave any visible signs. But over time, these minute bleeds accumulate, causing more tissue damage and other complications," explained Dr Vijayakumar.
One of the severe characteristics of microbleeds is that they may lead to joint damage. People with haemophilia often experience bleeding into their joints, which can result in chronic inflammation, cartilage erosion, and joint issues. As more microbleeds develop, the condition worsens, increasing the risk of arthritis and other mobility impairments.
"Also, microbleeds may be present in the brain, causing cognitive impairment and neurological complications. Individuals with haemophilia may experience 'silent cerebral microbleeds,' which can cause difficulty in remembering, and walking, and also put them at risk of having a stroke," added Dr Vijayakumar.
Also Read: The Silent Killer: Here's How To Spot And Treat Internal Bleeding To Avoid Complications
Why Is It Essential To Detect Problems Early?
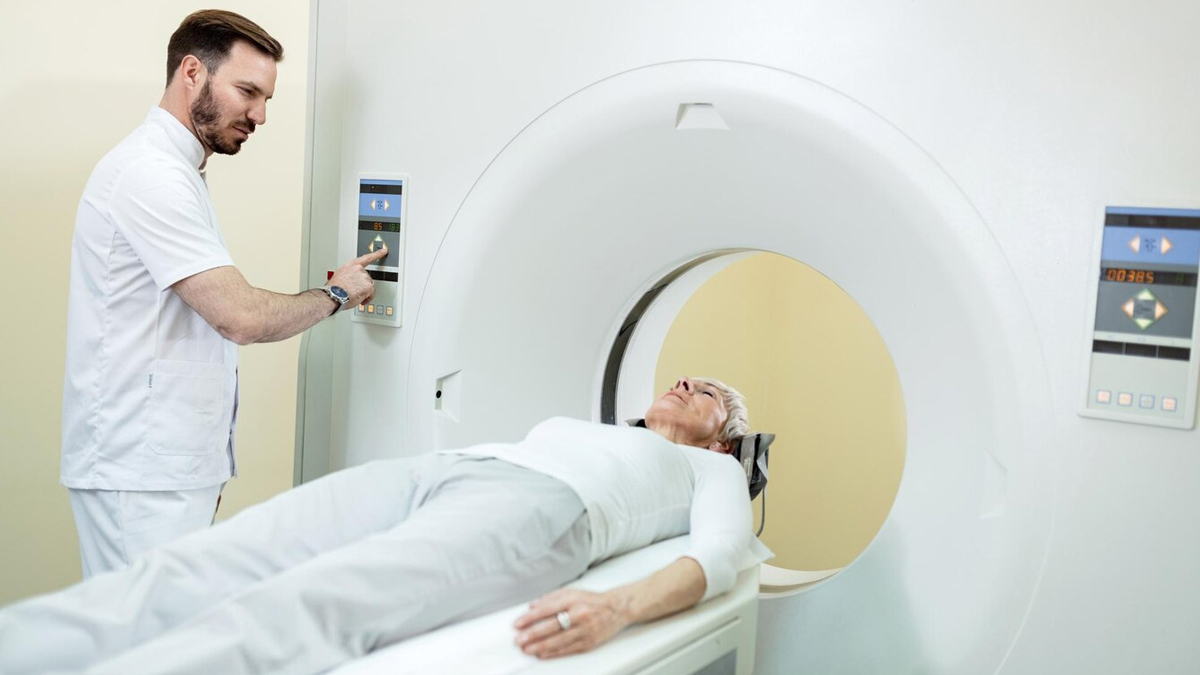
Microbleeds are minute, making it hard to identify them initially. New technology, including MRI scans, has enabled doctors to detect small bleedings before they cause permanent damage.
"Through monitoring the patient regularly, physicians are able to determine how serious the bleeding is and apply preventive measures to reduce complications. Microbleeds are usually asymptomatic for joint health as their presence over time can permanently damage the joint," added Dr Vijayakumar.
Even cases of mild haemophilia can develop some level of joint deterioration if microbleeds are allowed to continue unnoticed. A 2013 research observed that acute bleeds cause quicker damage, and the microbleeds may add up to the degeneration of joints with time.
Detecting these bleeding early allows patients to receive targeted treatments, such as physical therapy and clotting factor replacement, to preserve joint function.
Also Read: Haemophilia: What Men Need to Know About This Genetic Bleeding Disorder
Preventive Care: A Lifeline For Haemophilia Patients

- Prophylactic treatment: Administering regular infusions of clotting factor concentrates regularly can help prevent spontaneous bleeding and reduce the risk of microbleeds.
- Join protection: Engage in low-impact exercises to keep your knees healthy, such as swimming and biking. These can help strengthen your muscles and make your joints feel better.
- Routine monitoring: Regular check-ups and imaging scans allow doctors to identify bleeding trends and adjust treatment methods accordingly.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding high-risk activities and maintaining a healthy diet can support overall well-being.
Bottomline
Dr Vijayakumar concluded, "While microbleeds are 'invisible,' they result in considerable damage. People with haemophilia should be cautious of minor cuts because they have the potential to result in joint damage and neurological issues. They can have healthier, more active lifestyles through prioritising regular screening, preventive treatment and making lifestyle changes."
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your professional if you are dealing with any health issue to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version