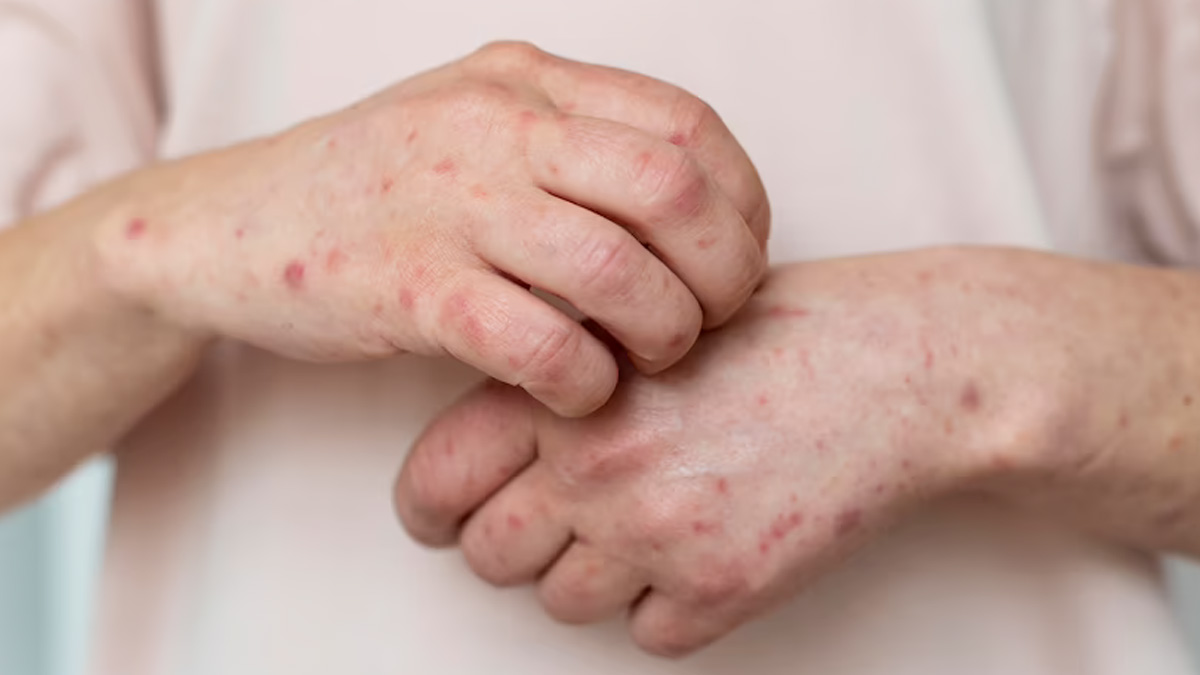
Fungal infections are a common occurrence that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. In an interaction with Only My Health, Dr S K Gupta, dermatologist at DMCH, Darbhanga, Bihar, explained the different stages of fungal infections is vital for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and prompt treatment.
Table of Content:-
Initial Infection
The first stage of a fungal infection occurs when the fungal organism gains entry into the body. This can happen through direct contact with contaminated surfaces, inhalation of fungal spores, or compromised skin barriers. Initially, the infection may appear as a small red patch, a rash, or localised itching.
In some cases, the affected area may be accompanied by slight inflammation or swelling. It is important to identify these early signs and seek medical attention to prevent the infection from progressing further.
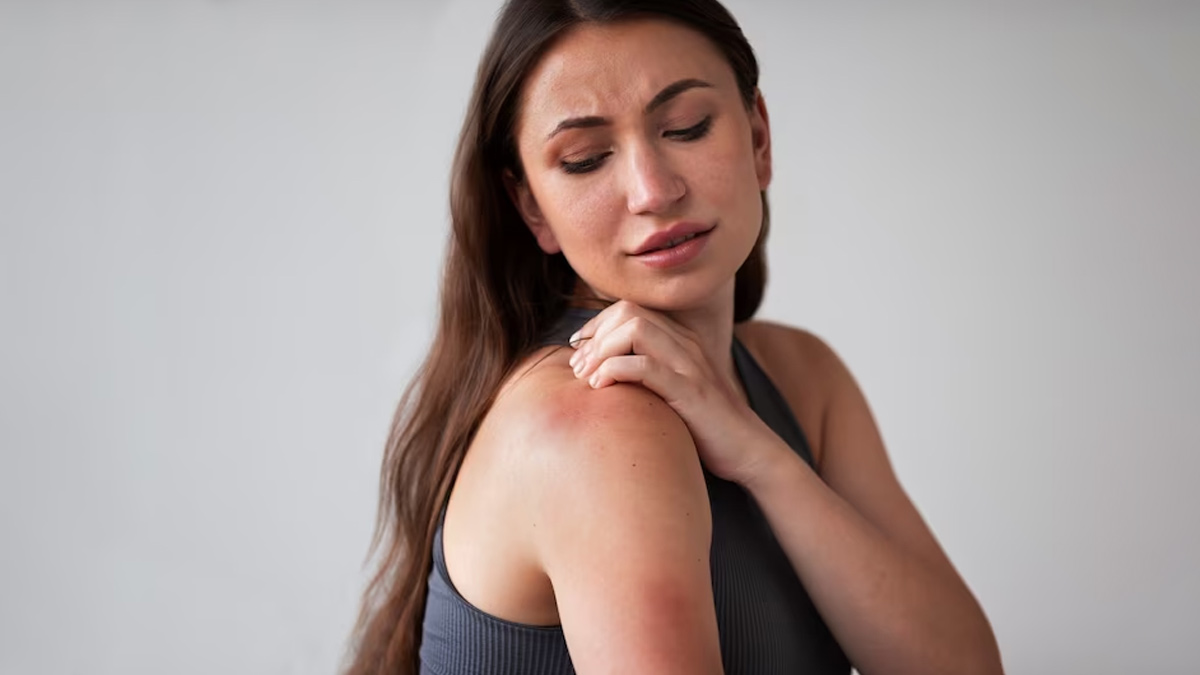
Progression and Spreading
If left untreated, a fungal infection can progress to the second stage, where the fungus begins to multiply and spread. At this point, the infection may become more noticeable and exhibit characteristic symptoms.
These symptoms can vary depending on the type of fungal infection and the area of the body affected.
Common signs include increased redness, itching, burning sensation, the formation of blisters or pustules, and peeling or scaling of the skin. In some cases, the infection may extend to adjacent areas, leading to the formation of clusters or patches of affected skin or nails.
Also read: First Case of Black & White Fungus Reported in Uttar Pradesh. Know About The Disease In Detail
Chronic or Recurrent Infection
In certain instances, fungal infections may enter a chronic or recurrent stage. This can occur due to various factors, such as inadequate treatment, underlying health conditions, weakened immune system, or repeated exposure to the fungus.
As per research, chronic fungal infections often present with persistent symptoms and a tendency to recur even after treatment. The affected area may show signs of prolonged inflammation, persistent itching, thickening or discolouration of the skin or nails, and the formation of cracks or fissures.
Treating chronic or recurrent infections may require a more comprehensive and targeted approach, including prolonged antifungal therapy and addressing any underlying health issues.
Serious Case Of Fungal Infection
In severe cases or when the immune system is significantly compromised, fungal infections can progress to the fourth stage, where the infection spreads to other parts of the body. This is known as disseminated or systemic fungal infection, and it can pose significant health risks.
Symptoms may include fever, fatigue, weight loss, organ-specific symptoms (e.g., lung or bloodstream involvement), and skin lesions that extend beyond the primary site of infection.
Systemic fungal infections are medical emergencies and require immediate medical attention for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
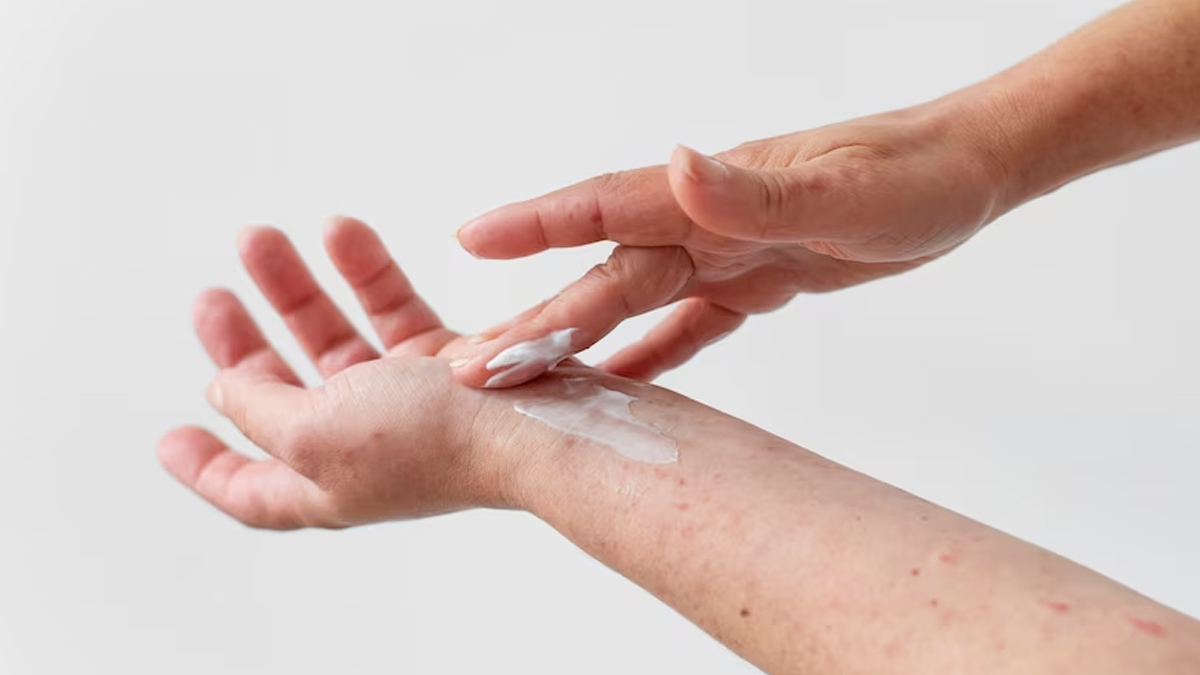
Treatment Approaches
Treating fungal infections typically involves antifungal medications, either topical or systemic, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
In addition to medication, other measures may be recommended, such as keeping the affected area clean and dry, wearing breathable fabrics, practising good hygiene, and avoiding factors that promote fungal growth (e.g., excessive moisture or tight-fitting shoes).
In cases of chronic or systemic infections, a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals specialising in dermatology, infectious diseases, or immunology may be necessary.
Also read: 6 Myths About Fatality Of Black Fungus, Here Are Real Facts Which You Must Know
Prevention
Preventing fungal infections involves practising good hygiene, keeping the skin dry and clean, avoiding sharing personal items, wearing appropriate footwear in public places, and maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest.
Prompt treatment of any underlying health conditions and addressing risk factors can also contribute to preventing fungal infections.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
