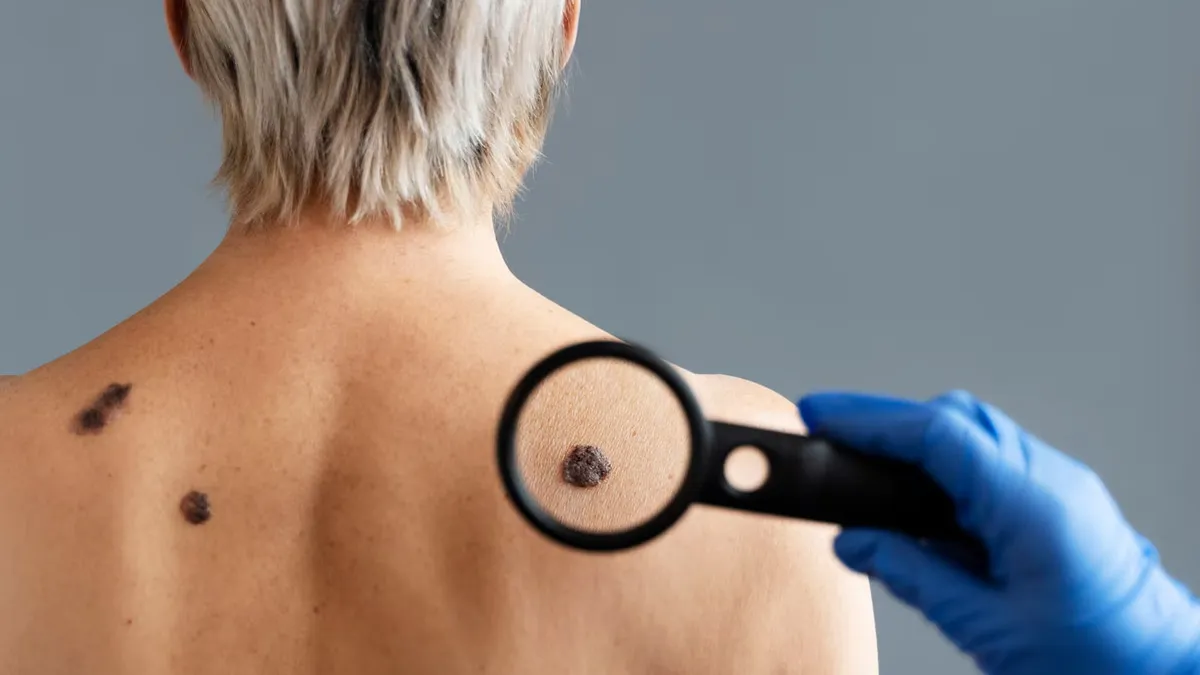
A recent analysis by Cancer Research UK has highlighted how clothing choices and sun exposure habits may influence melanoma risk. Melanoma is one of the most serious types of skin cancer, which affected an estimated 33 lakh people worldwide in 2022, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Table of Content:-
Interestingly, the new analysis also revealed stark gender differences in melanoma locations, meaning men and women may develop skin cancer in different parts of the bodies.
Also Read: Can Having More Moles Increase Your Skin Cancer Risk?
About The Study
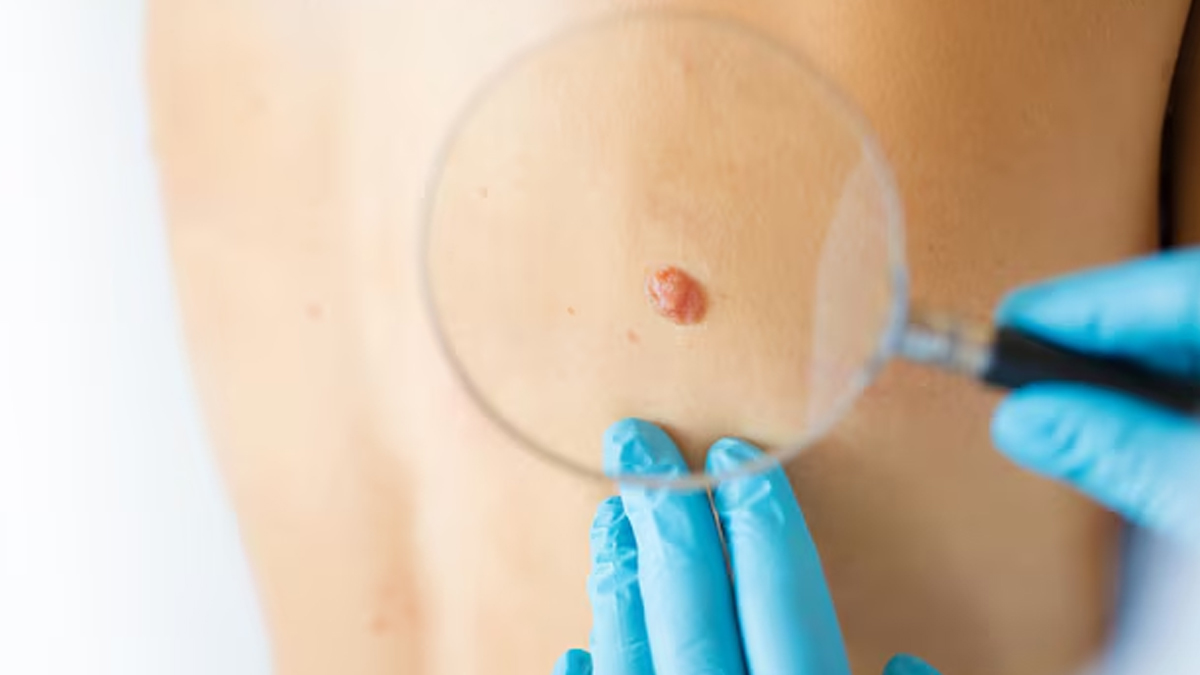
The recent data from 2018 to 2021 reveal that where melanoma appears on the body may be closely linked to how we dress in the sun. The findings showed that 40% of melanomas in men were diagnosed on the torso – areas often exposed when shirts come off in hot weather – while in women, over a third of cases were found on the lower limbs, which are commonly uncovered when wearing shorts or skirts.
Speaking with the OnlyMyHealth team, Dr L. Rohit Reddy, Consultant Medical Oncologist and Hemato-Oncologist, Yashoda Hospitals, Hyderabad (who was not part of the study), shares that women most often develop skin cancer on their legs, from the hips down to the ankles. Some may also develop skin cancer on the torso, though this is far less common. Meanwhile, men are nearly twice as likely as women to be diagnosed with melanoma on their head or neck.
Providing an explanation for the same, Dr Reddy says, “As soon as the weather gets warmer, different areas of the bodies of men and women are likely to get exposed to beat the heat. Also, the shapes of our bodies could be blamed for this much difference. For example, men's torsos are typically bigger than women's, while the legs of women take up a larger proportion of their body surface area. Hairs over the body, which differ in genetics and style, may also contribute to these gender-based differences.”
These patterns highlight how everyday sun exposure, shaped by our clothing choices, can increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Experts point out that ultraviolet (UV) radiation is responsible for nearly 90% of all melanoma cases, and repeated sunburns can significantly raise your lifetime risk.
Does Melanoma Affect Men And Women Differently? If So, Why?
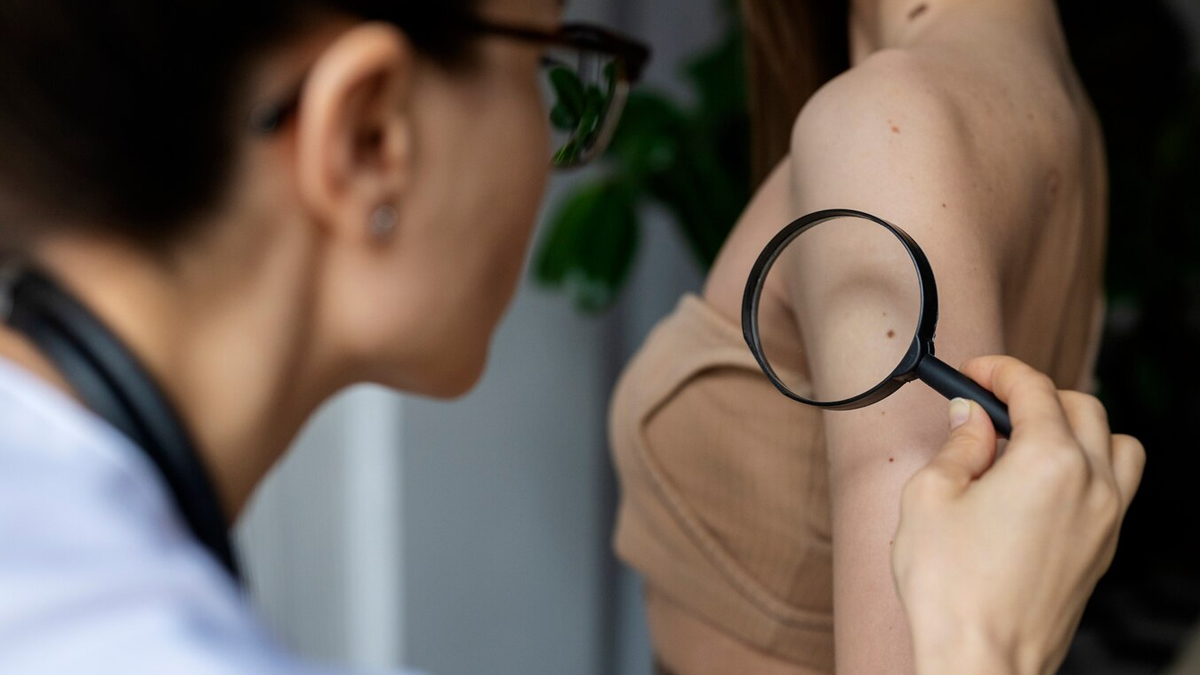
According to Dr Reddy, skin cancer affects men and women differently, suggesting that men are more likely to develop melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers (like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) than women.
Some of the common explanations behind this difference include:
- Oestrogen, one of the main female sex hormones, may protect against melanoma, which could partly explain why premenopausal women have lower rates than men of the same age.
- Skin thickness and hair coverage also differ by sex and may affect UV exposure and skin cancer risk.
- Women are generally more likely to use sunscreen and seek medical advice for skin changes, which can lead to earlier diagnosis.
- Men are more likely to work outdoors and expose more skin to UV radiation without protection.
Signs Of Skin Cancer To Watch Out For
Possible signs of skin changes to watch for:
- A new or changing growth, spot, bump, or mole on the skin
- A sore that won’t heal or keeps bleeding
- A rough, scaly, or crusty patch that may bleed
- A wart-like growth or a scab-like spot
- A mole or freckle that changes in size, shape, or color
- A mole with uneven edges, odd shapes, or mixed colours
- Itchy or painful skin around a growth
How Often Should One Get Screened For Skin Cancer?
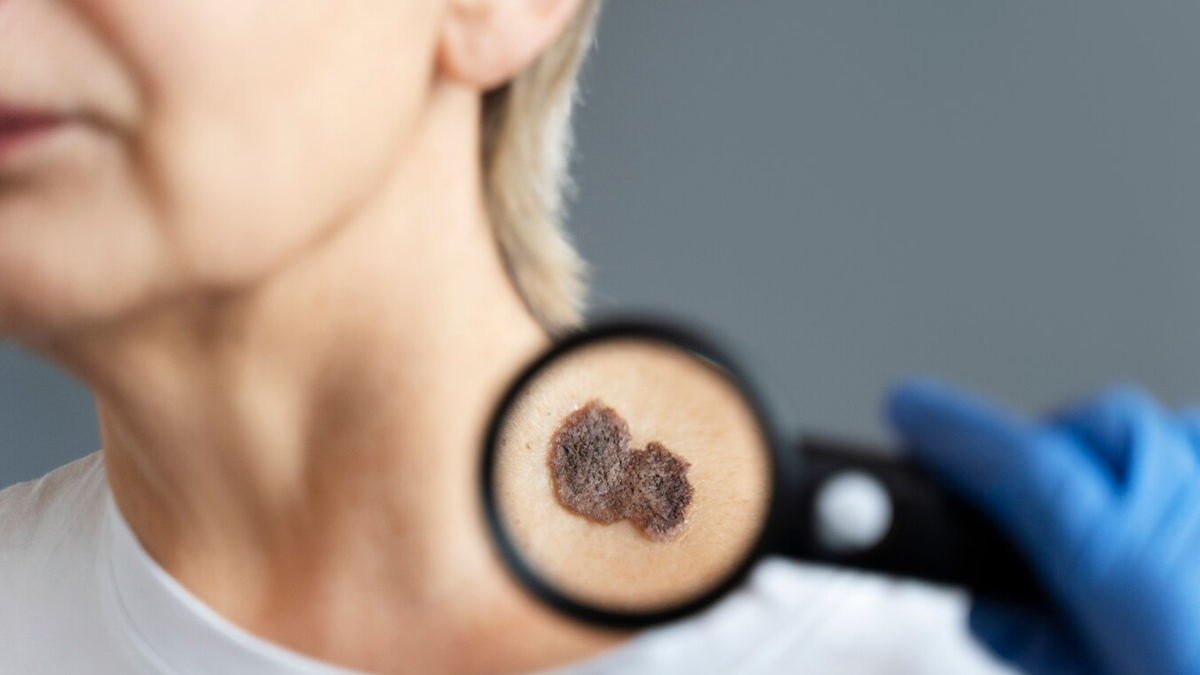
“For high-risk individuals who have a family history of skin cancer or more chances of exposure to UV radiation, who often tan, they should consult a dermatologist or skin cancer specialist at least once every six months for a full-body skin cancer screening,” advises Dr Reddy.
He adds, “Most adults aged above 50 should go for full-body skin cancer screening once a year. For people with little or no history of skin irregularities, diseases or skin-cancer-related familial skin conditions are recommended for annual checkup.”
Conclusion
The recent analysis highlights paying attention to sun exposure and how our daily habits, like what we wear and how often we slather up with sunscreen, are able to impact our risk of getting melanoma.
With increasing cases of skin cancer, particularly among men, taking preventative steps like applying sunscreen, covering up and having regular skin checkups is important. It's also important to understand the gender-specific trends in melanoma so that individuals are more aware about looking out for changes in areas commonly affected. And as Dr Reddy points out, early detection and regular protection are our best bet against this killer disease.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version