Diabetes occurs when the body fails to make enough insulin or when it is unable to use it efficiently. Insulin is a type of hormone that allows glucose in the blood to enter cells, providing them with the energy to function. Unmanaged, uncontrolled blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves, which can in turn lead to complications in many areas, including the heart and circulatory system, kidneys, eyes, and skin. In addition, it also impacts the mouth, leading to oral health issues, which is what we’re going to discuss in this article.
Table of Content:-
According to Dr Sonali Kagne, Deputy Consultant, Department of Endocrinology, Sir HN Reliance Foundation Hospital, Mumbai, when blood sugar isn't properly managed, it weakens White Blood Cells (WBCs), which are the body’s main defence against bacterial infections that can occur in the mouth.
Moreover, diabetes can thicken the blood vessels, which slows the flow of nutrients to and waste products from body tissues, including the mouth. All of these factors deprive the body of its ability to fight infections, thus predisposing people with diabetes to various oral health issues, the doctor adds.
Here's a look at common oral health problems associated with diabetes.
Also Read: How Diabetes Can Affect Different Parts Of The Body
Dry mouth

Dry mouth is extremely common among diabetes patients. As per the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDKD), diabetes and some medicines used to treat diabetes can cause the salivary glands in your mouth to make less saliva. Saliva is the fluid that keeps your mouth wet. This is why reduced saliva flow can result in dry mouth, says Dr Kagne, adding that it can further lead to soreness, ulcers, infections, and tooth decay.
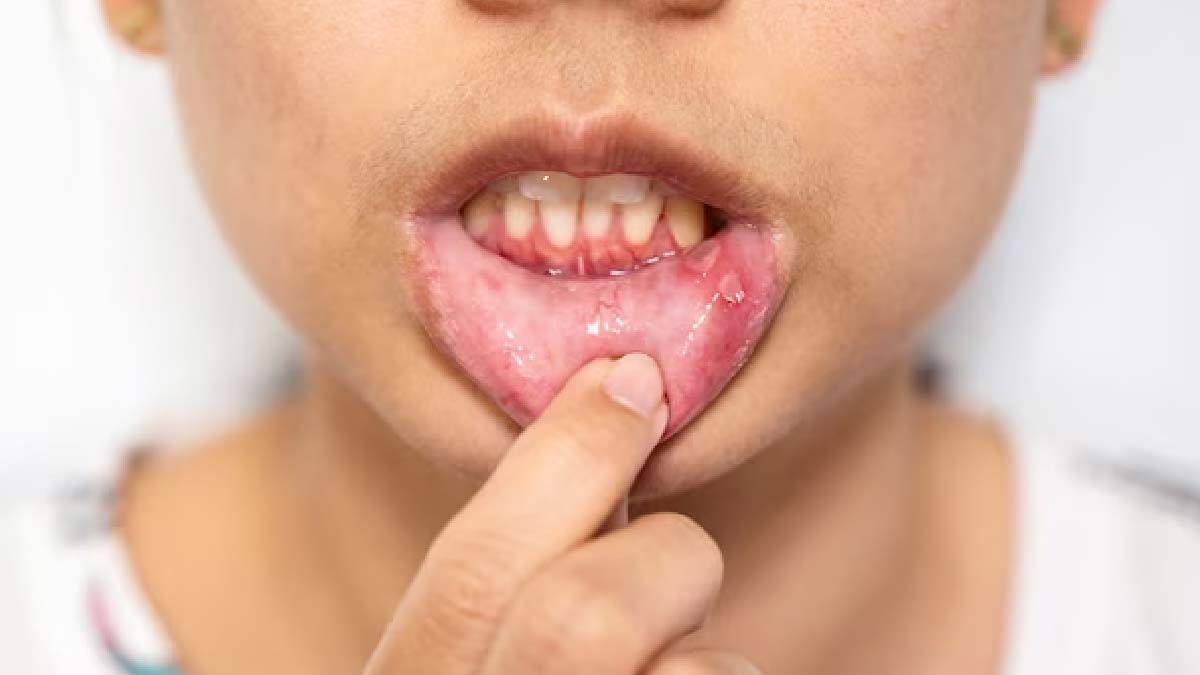
Gingivitis Or Gum Inflammation
Gingivitis is the most common type of gum disease, which occurs when plaque and bacteria start to build up in the teeth and cause infection. In the case of diabetes patients, the risk of gum disease or gingivitis is much higher. This is because the condition leads to reduced saliva, which means less protection, or an increase in the amount of glucose in the saliva, leading to more bacterial growth and plaque buildup, as explained by the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Oral Thrush

Oral thrush, a fungal infection in the mouth, is more common in people with diabetes. The fungus Candida albicans thrives on high blood sugar, which is often a problem for those with uncontrolled diabetes. This can lead to a white coating on the tongue or mouth lining and, sometimes, a burning sensation. Diabetics who frequently take antibiotics are at even higher risk, as antibiotics can disrupt the mouth's natural balance of bacteria, allowing the fungus to overgrow, explains Dr Kagne.
Poor Wound Healing In The Mouth
If your blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can damage nerves and blood vessels, so much so that it can reduce blood flow to the infection site in the mouth, resulting in poor wound healing. According to Dr Kagne, uncontrolled diabetes does not allow wounds to heal quickly after oral surgery or other dental procedures because blood flow to the treatment site can be compromised.
Also Read: Why Wounds Of Diabetic People Don’t Heal Easily? Here Are Some Tips To Keep In Mind
Dental Issues

High sugar levels in the blood also mean high sugar levels in the saliva, which creates the perfect environment for bacteria to grow in the mouth. Therefore, tooth decay and cavities are some of the most common dental issues associated with diabetes.
As per a 2022 study published in Frontiers in Oral Health, researchers found more diabetics had cavities than non-diabetics. Several factors were linked to higher cavity rates, including poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, sugary drinks, and inadequate knowledge about oral health. This indicates that high blood sugar levels contribute to the risk of developing dental issues.
Conclusion
To avoid oral health issues due to diabetes, it is crucial to manage your blood sugar levels. Eating healthy and avoiding foods with added sugar and those made with refined ingredients should be avoided. Regular exercise is key, whereas quitting smoking and limiting alcohol can provide added benefits. Moreover, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to stay up-to-date on your health. When it comes to your oral health, brush your teeth twice daily, scrape your tongue, and avoid sugary and processed treats that damage your teeth.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version