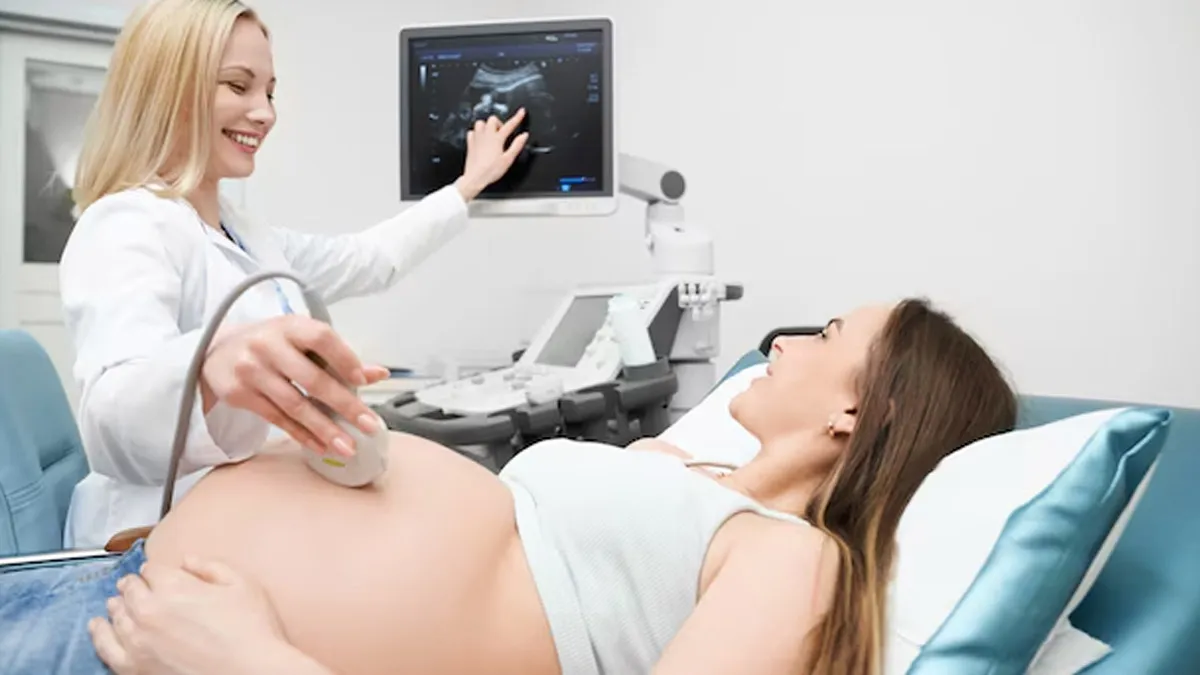
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is an extremely useful diagnostic tool. One of the most common uses of an ultrasound is during pregnancy. Not only does it detect pregnancy, but it can also assess foetal development, heartbeat, position, and potential abnormalities. In fact, it is a reliable method to detect pregnancy and monitor its progression.
Table of Content:-
However, ultrasound use is not limited to pregnancy; it plays an important role in reliable methods to detect pregnancy and monitor its progression. Here's how it works and the conditions that it can help detect.
Also Read: What To Expect During A Routine Prenatal Ultrasound: Signs To Take More Care
How Does An Ultrasound Work?
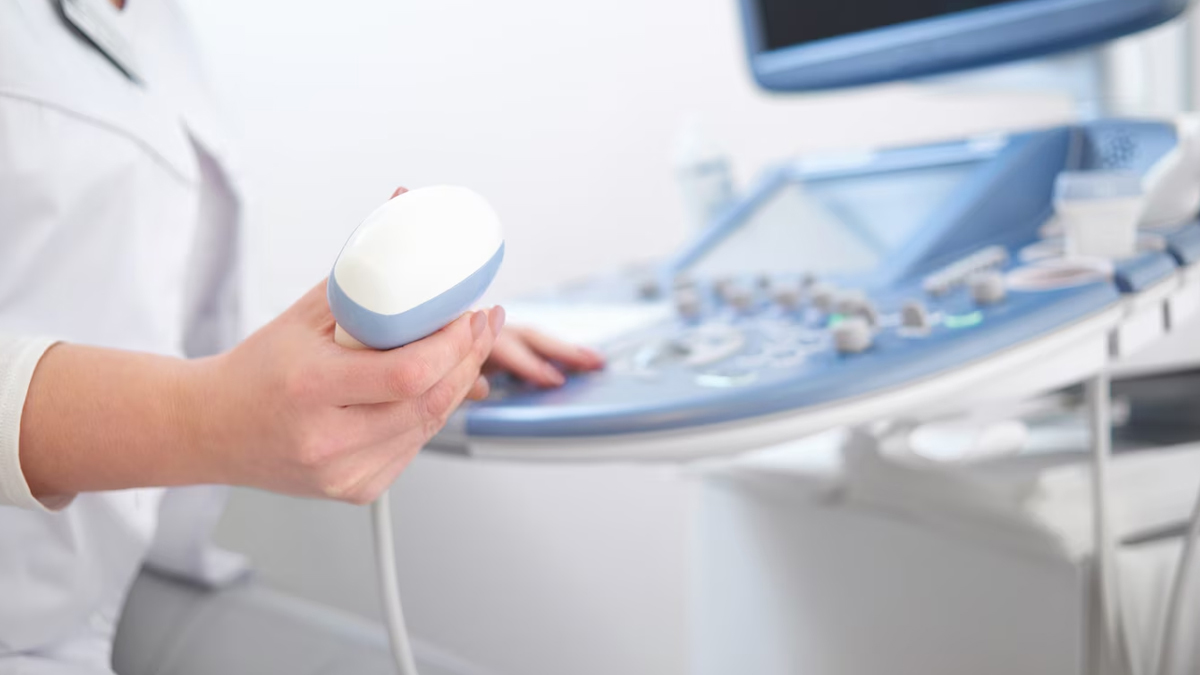
An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. A transducer, which comes with the ultrasound machine, emits and receives these sound waves. It is placed on the skin with a gel to improve sound transmission, and once the sound waves bounce off internal structures, the echoes are processed by a computer to generate a real-time image on a monitor.
Ultrasound Uses Beyond Pregnancy
In addition to monitoring pregnancy progression, an ultrasound can also be used to examine the abdomen, heart, blood vessels, and muscles, says Dr Shalini G R, Consultant – Foetal Medicine and Radiology, Motherhood Hospitals, Banashankari. "It also assists in the diagnosis of gall or kidney stones, liver disease, and even thyroid nodules, and can assist in carrying out non-invasive biopsies and drainage procedures."
Here are other uses:
- Cardiology – echocardiography to evaluate heart structure and function
- Abdomen – liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, spleen.
- Pelvis – uterus and ovaries
- Urology – prostate, bladder, testicles.
- Musculoskeletal – tendons, ligaments, joints, and soft tissues
- Thyroid and Neck – thyroid nodules, lymph nodes
- Breast – evaluating lumps
- Arterial and venous Doppler
Dr Shalini explains, "Ultrasound imaging depicts the size, structure, and texture of organs. In the liver, it identifies fatty changes, cirrhosis, or tumours. In kidneys, it identifies stones, cysts, or obstruction. In the thyroid, it is able to distinguish between solid and cystic nodules and can even be utilised to precisely guide fine-needle aspiration biopsies."
She adds, "Sports medicine and rheumatology are aided by high-resolution ultrasound as it provides visualisation of synovitis, rupture of tendons, and muscle damage, as well as visualisation of joints. Soft tissue can be rapidly evaluated without radiation using ultrasound."
Also Read: How Focused Ultrasound Can Help In Tremors And Epilepsy
Ultrasound Vs. CT And MRI: A Comparison
Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs are all medical imaging techniques. However, they differ significantly in how they create images, the types of information they provide, and their associated risks and costs.
Comparing the different types of imaging techniques, Dr Shalini shares, "Ultrasound does not image deeply seated organs and air-filled organs, such as lungs and bones. Some cancers of the brain, spine, and spinal cord are also included and need more information than ultrasound can provide in comparison to CT or MRI. Operator skill and patient body habitus can also affect accuracy."
Is Repeated Ultrasound Screening Safe?
Ultrasounds are generally safe and do not produce ionising radiation like that produced by X-rays. Dr Shalini shares, "Ultrasound can be repeated since it is not harmful, and the chronic conditions, such as liver diseases and nodules, can be monitored using ultrasound because the patient is not exposed to radiation. Until now, there have been no side effects that have been discovered with repeated ultrasounds because they are very safe."
However, according to the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), ultrasound is capable of producing some biological effects in the body under specific settings and conditions.
Conclusion
Ultrasound is a great way to detect pregnancy as well as monitor its progression. However, its use goes beyond that. From abdominal scans to imaging of the thyroid gland, an ultrasound can reveal various other abnormalities in the liver, kidneys, and reproductive system. Additionally, they can also identify stones, cysts, or obstruction and keep a check on thyroid health. Depending on your symptoms, consult a doctor to know whether or not you need an ultrasound or should resort to any other screening method.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version