The United States is currently witnessing a concerning surge in cases of parvovirus B19, prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to issue a health advisory. This virus, while commonly associated with childhood illness, has broader implications, particularly for certain vulnerable populations. As the CDC’s Health Alert Network (HAN) signals, healthcare providers, public health authorities, and the general public must be informed and vigilant about the rising activity of human parvovirus B19 in the country.
Table of Content:-
Understanding Parvovirus B19: A Seasonal Threat
Parvovirus B19 is a seasonal respiratory virus primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets. This means that it spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes, dispersing the virus into the air, where it can be inhaled by others. Both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals can transmit the virus, making it challenging to contain. The virus typically spikes in activity during the winter and spring months, but recent trends indicate that cases are on the rise beyond the usual season, raising concerns among health officials.
The Nature of Parvovirus Infection
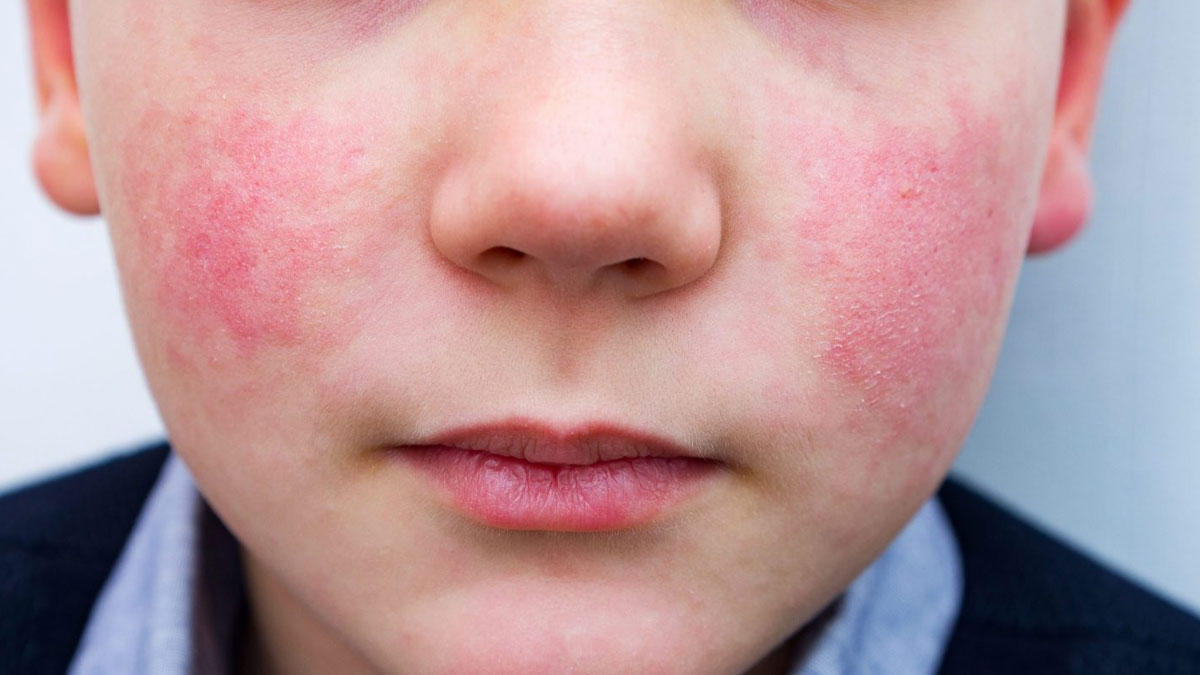
As per Dr Nivedita Dadu, Dermatologist, Founder & Chairman at Nivedita Dadu's Dermatology Clinic, Parvovirus B19 is particularly notorious for causing "fifth disease," a common and highly contagious illness among children. It is sometimes referred to as "slapped-cheek disease" due to the distinctive bright red rash that appears on a child’s face. Historically, the fifth disease was classified as one of several childhood illnesses marked by a rash, hence its numerical name.
While the infection is usually mild in children and often requires minimal treatment, it can be more serious in adults and certain high-risk groups. Pregnant women, individuals with certain types of anaemia, and those with compromised immune systems are particularly vulnerable to severe complications from the virus.
Symptoms: A Varied Presentation
The symptoms of parvovirus B19 infection can vary significantly depending on the age and health status of the infected individual.
Also Read: Nagpur Declares Public Health Emergency Amid Surge in Chikungunya and Dengue Cases
In Children
The early symptoms in children can mimic those of other common illnesses, including a mild fever, upset stomach, headache, and a runny nose. However, the hallmark of parvovirus B19 infection in children is the distinctive facial rash that appears a few days after the onset of these symptoms. The rash, which gives the appearance of flushed or “slapped” cheeks, may spread to other parts of the body, such as the arms, trunk, thighs, and buttocks. It often has a pink, lacy pattern and can be itchy, particularly on the soles of the feet. Notably, the rash usually appears toward the end of the illness and can persist for up to three weeks, sometimes reappearing in response to temperature changes or sun exposure.
In Adults
Adults who contract parvovirus B19 typically do not develop the characteristic facial rash. Instead, they are more likely to experience joint pain, particularly in the hands, wrists, knees, and ankles. This joint soreness can last from a few days to several weeks, and while it is often temporary, it can be quite uncomfortable.
Causes and Transmission
Human parvovirus B19 is distinct from the parvovirus that affects dogs and cats, meaning that the infection cannot be contracted from pets or spread to them. The virus is most commonly spread among elementary school-aged children, especially during outbreaks in colder months. However, anyone can be infected at any time of the year.
The virus spreads similarly to the common cold, through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing, as well as through direct contact with infected saliva. It can also be transmitted via blood, which is particularly concerning for pregnant women who can pass the virus to their fetus.
An important note is that parvovirus B19 is most contagious during the early stages of infection, before the rash appears. Once the rash is visible, the individual is no longer considered contagious, and isolation is not necessary.
Also Read: From Ancient Remedies to Modern Science: The Evolution of Mosquito Repellents
Complications: Who is at Risk?
Anaemia and Parvovirus
For individuals with anaemia, parvovirus B19 can lead to serious complications. The virus can halt the production of red blood cells, causing an anaemia crisis. This is particularly dangerous for those with sickle cell anaemia, where the risk of severe complications is heightened.
Pregnancy Risks
In pregnant women, especially during the first half of pregnancy, parvovirus B19 can pose significant risks to the fetus. The virus may cause severe anaemia in the unborn child, which can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth in rare cases.
Immunocompromised Individuals
People with weakened immune systems, whether due to conditions like HIV, cancer treatments, or organ transplant medications, are also at greater risk. In these individuals, parvovirus B19 can cause severe and sometimes life-threatening anaemia.
Prevention: Reducing the Risk
Currently, there is no vaccine available for human parvovirus B19, making prevention strategies crucial. Once a person has been infected, they typically gain lifelong immunity. However, to reduce the risk of infection, individuals are advised to practice good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing, avoiding touching the face, steering clear of people who are ill, and not sharing food or drinks.
Bottomline
The rise in parvovirus B19 cases in the United States is a reminder of the ever-present nature of infectious diseases and the need for public awareness. While often mild, parvovirus B19 can have serious consequences for certain individuals. Understanding the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of this virus is essential in managing its spread and protecting vulnerable populations. As the CDC continues to monitor the situation, staying informed and practicing preventive measures will be key in mitigating the impact of this viral infection.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version