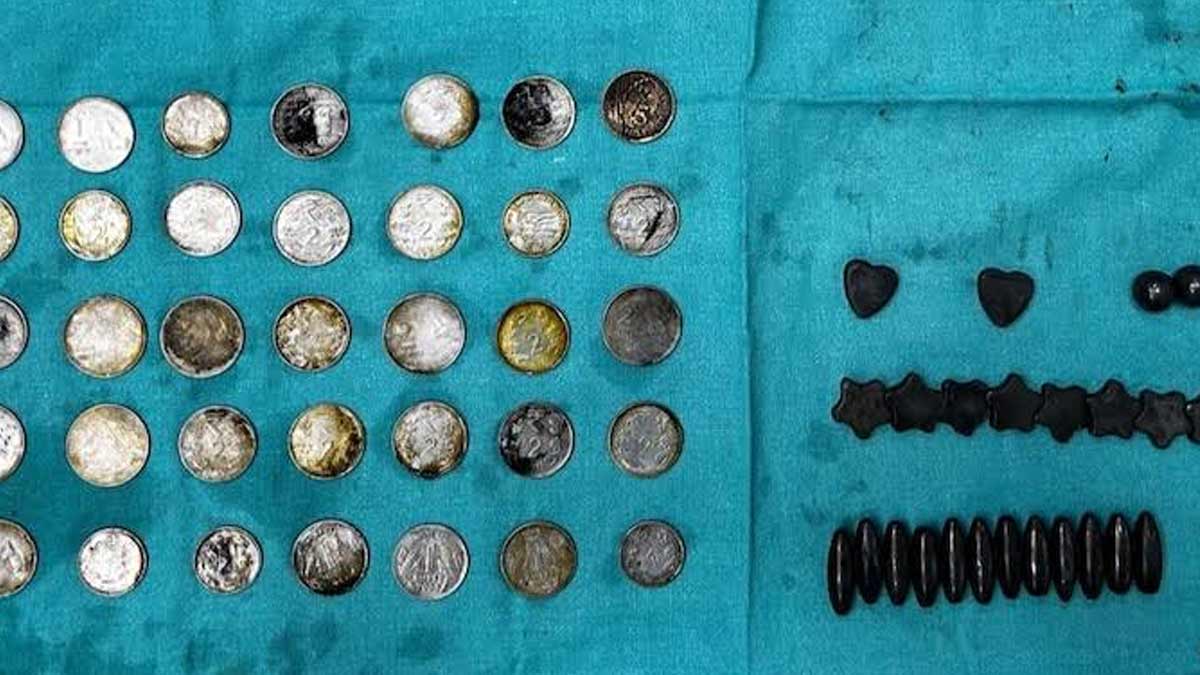

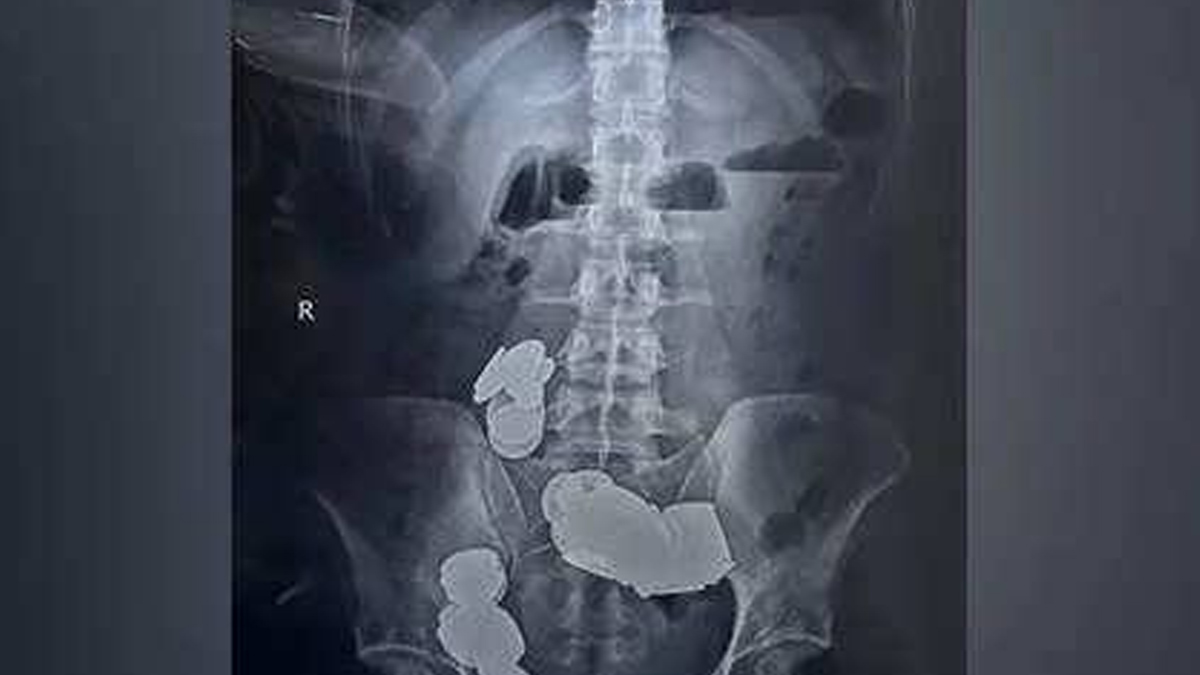
In a bizarre affair, a 26 year old man living in Delhi found a creative way to fulfill his body's requirement of dietary zinc. Reportedly, he was told that consuming a zinc rich diet helps in body building. His solution? Swallow 39 coins and 37 magnets.
Table of Content:-
The incident became famous after the boy visited Sri Ganga Ram Hospital's emergency ward, complaining about unstoppable vomiting, inability to eat anything and abdominal pain, all of which has been troubling him since the last 20 days.
At least the boy had the good sense to include coins and magnets as a part of his daily diet. His relatives shared that he had been investigating these delectable, zinc loaded items for several weeks and not all at once. Unsurprisingly, he was also being treated for a known psychiatric condition.
The coins and magnets had blocked his intestine and stomach, calling for immediate surgical intervention. During the surgery, the doctors discovered that the magnets' attraction had started to pull other objects in his body, causing the intestinal wall to erode and form two separate loops. Fortunately, he is back to normal now after a week long stay at the hospital, equipped with a repaired intestine and the sense that magnets and coins are not to be eaten. If you too have some similar ideas, let me tell you that there are much better and healthier options to have a zinc rich diet.
Zinc Health Benefits
According to the Harvard School of Public Health, the two main functions of zinc in our body are:
Immune Function
Zinc plays a crucial role in immune function, helping to support the body's defense against infections and illnesses. Even a mild to moderate deficiency of zinc can retard the functioning of immune cells, contributing to stunted growth, diarrhea, pneumonia, and malaria in kids, and increased risk of infection and skin ulcers in adults.
Wound Healing
Zinc aids in wound healing by contributing to cell growth and repair. It also helps the body to combat inflammation caused by a wound. That is why it is often recommended for treating cuts and burns, where it can even be used as a topical treatment.
Before be jump into the dietary sources of zinc, here are some other health benefits of zinc:
- Skin Health: Zinc is important for maintaining healthy skin, and it may help with conditions like acne and eczema.
- Metabolism: Zinc is involved in various metabolic processes, including protein and DNA synthesis, as well as carbohydrate metabolism.
- Senses: It is essential for proper taste and smell sensation.
- Eye Health: Zinc is found in high concentrations in the retina, and it helps to maintain healthy vision.
- Reproductive Health: Zinc is crucial for both male and female reproductive systems, supporting fertility and reproductive health.
Also Read: Nutrition Week 2023: Consuming Zinc-Rich Foods Can Help Your Child Combat Malnutrition
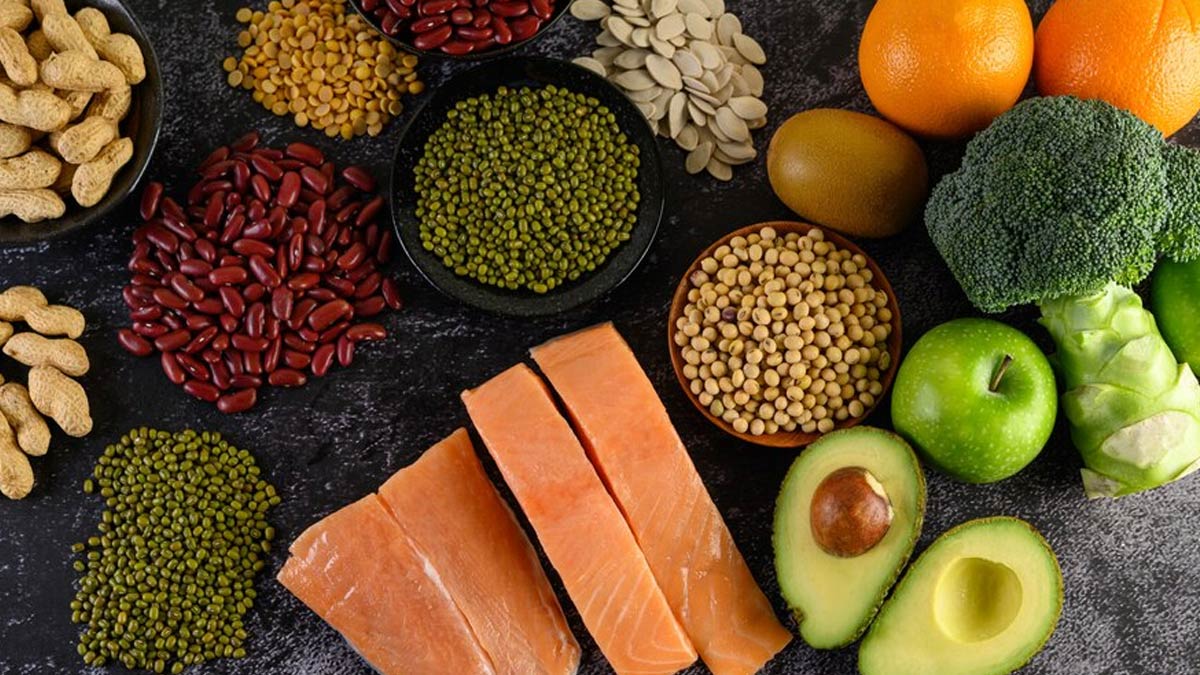

Zinc Dietary Sources
Before you reach for a handful of coins and magnets, remember that dietary zinc is always, in all scenarios, a much better option. The Australian government's health department recommends the following sources:
- Oysters: Approximately 30 mg in a 90g serving
- Beef (steak): 3.8 mg in a 90g serving
- Pumpkin seeds: 2.2 mg in a 30g serving
- Crab: 3.2 mg in a 90g serving
- Oats (rolled, cooked in water): 2.3 mg in a 1 cup serving
- Cheddar Cheese: 1.5 mg in a 45g serving
- Sardines (canned in oil, drained): 1.1 mg in a 90g serving
- Milk (1% fat): 1 mg in 1 cup
- Peanuts: 0.8 mg in a 30g serving
- Egg: 0.6 mg in 1 large egg
- Salmon (cooked): 0.5 mg in a 90g serving
- Rice (white, long-grain): 0.3 mg in ½ cup cooked rice
- Bread (white): 0.2 mg in 1 slice
Also Read: Zinc And Healthy Gut: Here Are 5 Foods You Must Include In Your Diet
The Australian organisation also shared that most males need 14 mg of dietary zinc daily while women need 8 mg. So keep that in mind when customising your daily meals. A better option is to consult a certified dietician or a healthcare professional who can make a personalised diet plan for you which considers your body's requirement for all other nutrients as well.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
