
The United Kingdom (UK) has been put on high alert after a traveler who recently visited the country tested positive for Lassa fever. The individual, who had traveled from Nigeria to England, has since returned to Nigeria but was confirmed to have contracted the virus during their time in the UK. Health officials have now launched a proactive effort to trace any possible contacts to prevent further spread of the virus.
Table of Content:-
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has reassured the public that the overall risk of Lassa fever transmission is very low, as the virus does not spread easily between individuals. However, as a precaution, officials are closely monitoring any potential symptoms in those who may have come in contact with the infected individual.
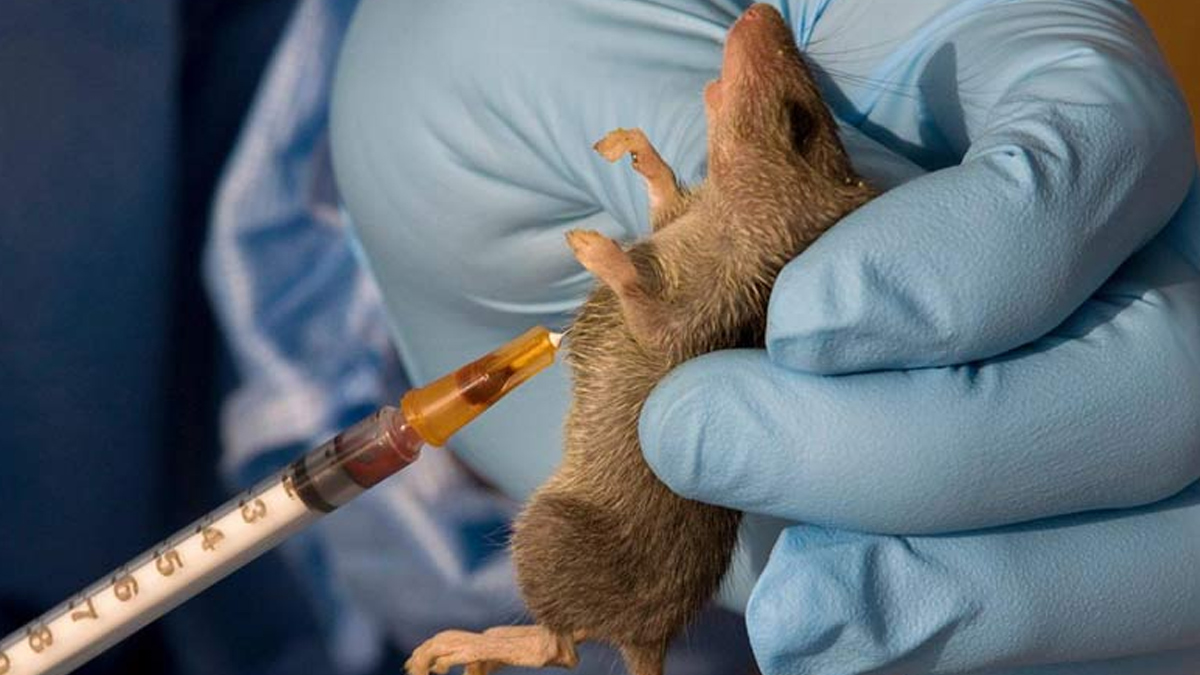
What Is Lassa Fever?
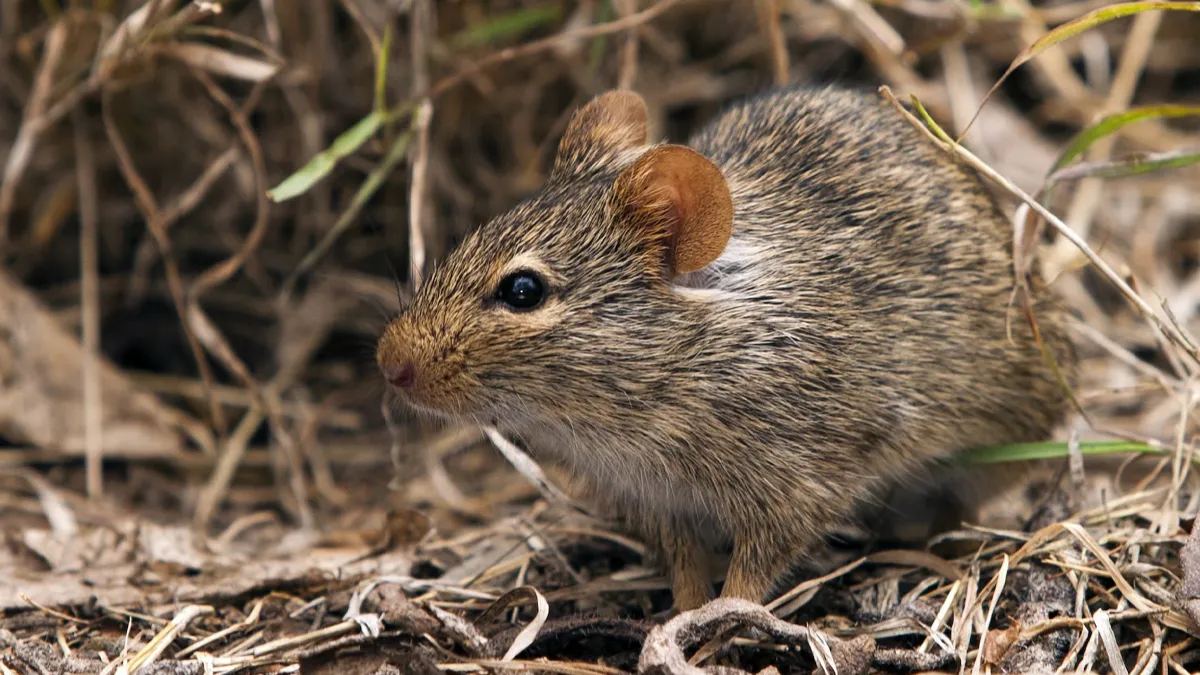
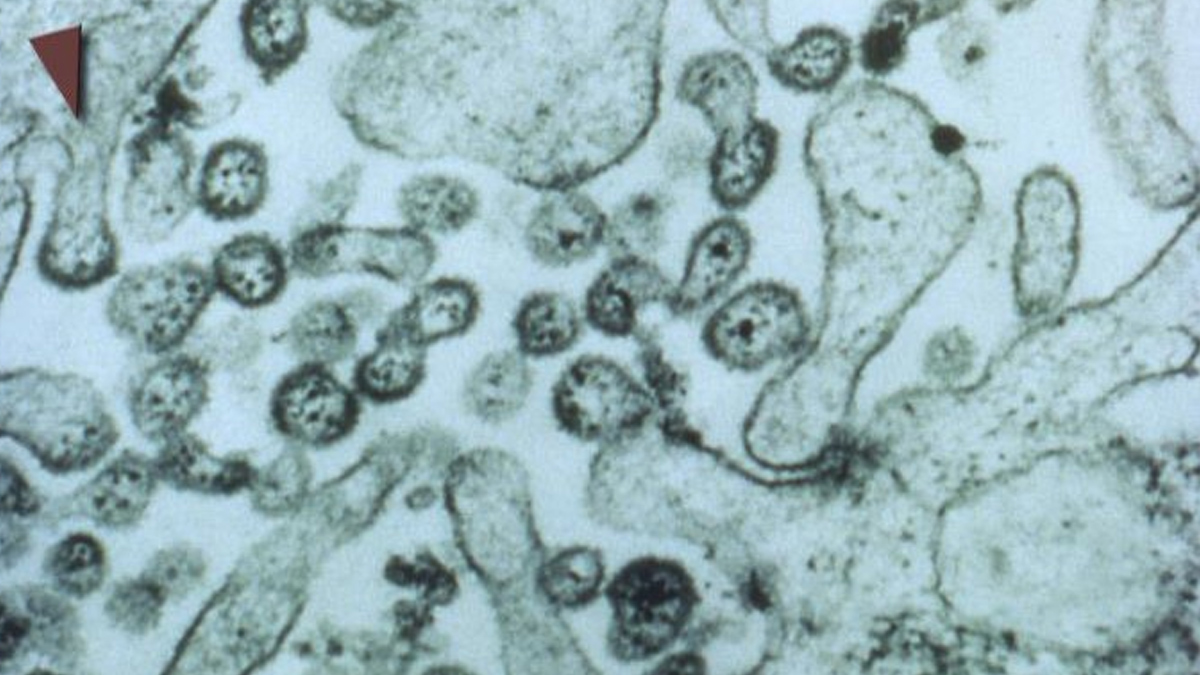
Lassa fever is a viral hemorrhagic illness caused by the Lassa virus, primarily transmitted to humans through contact with food or household items contaminated by the urine or feces of infected rats. The virus is endemic in several West African countries, including Nigeria, Ghana, Sierra Leone, and Liberia, where human-to-human transmission can also occur in some cases.
The disease gets its name from the town of Lassa in Nigeria, where it was first discovered in 1969. According to health experts, the virus is transmitted from rodents to humans, and in rare cases, it can spread from one human to another through exposure to bodily fluids such as blood, urine, saliva, or semen.
While most cases of Lassa fever are mild or asymptomatic, severe cases can lead to bleeding, organ failure, or death. Early detection and supportive care are crucial in managing the virus.
How Is The UK Responding To The Lassa Fever Case?
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has confirmed that they are taking swift action to trace any individuals who may have come into contact with the traveler during their time in the UK. Although the infected person has already returned to Nigeria, UK officials want to eliminate any potential risks by identifying and monitoring those who might have been exposed.
Also Read: WHO Warns Of Potential Tuberculosis Surge Amid USAID Funding Cuts; Global Health At Risk
Dr Meera Chand, the Deputy Director of UKHSA, stated, "Our health protection teams are working quickly to get in touch with people who were in contact with this individual while they were in England, to ensure they seek appropriate medical care and testing should they develop any symptoms."
Dr Chand further emphasised that the virus does not spread easily from person to person, and hence the overall risk to the public remains low. However, close contacts have been advised to monitor themselves for any possible symptoms and seek immediate medical attention if required.
Symptoms of Lassa Fever
The symptoms of Lassa fever can range from mild to severe, with some people remaining asymptomatic throughout their infection. However, in severe cases, the following symptoms may appear:
- High fever
- Weakness or fatigue
- Muscle and joint pain
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Chest pain and sore throat
- Bleeding from the nose, gums, or internal organs in severe cases
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face or neck
In the most severe cases, Lassa fever can cause multi-organ failure, internal bleeding, and death. According to WHO, around 1 in 5 Lassa fever infections lead to severe disease, with a higher mortality rate in hospitalized patients.
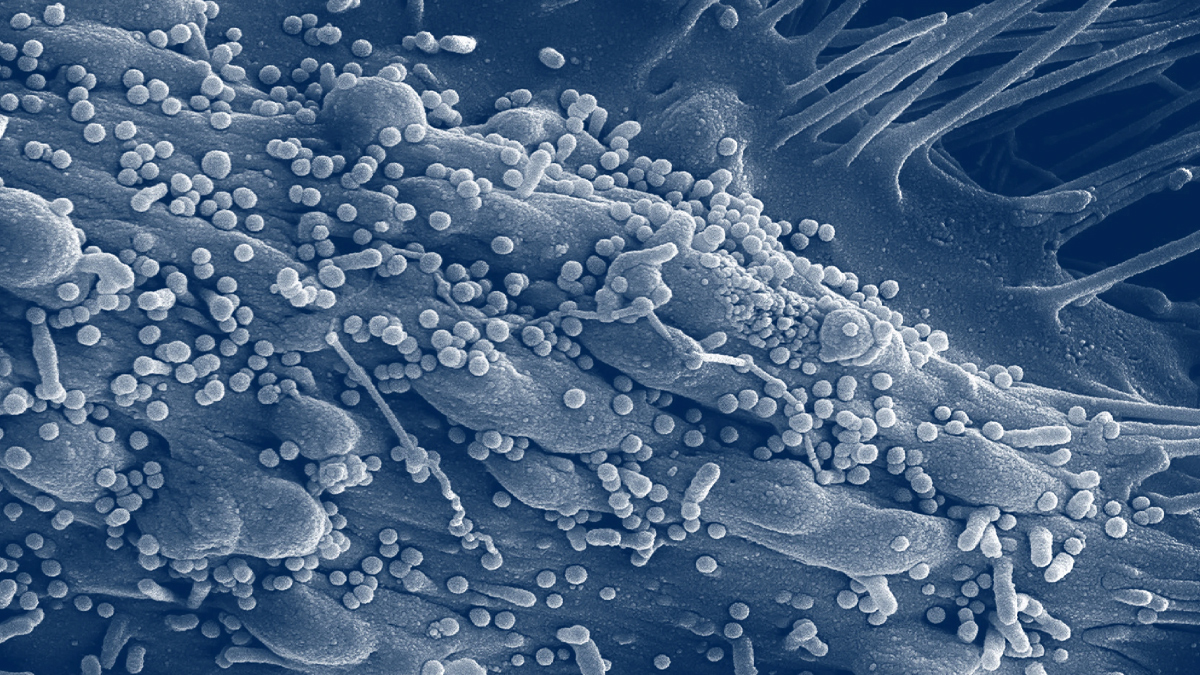
How Does Lassa Fever Spread?
Lassa virus is primarily spread to humans through:
- Contact with rodents: People can get infected by coming into contact with food, surfaces, or household items contaminated with rat urine or feces. In some parts of West Africa, where the virus is endemic, poor sanitary conditions contribute to the spread of the virus.
Also Read: Delhi Battles Worst H1N1 Swine Flu Outbreak In Years; Here’s How To Stay Safe
- Human-to-human transmission: In some rare cases, Lassa fever can spread from an infected person to another person through contact with bodily fluids such as blood, saliva, urine, or semen. Healthcare workers treating infected individuals without proper protective gear are at high risk.
- Laboratory exposure: Individuals working in laboratories handling Lassa virus specimens are also at risk if proper biosafety measures are not followed.
How Is Lassa Fever Treated?
As of now, there is no specific vaccine or cure for Lassa fever. Treatment mainly involves supportive care, which includes:
- Providing fluids and electrolytes to avoid dehydration
- Treating any underlying bacterial infections
- Monitoring and managing blood pressure and oxygen levels
- Administering antiviral drugs like Ribavirin, which have shown some effectiveness when given early in the infection
In cases of severe Lassa fever, patients may require hospitalization, intensive care, or isolation to prevent the spread of the virus to others.
Bottomline
The confirmation of Lassa fever in a traveler from Nigeria has put UK health authorities on high alert. Although the risk of public transmission remains very low, the incident has once again highlighted the vulnerability of global health systems in preventing the spread of deadly viruses.
Officials are working swiftly to trace, test, and treat any individuals who may have come into contact with the infected traveler. This event also underscores the need for stronger global health surveillance, improved sanitary conditions, and the development of vaccines to protect people from emerging infectious diseases like Lassa fever.
While there is no widespread threat at the moment, the situation serves as a stark reminder that infectious diseases know no borders — and global preparedness is the key to preventing large-scale outbreaks.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Lorazepam Explained: The Anti-Anxiety Drug Sparking Curiosity After The White Lotus Mention
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version