
Diabetes is a chronic condition that may affect different parts of the body, including your eyes, nerves, and kidneys. But what many people often overlook is its impact on reproductive health, particularly in women.
Table of Content:-
Experts suggest that diabetes can affect fertility in both men and women and impact chances of pregnancy. The primary culprit: hormonal imbalance. To understand the link between the OnlyMyHealth team, spoke to Dr Jalagam Kavya Rao, MBBS, MS OBG, FRM, FIGL, Regional Medical Head and Fertility Specialist, Oasis Fertility, Warangle.
Also Read: Fertility Treatments For Women With PCOS: What Works And What Doesn't
How Type 2 Diabetes Affects Your Chances Of Getting Pregnant
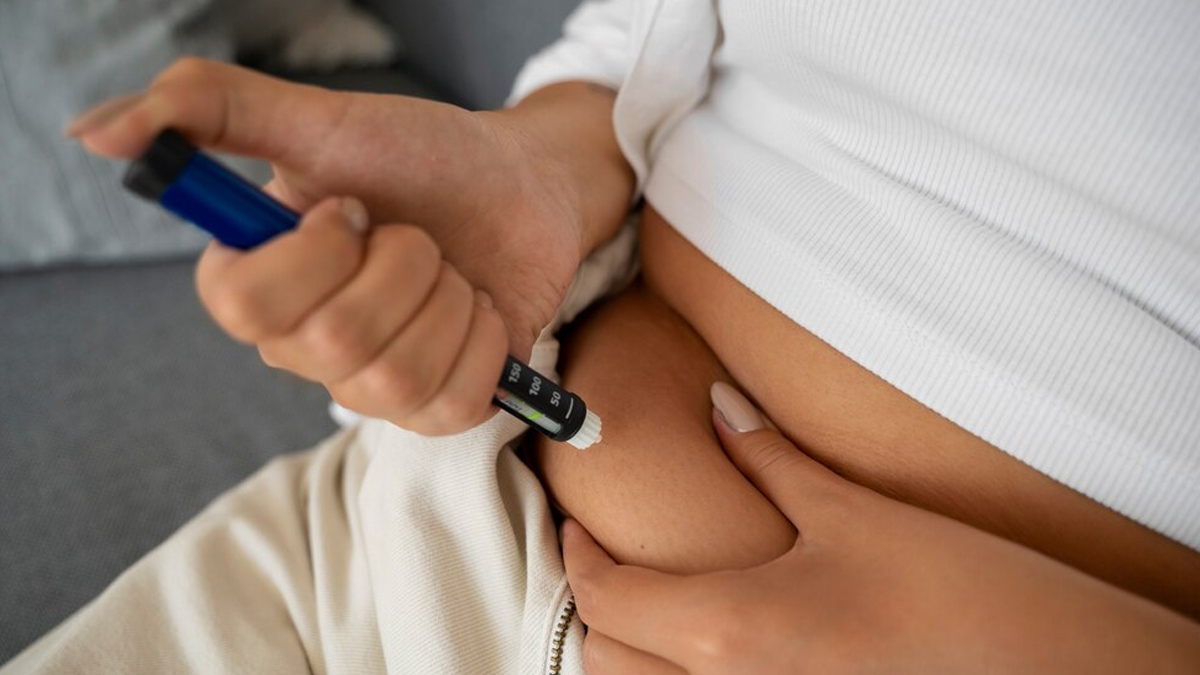
According to Dr Rao, type 2 diabetes can reduce fertility, especially if it is not well managed. It can cause hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular ovulation, poor egg quality, the development of aneuploid embryos (embryos with abnormal chromosomes), and implantation failure, she said, adding that once pregnant, uncontrolled diabetes can increase the risk of pregnancy complications.
She further explained that type 2 diabetes is closely linked to body weight and Body Mass Index (BMI). Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, which can further disrupt hormonal balance. Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and diabetes often experience elevated androgen levels, which can interfere with ovulation and reduce fertility.
Therefore, taking proactive steps to manage type 2 diabetes through diet, exercise, and medical treatment can significantly enhance your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Fertility Treatments Safe For Diabetic Women

Assisted Reproductive Treatments (ART) like In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF), Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), and hormonal therapy can support conception in women with diabetes by stimulating ovulation and improving egg quality, shared Dr Rao.
He added that combined with proper blood sugar control, medications, and weight management, these treatments can enhance fertility and significantly increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Also Read: Silent Threats to Fertility: How Environmental Toxins Impact Women's Reproductive Health
Lifestyle Changes To Adopt
According to Dr Rao, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress effectively can help stabilise blood sugar and hormones, improving ovulation and pregnancy chances. Even before, during, and after pregnancy, women should consult an endocrinologist for managing diabetes and hormone levels.
How To Prepare For A Pregnancy With Diabetes

According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), it is important to make physical activity a regular part of your routine before trying to conceive. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, each week.
If you and your partner are having difficulty getting pregnant, consult a healthcare professional to determine if further evaluation is needed. Diabetes can lead to health issues like erectile dysfunction and infertility, which may affect your ability to conceive.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version