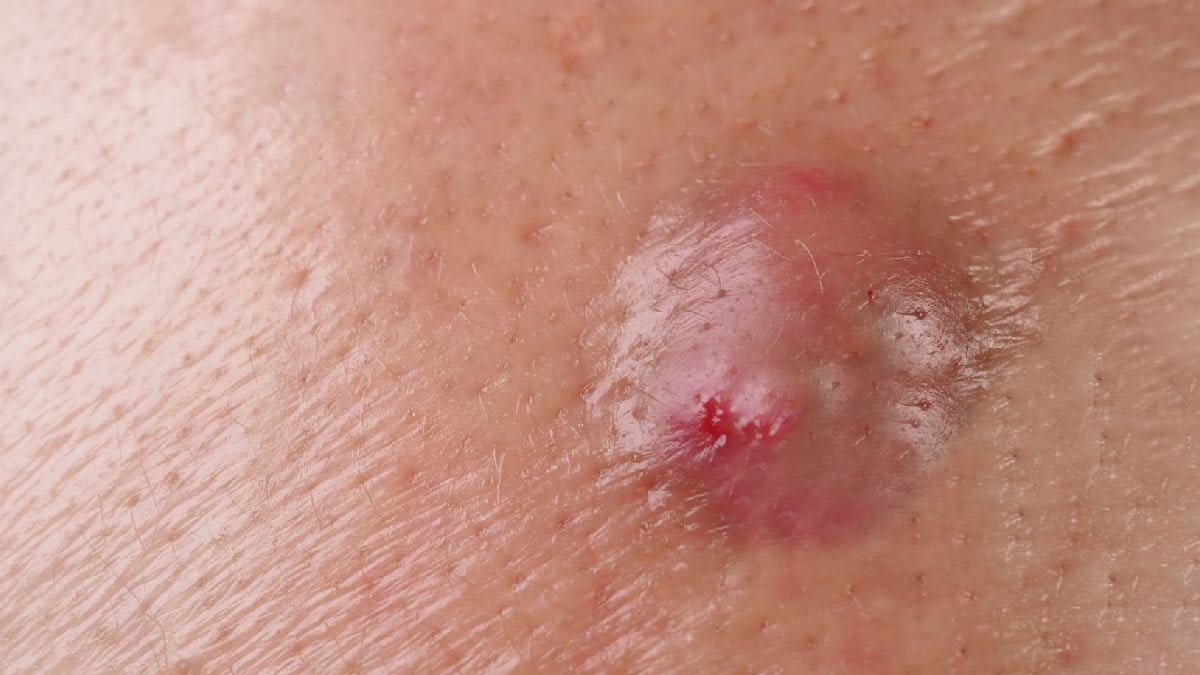
Vaginal boils, medically known as vaginal furuncles or abscesses, can be a distressing and uncomfortable condition for many women, not to mention the embarrassment we often feel when getting intimate with a partner. These painful bumps can develop due to various reasons such as bacterial infections, ingrown hairs, or blocked sweat glands. If you're experiencing vaginal boils, it's essential to understand how to treat them effectively and take preventive measures to avoid recurrence.
Table of Content:-
What Causes Vaginal Boils?
The Institute For Quality And Efficiency in Health Care defined boils as localised infections that result in the formation of tender, red, and swollen bumps. When it happens near the vagina, it is called vaginal boils. They may be accompanied by pain, itching, and a sensation of warmth. Boils can range in size from small pustules to larger, more painful abscesses filled with pus. Here’s what may be causing them:

- Bacterial Infections: The most common cause of vaginal boils is bacterial infections, particularly by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. These infections can occur when bacteria enter hair follicles or minor breaks in the skin, leading to inflammation and the formation of boils.
- Ingrown Hairs: Ingrown hairs, resulting from improper shaving or hair removal techniques, can also contribute to the development of boils in the vaginal area. When hair follicles become blocked or irritated, they can become infected and form boils.
- Blocked Sweat Glands: Sweat glands in the vaginal area can become blocked due to sweat, dead skin cells, or excess moisture, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth and boil formation.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hygiene practices, such as using harsh soaps or wearing tight, non-breathable clothing, can irritate the skin and increase the risk of developing vaginal boils.
Treating Vaginal Boils
If you're experiencing vaginal boils, here are some tips to help treat them and promote healing:
Also Read: Do Not Pop Vaginal Boils: Gynaecologist Explains Why And How To Treat Them Safely

- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected area several times a day can help reduce pain and swelling, and promote drainage of the boil. Use a clean cloth soaked in warm water and apply gentle pressure for 10-15 minutes each time.
- Maintain Hygiene: Keep the affected area clean and dry. Use mild, fragrance-free soap to avoid further irritation. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scented products near the vaginal area, as they can exacerbate symptoms.
- Avoid Squeezing: Refrain from squeezing or popping the boil, as this can lead to further infection, scarring, and spread of bacteria. Let the boil drain naturally or seek medical assistance for safe drainage.
- Wear Loose, Breathable Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting cotton underwear and clothing to allow proper airflow and reduce friction in the vaginal area. Avoid tight clothing that can trap moisture and irritate the boil.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support your immune system. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can promote overall skin health and aid in healing.
- Seek Medical Evaluation: If the boil is large, persistent, or accompanied by fever, seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider may need to drain the boil or prescribe antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Also Read: Try These Tips To Maintain Your Vaginal Health With Changing Season
Preventing Vaginal Boils
The good news is, in most cases, vaginal boils can be prevented as long as the underlying cause is not hormonal imbalance or a disease. If your vaginal boils are a cause of your lifestyle, these practices can help you prevent vaginal boils:
- Maintain proper hygiene, including gentle cleansing of the vaginal area with mild soap and water.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or douching, as they can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and increase the risk of infections.
- Choose breathable, loose-fitting clothing and underwear to prevent friction and moisture buildup in the vaginal area.
- Use gentle techniques such as trimming or shaving in the direction of hair growth to reduce the risk of ingrown hairs and irritation.
- Support your immune system by staying active, eating a nutritious diet, getting adequate rest, and managing stress.
By following these comprehensive guidelines for treating and preventing vaginal boils, you can effectively manage this condition and promote healing and comfort in the vaginal area. Remember to consult your healthcare provider for personalised advice and treatment recommendations based on your individual needs and medical history.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version