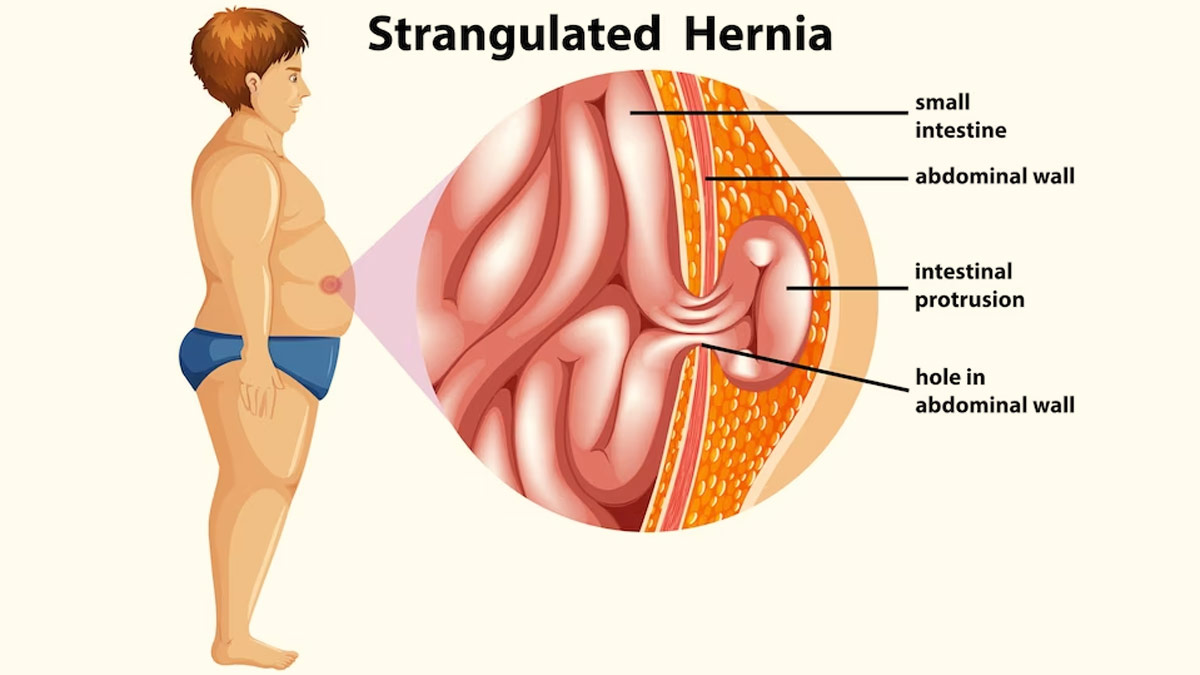
Hernias occur when an organ or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias can cause discomfort and may require medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hernias.
Table of Content:-
Types of Hernias
According to Dr Jagan Mohan Reddy, Surgical Gastroenterologist, Apollo Spectra Hospital, Kondapur, Hyderabad, hernias can occur in various parts of the body. The most common types include:
a) Inguinal Hernia: This type affects the groyne area and is more common in men.
b) Femoral Hernia: Similar to inguinal hernias, but they occur lower in the groyne.
c) Umbilical Hernia: Occurs near the navel and is common in infants and overweight individuals.
d) Incisional Hernia: Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision.
e) Hiatal Hernia: Involves the upper part of the stomach protruding through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hernias often develop due to a combination of factors, including:
a) Weakness in the abdominal wall: This can be present at birth or develop later in life.
b) Straining: According to study, excessive physical exertion, chronic coughing, or constipation can contribute to hernia formation.
c) Age and gender: Some hernias are more common in certain age groups or sexes.
d) Obesity: Carrying excess weight puts additional strain on the abdominal wall.
e) Pregnancy: The pressure exerted by the growing uterus can increase the risk of hernias.
Common Symptoms
While some hernias are asymptomatic and are discovered incidentally, others may cause noticeable symptoms such as:
a) A visible bulge or lump at the hernia site.
b) Discomfort or pain, especially when lifting heavy objects or straining.
c) Aching or burning sensation at the site of the hernia.
d) Feeling of pressure or weakness in the affected area.
e) Nausea, vomiting, or difficulty passing stool (in the case of hiatal hernias).

Diagnosis and Treatment Options
To diagnose a hernia, a healthcare professional will perform a physical examination and may order additional tests, such as ultrasound or imaging scans. Treatment options depend on the type and severity of the hernia:
a) Watchful waiting: Small, asymptomatic hernias may not require immediate treatment but should be monitored regularly.
b) Lifestyle modifications: Making changes like weight loss, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing chronic cough can help prevent worsening of hernias.
c) Hernia trusses or supports: These devices may be used temporarily to provide support and relief for certain types of hernias.
d) Surgical repair: In cases where the hernia causes symptoms or poses a risk of complications, surgery may be recommended. Laparoscopic or open surgery techniques can be employed for hernia repair.

Hernias are common medical conditions that can affect people of all ages and genders. While some hernias may not cause significant symptoms, others may require medical intervention. Understanding the causes, recognising the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment are essential for managing hernias effectively. If you suspect you have a hernia or are experiencing any related symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version