Do you know what Gout is? It is a kind of arthritis that mostly causes discomfort and swelling in the joints of many body parts, including the ears, wrists, knees, ankles, and even the hands. Ankle discomfort and inflammation are the most typical symptoms. The main cause of gout is an increase in the levels of uric acid in the body.
Table of Content:-
“Gout is a form of arthritis characterised by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints”, said Dr Ganesh Chaudhary, PHC, Darbhanga, Bihar.
What Are The Potential Signs of Gout
Sudden Joint Pain
Gout attacks come on suddenly and cause intense pain, often described as a throbbing or crushing sensation. The affected joint becomes extremely tender and painful to the touch.

Swelling and Redness
The affected joint, most commonly the big toe, can become swollen and red. Swelling may also make it difficult to move the joint.
It Limits The Mobility
Due to the pain and swelling, mobility in the affected joint is often severely restricted during a gout attack.
- Warmth: The joint may feel warm to the touch.
- Recurrent Attacks: Gout tends to be episodic, with recurrent flare-ups interspersed with periods of no symptoms.
Causes of Gout
High Uric Acid Levels
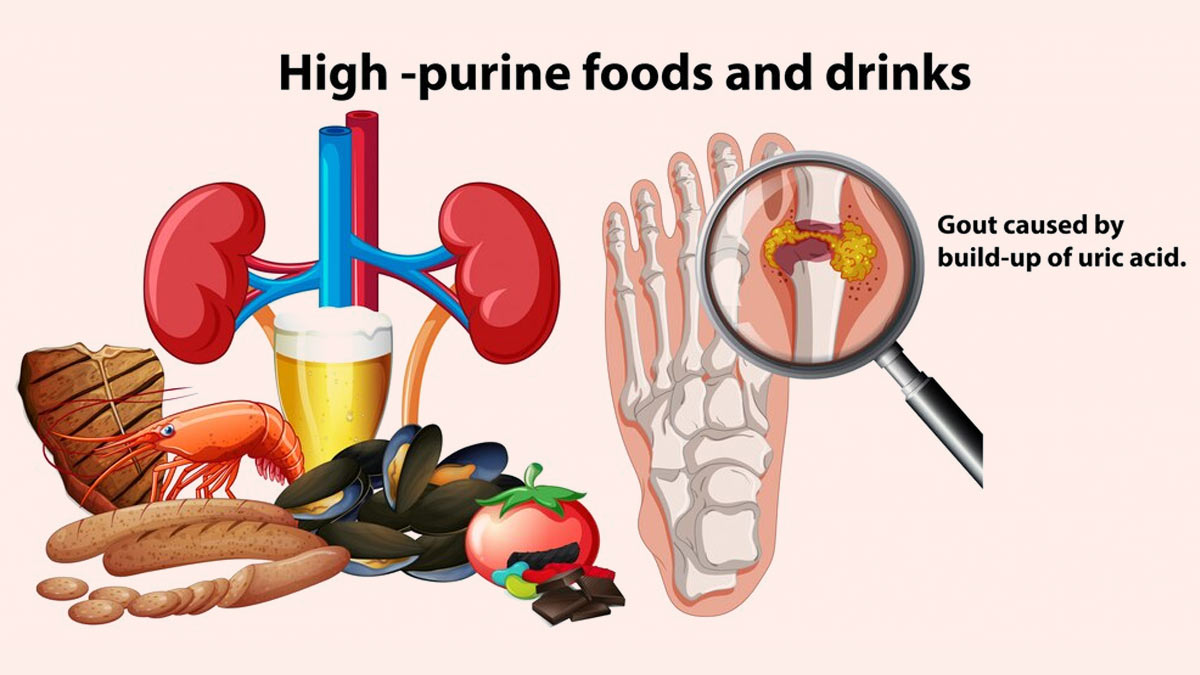
Gout occurs when there is an excessive buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream. Uric acid is a waste product that forms when the body breaks down purines, which are found in certain foods and are produced by the body.
Also read: 9 Ways To Naturally Reduce Uric Acid In The Body
Dietary Factors
Consuming a diet rich in purine-containing foods, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels and increase the risk of gout.
Genetics
Some people are genetically predisposed to higher uric acid levels and are more susceptible to gout.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, like kidney disease, hypertension, and diabetes, can increase the risk of gout.
Also read: How to Lower Your Uric Acid Naturally
Medications
Some medications, including diuretics and aspirin, can raise uric acid levels and potentially trigger gout attacks.
Treatment for Gout
Medications
A doctor may prescribe medications to treat and prevent gout attacks. According to the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids to relieve pain and reduce inflammation during an attack.
Dietary Changes
Making dietary modifications can help manage gout. Limiting the consumption of purine-rich foods and reducing alcohol intake can be beneficial. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water may also help prevent attacks.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy body weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help prevent gout and reduce the severity of attacks.
Joint Care
During a gout attack, resting and elevating the affected joint can provide relief. Applying ice may help reduce swelling and pain.
Consulting a Specialist
If you experience recurrent gout attacks or have difficulty managing the condition, consider consulting a rheumatologist, a specialist in arthritis and related conditions.
Gout can be a painful and disruptive condition, but with proper management, including medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments, it is possible to control symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. If you suspect you have gout or have been diagnosed with it, working closely with a doctor is essential to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version