Gout is a form of arthritis known for causing sudden, severe pain, redness, and tenderness in the joints. While it often targets the big toe, it can also affect other joints in the body. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of gout can significantly help in managing this painful condition. We spoke to our expert Dr Basavaraj CM, HOD and Senior Consultant Orthopedics and Joint Replacement Surgeon, Gleneagles BGS Hospital, Kengeri, Bengaluru, who explained this health condition, symptoms, causes, risk factors, treatment, and preventive measures.
Table of Content:-
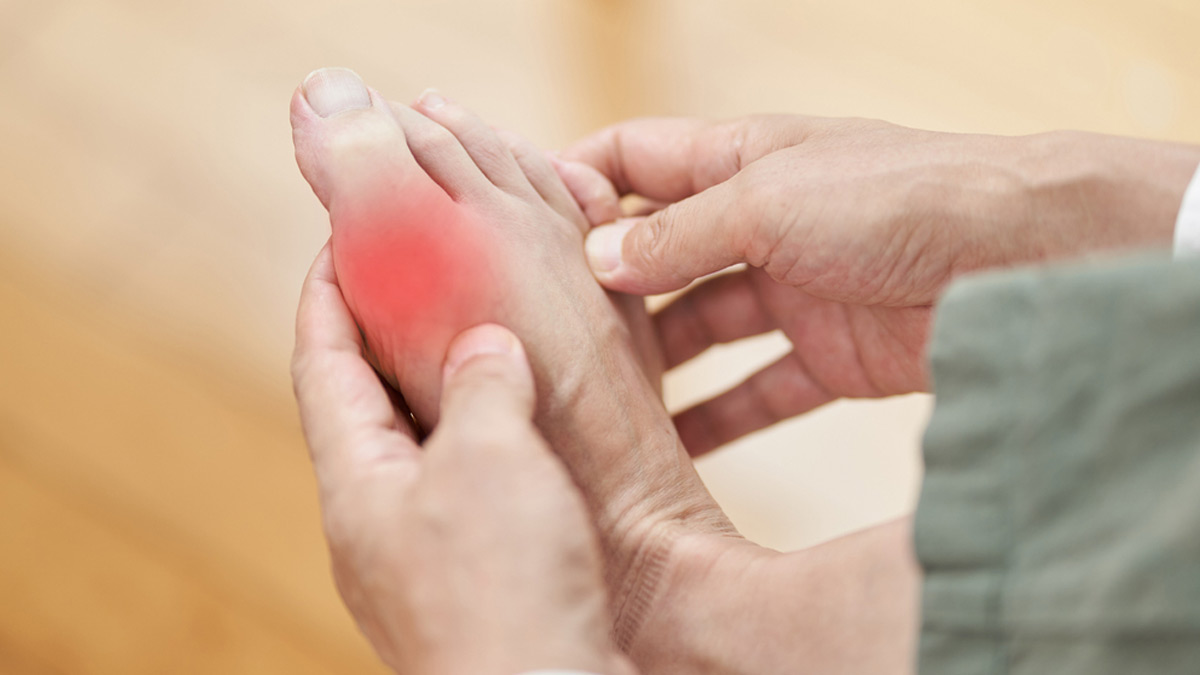
What Does Gout Feel Like in the Foot?

Gout typically presents with intense pain, which often begins suddenly, usually at night. The affected joint may feel like it is on fire. Dr Here are the key sensations and symptoms people with gout in the foot often report:
- Intense Pain: The pain is often described as excruciating and throbbing. It can be so severe that even the weight of a bed sheet can be intolerable.
- Swelling and Redness: The joint becomes swollen, red, and warm to the touch. This inflammation and discolouration are due to the body’s immune response to the urate crystals deposited in the joint.
- Tenderness: The affected area is extremely tender, making it difficult to walk or even stand.
- Stiffness: There can be a loss of range of motion in the affected joint, making movement painful and difficult.
- Fever: In some cases, individuals may experience a mild fever, as the body responds to the inflammation.
These symptoms usually peak within 12-24 hours after they begin and can last for several days to a week. Some people may experience recurrent episodes, leading to chronic gout.
Also Read: Dealing With Gout? Expert Explains Its Causes, Symptoms, And Tips For Management
Causes of Gout

"Gout is primarily caused by hyperuricemia, a condition characterised by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks," said Dr Basavaraj. When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete enough through the kidneys, uric acid can form sharp, needle-like crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue, causing pain, inflammation, and swelling.
Risk Factors Leading Development Of Gout

- Diet: Eating foods and drinking beverages high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol (especially beer), can elevate uric acid levels.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases the risk of hyperuricemia, which can lead to gout.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease are associated with higher uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Having a family history of gout can raise the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics (used to treat hypertension) and low-dose aspirin, can raise uric acid levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment
"Diagnosing gout generally requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A doctor may perform a joint fluid test to check for the presence of urate crystals or a blood test to measure uric acid levels," added Dr Basavaraj.
Also Read: Healthy Diet For Gout: Here's A Breakdown Of Foods You Should Eat And Avoid
How To Treat Gout?
Treatment for gout focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing future attacks. This may include:

- Medications: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and colchicine can help reduce inflammation and pain during acute gout attacks. Long-term medications like allopurinol or febuxostat can help lower uric acid levels and prevent future episodes.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, weight loss, and reducing alcohol consumption can help manage uric acid levels. Staying hydrated is also crucial.
- Home Remedies: Applying ice to the affected joint, elevating the foot, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can provide some relief.
How To Prevent Gout?
Preventing gout entails managing risk factors and adopting lifestyle changes. Here are some strategies:
- Healthy Diet: Limiting purine-rich foods, consuming low-fat dairy products, and incorporating more fruits and vegetables can help.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can reduce the risk of gout.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute uric acid and promotes its excretion.
- Medication Adherence: For those with chronic gout, taking prescribed medications regularly can prevent flare-ups.
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by an expert and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your professional if you are dealing with any health issues to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version