The World Health Organisation has marked May 8 as World Thalassemia Day. The day focuses on making people aware of the disease. It is a hereditary disease which affects the blood of the patient. On this day, here is everything you need to know about the disease. Lesser known to many and also nothing less than a baseless taboo when it comes to marriages, thalassemia is all about understanding the health concern for a healthier living. Dr (Maj.) Manish Mannan, HOD, Pediartrics and Neonatology, Paras hospital Gurgaon explains, “Thalassemia is a hereditary blood condition which is caused when the body is not capable of making enough of a protein called haemoglobin, an important part of red blood cells. If a body doesn’t make enough of hemoglobin then the red blood cells don’t work properly in carrying oxygen to all the cells of the body. Not getting enough of oxygen in the body leads to short of breath and tiredness. It is an inherited disease, which means at least one of the parents must be the carrier of this disease.”
Table of Content:-

Also Read: Brain Attack: Causes, Signs And Symptoms
Causes of Thalassemia
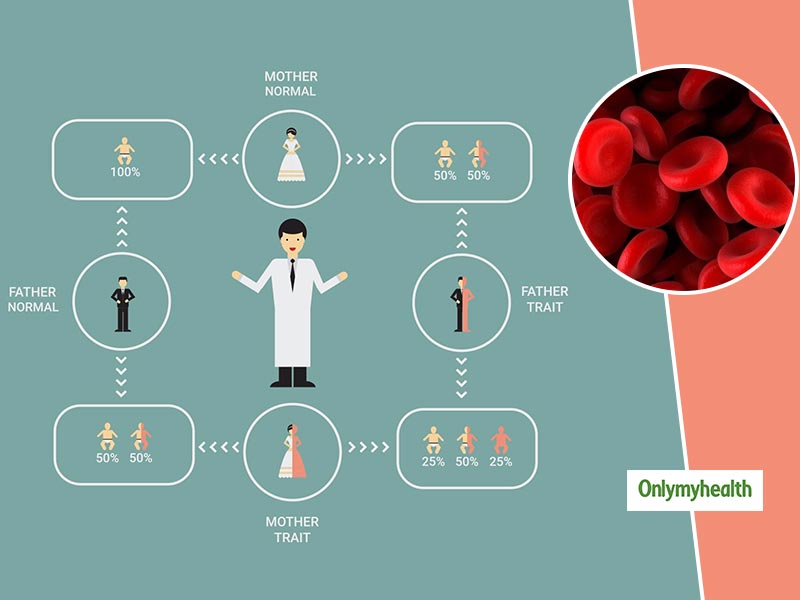
The condition usually occurs when an abnormality or mutation takes place in one of the genes involved in the production of haemoglobin. The defect is inherited from parents. Dr Mannan explains that thalassemia mutations are passed to the offsprings from parents. It is alpha and beta haemoglobin molecules chain that are affected due to mutations. In cases of thalassemia, there is misproduction in alpha or beta chains. “In cases where only one of the parents is a carrier of thalassemia, you may develop the disease called thalassemia minor. In such cases, no symptoms as such will be seen. However, some people might experience minor symptoms. If both the parents are carriers of thalassemia, the child has 25 per cent chances of inheriting a serious form of the disease,” adds Dr Mannan.
Symptoms of Thalassemia
Following are some of the notable symptoms of Thalassemia as per its type:
- The symptoms of thalassemia depend entirely on its type. While patients with thalassemia minor usually experience minor or no signs at all, the severe kind of thalassemia can be categorized as thalassemia major and thalassemia intermedia.
- The symptoms of thalassemia significant start usually appearing before the child’s second year of birth. The severe anaemia which is related to this condition can be life-threatening for the patient.
- Thalassemia intermedia is comparatively a less severe form of beta-thalassemia. Although people with this type of thalassemia suffer from anaemia, blood transfusion is not needed in these cases.
Health Complications Associated With Thalassemia
Dr Manna says, “They can have either iron overload or infection. Thalassemia patients are susceptible to getting too much iron in the body because of the frequent blood transfusion. Too much iron isn’t good for heart, liver and endocrine system. Thalassemia patients with a removed spleen have an increased risk of infection.”
Thalassemia Treatment
Treatment of the condition entirely depends on the type and severity of the disease. The course of treatment will include:
- Blood transfusion
- Bone marrow transplant
- Medications and supplements
- Possible surgery to remove the spleen and/or gallbladder
thalassemiadayspecial2020.jpg)
Also Read: Signs of Blood Cancer You Should Watch Out for
Tips To Prevent Thalassemia
Since it’s an inherited disorder, it is tough to prevent. But, if you have any knowledge of anyone in the family with thalassemia or are getting married, so it is best to get yourself checked of thalassemia. You can talk to doctors too but always stay informed to live a healthy life.”
With Inputs from Dr. (Maj.) Manish Mannan, HOD, Pediartrics and Neonatology, Paras hospital Gurgaon
Read more articles on Other Diseases
Read Next
World Thalassemia Day 2020: Five Things To Bear In Mind When Living With This Blood Disorder
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version

