An ear infection can be bothersome as it can cause ear pain, headaches, fever, and other health conditions like meningitis. But what happens when the infection happens in both ears? This condition in which both the middle ears become infected and inflamed is known as a double ear infection. It can cause various complications and may even lead to hearing loss and rupture of your eardrum if not treated on time. We spoke to our expert Dr Prachi Bhosle Narendra, MBBS, DCH and Developmental Paediatrics, Apollo Cradle and Children Hospital, Marathahalli, Bangalore, who explained double ear infections, their symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Table of Content:-
What Is Double Ear Infection?

A double ear infection, medically termed bilateral otitis media, occurs due to the inflammation or infection in both ears' middle ear, typically caused by bacteria or virus.
“The middle ear is located behind the eardrum and is susceptible to infections caused by bacteria or viruses. This condition primarily affects children, although it can occur in adults. It involves the inflammation and buildup of fluid behind the eardrums leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated”, said Dr Narendra.
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), it is estimated that by the time they are three, five out of six kids will have experienced an ear infection. When it comes to child visits to the doctor, ear infections are really the most frequent cause.
Also Read: Headphones Or Earphones: What’s Good For Your Ears? Expert Explains Their Impact On Hearing
Symptoms Of Double Ear Infection

The symptoms of a double ear infection can be distressing, Dr Narendra listed some of them as follows:
- Aching in both ears or discomfort, often severe
- Drainage of fluid from the ears
- Difficulty hearing or temporary hearing loss
- A moderate to high fever may accompany the infection
- Irritability is observed in children who might be unable to express their discomfort verbally
- Difficulty in sleeping due to increased pain while lying down or dizziness
Causes Of Double Ear Infection
Several factors contribute to the development of double ear infections. Here are some of them listed by Dr Nardendra:
- Viral or Bacterial Infections: Common cold viruses or bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae, can cause infections.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: The Eustachian tubes fail to equalise pressure, leading to fluid buildup and susceptibility to infections.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions or sinus congestion can obstruct the Eustachian tubes, increasing the risk of infections.
- Respiratory infections: Infections like the flu or cold can pave the way for ear infections.
Complications Of Double Ear Infection

If a double ear infection is left untreated, it can result in severe complications, which include:
- Hearing Loss: Prolonged infections can damage the eardrum or middle ear structures, causing temporary or even permanent hearing impairment.
- Ruptured Eardrum: Pressure from fluid buildup can cause the eardrum to burst, leading to temporary hearing loss and drainage. Severe infections can result in a ruptured eardrum, causing sudden relief from pain but necessitating medical attention.
- Spread of Infection: In rare cases, the infection might spread to nearby structures, causing mastoiditis or meningitis
- Speech and developmental delays: Particularly in young children, recurrent infections might hinder speech and development.
Also Read: Can A Sinus Infection Cause Ringing In The Ears, Expert Answers
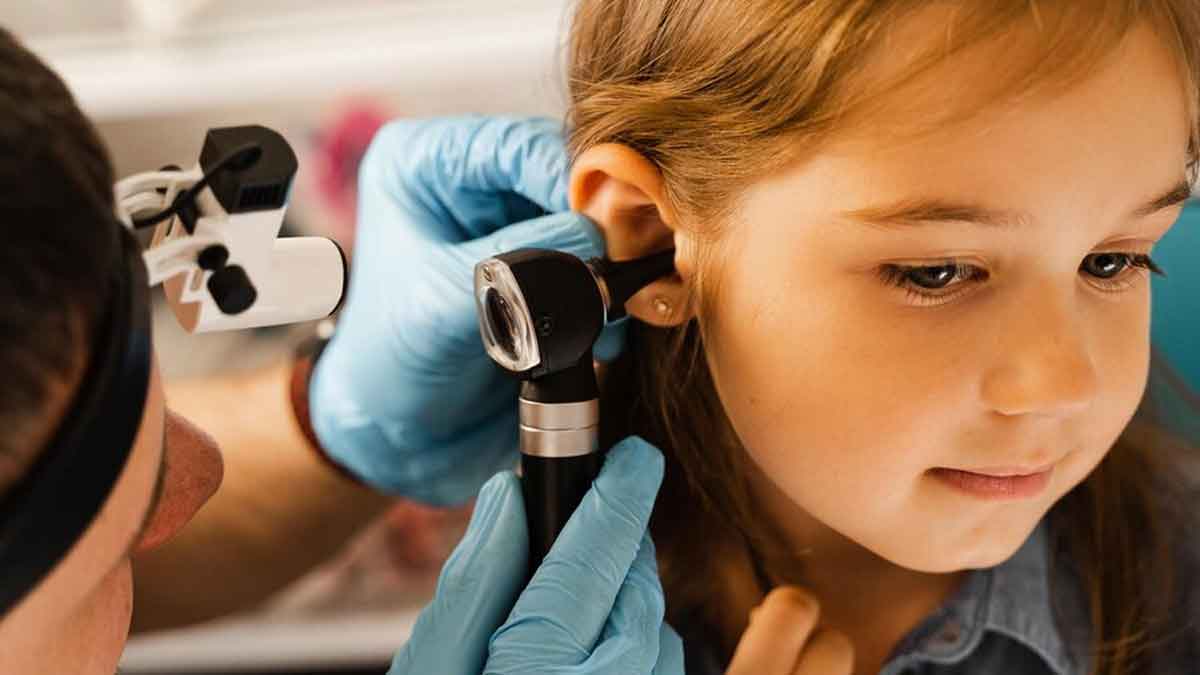
How To Diagnose Double Ear Infection?
“Diagnosis involves a physical examination of the ears using an otoscope to check for redness, fluid buildup or pus behind the eardrums”, said Dr Narendra.
He added, “In some cases, a tympanometry, which measures the movement of the eardrum in response to air pressure changes or a hearing test might be recommended. A fluid analysis can be done to examine if fluid drainage is present and analyse it for infection-causing agents.”
How To Treat Double Ear Infection?
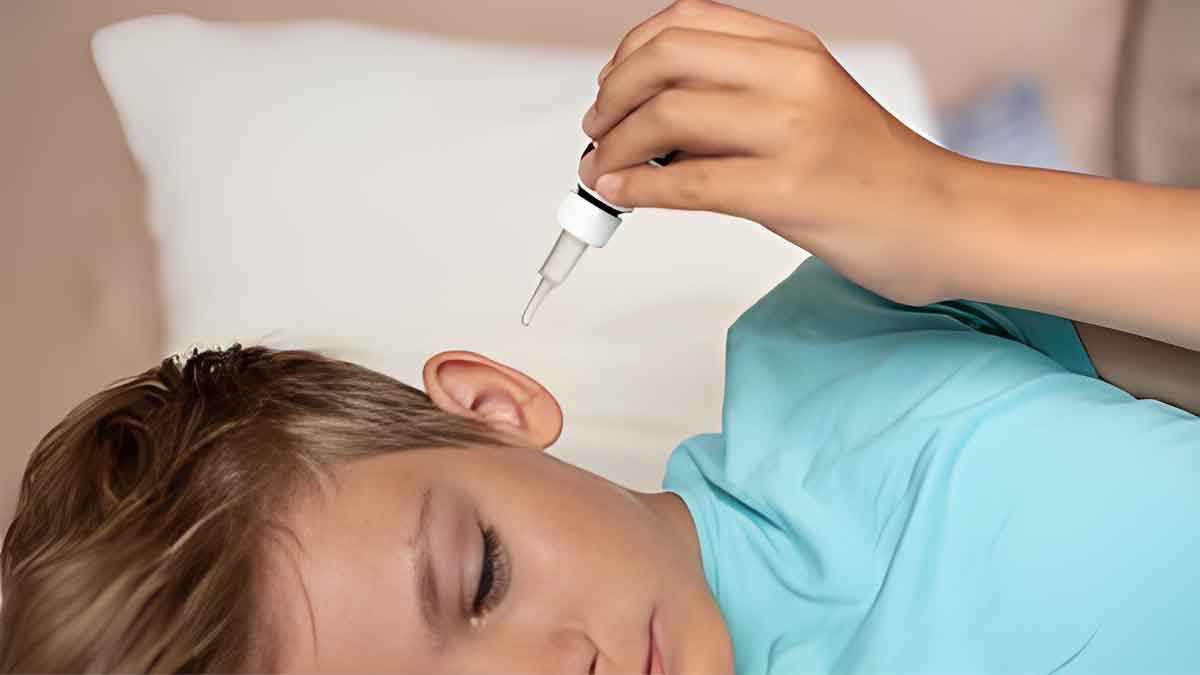
Some of the treatments are listed below to alleviate symptoms and clear the infection:
- Antibiotics: If the infection is bacterial, antibiotics are often prescribed to eradicate the causative bacteria.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate discomfort.
- Ear Drops: Prescribed ear drops can help ease pain and reduce inflammation.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the affected ear may provide some relief.
- Ear Tube Placement: In severe cases or instances of frequent occurrences, further intervention like the placement of ear tubes might be recommended by a medical expert. These tubes assist in draining fluid and equalising pressure, reducing the likelihood of future infections.
Bottomline
Dr Narendra concluded, “While double ear infections can be uncomfortable and concerning, timely identification and appropriate treatment can significantly reduce their impact. It's crucial to consult a medical expert if symptoms arise, especially in children, to ensure proper management and prevent potential complications. Early intervention remains key to a swift recovery and the prevention of recurrent infections.”
[Disclaimer: This article contains information provided by a registered healthcare professional and is for informational purposes only. Hence, we advise you to consult your expert if you notice any symptoms to avoid complications.]
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version