
Genital warts are a type of sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain strains of the virus known as human papillomavirus (HPV). In this article we will understand causes, symptoms, and treatment options for genital warts is important for anyone who is sexually active.
Table of Content:-
To understand its causes and what parts it affects, OnlyMyHealth interacted with Dr Kiran Dhake Senior Physician and Sonologist, Mumbai.
Explaining genital warts, Dr Dhake said, “Typical warts manifest as flesh-coloured bumps or a group of bumps, either flat or raised, and may feel soft or firm, with variable size and texture, in the genital or rectal areas. They may be painful or itchy sometimes.”
A study published by the National Institute of Health stated, “Warts are a recognized symptom of genital HPV infections. About 90% of those exposed who contract HPV will not develop genital warts. Only about 10% who are infected will transmit the virus.”

Genital warts can affect the following sites:
1. Groin area
2. Penis & scrotum
3. Vulva, vagina and cervix
4. Anus and rectum
5. Lips, tongue, or throat region
Causes Of Genital Warts
“The primary cause of genital warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), specifically strains (types), HPV-6 and HPV-11,” said Dr Dhake. These strains are transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during intercourse activities with an infected individual. Genital warts can also be transmitted through oral or anal coital activities. As a result, it may lead to pain or discomfort during intercourse activities.

Risk Factors
There are several risk factors that can cause genital warts, the most common being sexual intercourse. Dr Dhake listed down a few risk factors.
1. Skin-to-skin Transmission
Warts are known to spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected region, so any coital activity involving genital or anal contact is likely to transmit the virus, as per Dr Dhake.
2. Coital activities
Engaging in coital activity with an infected person increases the risk of contracting HPV and developing genital warts.
3. Unprotected intercourse activities
Not using barrier contraceptive methods such as condoms during intercourse activity can raise the risk of HPV transmission.
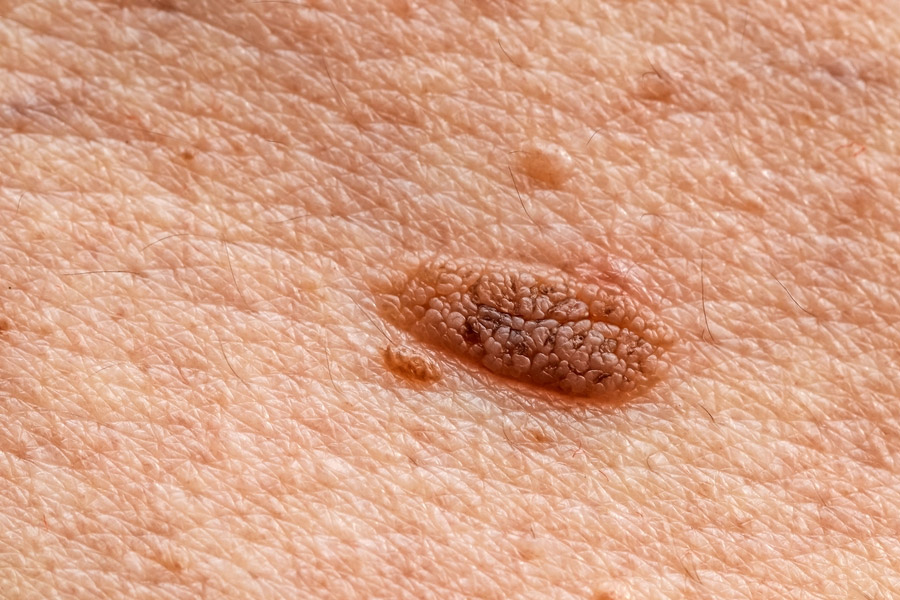
4. Multiple partners
“Having engaged in unprotected intercourse activities with multiple sexual partners or with someone who has had multiple partners increases the risk of exposure to HPV,” Dr Dhake said.
5. Impaired immunity
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are at higher risk of developing genital warts because their body system may not be able to offer protection against HPV infection.
Conclusion
Concluding, Dr Dhake said, “It is essential to note that not every individual infected with HPV will develop genital warts. Additionally, some individuals may carry the virus without exhibiting any symptoms, making them vulnerable to harbour the virus silently for a long time. Such individuals may be super-spreaders transmitting the infection unknowingly to individuals who encounter them.” Regular assessment, implementing protection during intercourse activities, early intervention if symptomatic, and getting vaccinated against HPV can help minimise the risk of genital warts and other HPV-related complications.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version