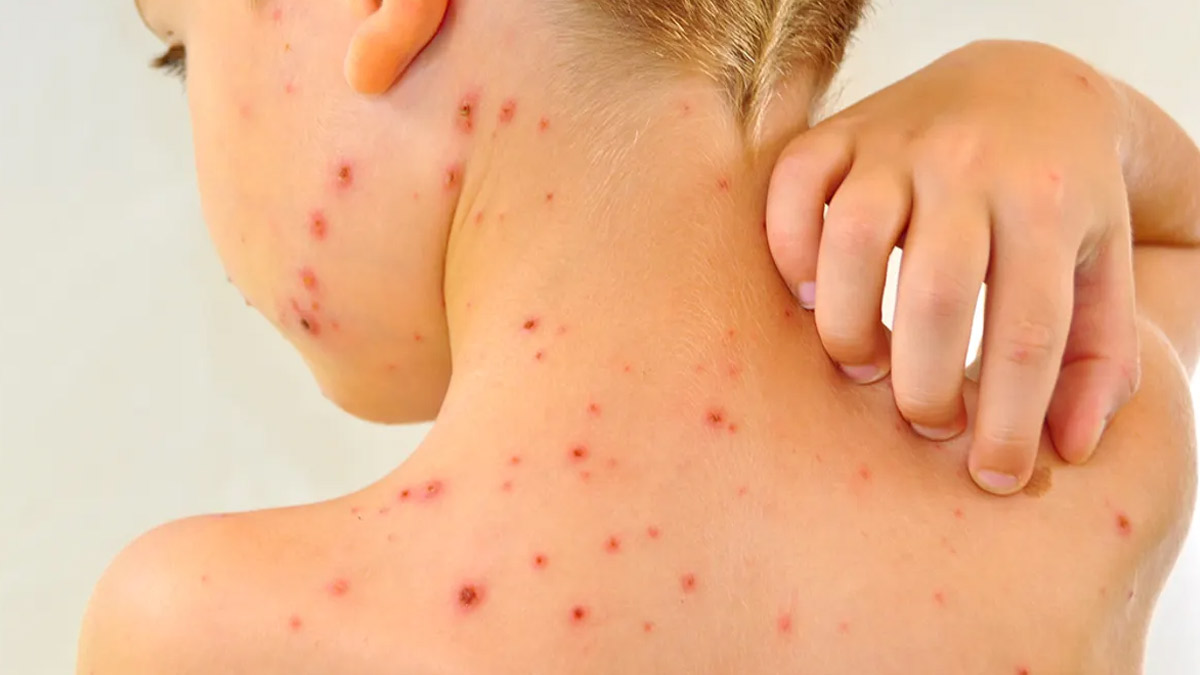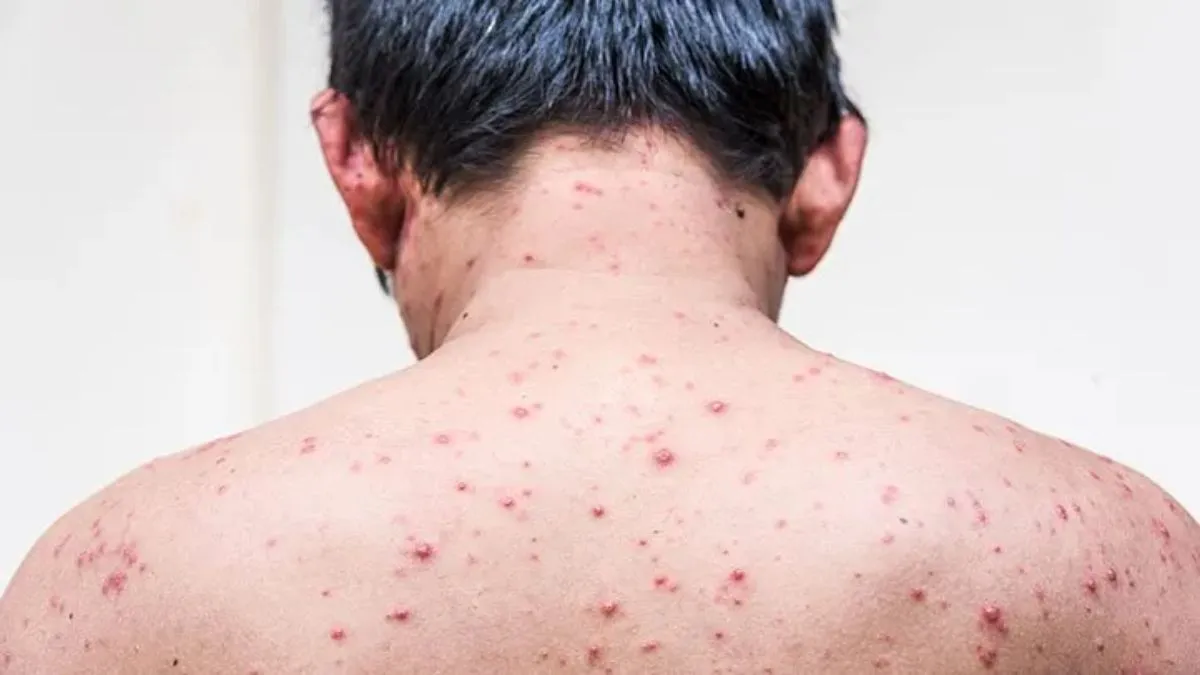
When most people think of chickenpox, they picture itchy red blisters on kids missing school. But here’s the surprising part: adults can get chickenpox too, and it tends to hit them much harder. Doctors say that even if you’ve made it through childhood without catching it, you’re not completely safe. So, what makes adults vulnerable, and how can you protect yourself?
Table of Content:-
To understand this better, we spoke to Dr. V R Yamunadevi, Consultant – Infection Control, Apollo Hospitals, Chennai, who explained the causes, risks, and precautions every adult should know.
Why Does Chickenpox Happen to Adults?![]()
“Chickenpox is caused by a virus called varicella-zoster,” explains Dr. Yamunadevi. “People who get infected often develop a rash that looks like fluid-filled blisters all over the body.” While it’s usually seen in children, adults can still catch the virus if they’re not immune through prior infection or vaccination. Once exposed, the virus spreads quickly and tends to cause more severe symptoms in grown-ups.
“Adults who get chickenpox may experience higher fever, more blisters, and a greater risk of complications like pneumonia, encephalitis, and secondary bacterial infections compared to children,” she adds.
ALSO READ: Eating Chicken During Chickenpox: Safe or Risky? Nutrition Tips for Faster Healing
Who Is at Risk for Chickenpox as an Adult?![]()
If you’ve never had chickenpox or the vaccine, you’re still at risk and no matter your age. Dr Yamunadevi says, “There isn’t really an age limit. Anyone without immunity can get chickenpox.”
The virus spreads easily:
- Through direct contact with fluid from blisters.
- Or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Because of how contagious it is, one infected person can quickly expose others in the same household or workspace.
Adults More Likely to Develop Severe Complications
Some adults face a higher risk of developing complications if they catch chickenpox. According to Dr Yamunadevi, these include:
- Pregnant women who have never had chickenpox.
- People on immune-suppressing medications like chemotherapy or steroids.
- Those with weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV or organ/bone marrow transplants.
“These groups must be extra cautious, as the infection can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia or brain inflammation,” warns Dr Yamunadevi.
Precautions and Preventive Actions![]()
The best defence is prevention. “The most effective way to avoid chickenpox is through vaccination,” says Dr Yamunadevi.
Here’s what to know:
- If you’ve never been vaccinated or had chickenpox, talk to your doctor about getting the chickenpox vaccine.
- The vaccine is given in two doses for children, adolescents, and adults.
- Most people who get both doses won’t catch chickenpox.
- Since it’s a live vaccine, always get your doctor’s prescription before taking it.
- Good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected people are also important steps in preventing infection.
A study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases found that adult cases of chickenpox are rising globally among people who missed vaccination in childhood. It noted that adults are 25 times more likely than children to be hospitalised due to complications.
ALSO READ: Is Camphor Safe and Effective for Chickenpox? What You Need to Know
Conclusion
Chickenpox in adulthood isn’t just “a late case of a childhood illness.” It’s a serious infection that can bring complications if ignored. Vaccination and awareness are your best shields. As Dr Yamunadevi sums up, “Adults should not assume they’re immune. A simple vaccine can prevent what could otherwise become a life-threatening illness.”
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
Nov 09, 2025 10:27 IST
Published By : Chanchal Sengar