
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, affecting not only one’s appearance but also emotional well-being. While there are various causes of hair thinning, one often overlooked factor is autoimmune diseases. These conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, and in some cases, this includes hair follicles.
Table of Content:-
We asked our expert Dr Sanjeev Gulati, Department of Dermatology, Sharda Hospital, how autoimmune diseases lead to hair loss and the ways to manage and cope with this condition. Here is what he shared with us.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses, begins to attack healthy tissues. The cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, but genetics, infections, and environmental factors can trigger them. These diseases can affect nearly any part of the body, including the skin, joints, and organs, and, in some cases, lead to hair loss.

Autoimmune Diseases That Can Cause Hair Loss
1. Alopecia Areata
One of the most common autoimmune-related causes of hair loss is alopecia areata. “This condition occurs when the immune system targets hair follicles, leading to round patches of hair loss on the scalp or other areas of the body. Alopecia areata can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing complete hair loss (alopecia totalis) or even all-body hair loss (alopecia universalis),” Dr Gulati explained. The cause of alopecia areata remains unclear, but stress and genetic predisposition are believed to contribute to its development.
Also Read: Can a Receding Hairline Be Reversed? Expert Insights And Solutions
2. Lupus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune condition that can cause inflammation throughout the body, including the skin and hair follicles. Hair loss in lupus patients may occur due to inflammation in the scalp, but it can also result from the medications used to treat the disease. The hair loss associated with lupus is often diffuse, meaning it’s spread throughout the scalp, and may come in cycles of shedding and regrowth. In some cases, permanent scarring of the scalp can lead to permanent hair loss.
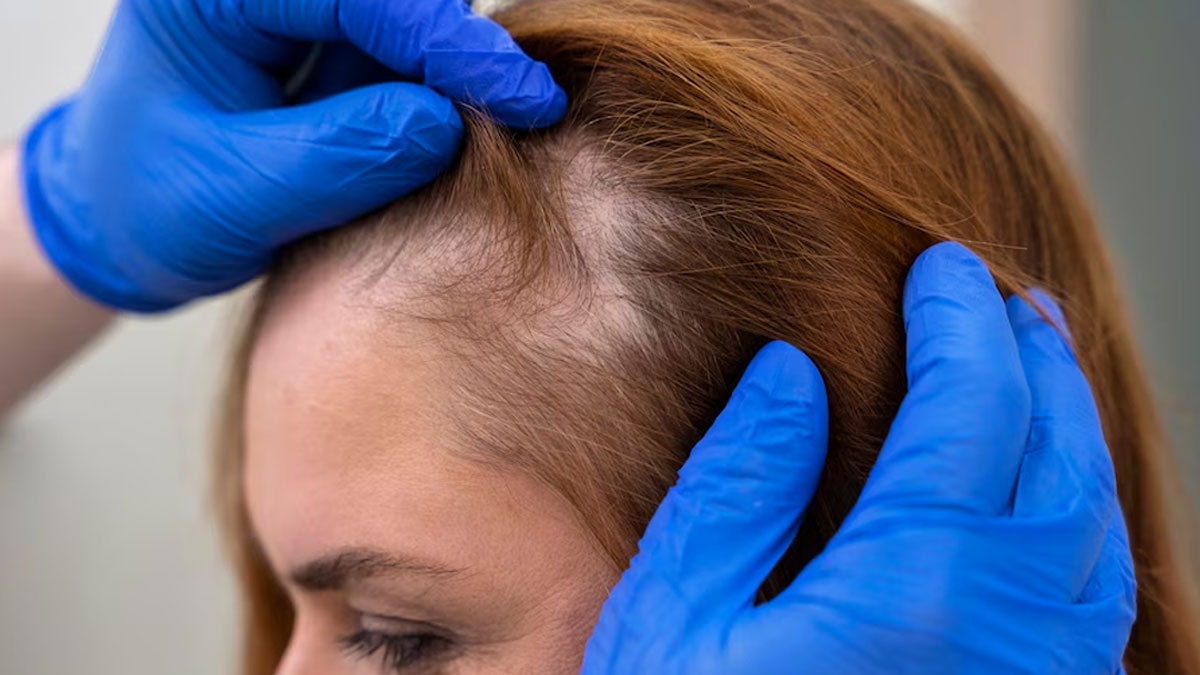
3. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is another autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the joints. While RA primarily affects joints, it can also cause hair thinning and loss, often due to inflammation and medications like methotrexate, which suppress the immune system. This hair loss may be temporary, but it can still be a significant concern for individuals managing the physical and emotional challenges of RA.
4. Vitiligo
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder that causes the skin to lose its pigment, leading to white patches on the skin. “In some cases, vitiligo can also affect hair follicles, leading to a loss of pigmentation in the hair,” Dr Gulati shared. Though vitiligo is primarily known for its effect on the skin, its impact on hair can be a cosmetic concern, especially when it affects the scalp or facial hair.
How Autoimmune Diseases Lead To Hair Loss
The hair loss associated with autoimmune diseases often stems from the immune system’s attack on the hair follicles, which are responsible for producing hair. Inflammatory processes can damage these follicles, disrupting their ability to grow hair. In some cases, hair loss occurs due to medications used to manage autoimmune conditions, which can have side effects that include thinning or shedding of hair.
The severity and type of hair loss can vary significantly depending on the autoimmune disease, the treatment used, and how the individual’s body responds. Some may experience hair regrowth, while others may face ongoing or permanent hair loss.
Coping Strategies To Deal With Hair Loss Due To Autoimmune Diseases
Dealing with hair loss can be emotionally challenging, especially when it’s caused by an autoimmune condition. Here are some expert-approved strategies to help cope with the impact of hair loss:
- Seek medical treatment
- Explore hair restoration options
- Practice self-care
- Consider nutritional supplements
Bottomline
Autoimmune diseases can have a significant impact on hair health, and the connection between the immune system and hair loss is an important consideration for individuals dealing with these conditions. While hair loss may be an unavoidable part of managing an autoimmune disease, there are treatment options and strategies available to help minimise its effects.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version