
In recent years, gluten has become a buzzword in the world of health and nutrition, with many people opting for gluten-free diets in hopes of improving their well-being. While celiac disease is a well-known condition that mandates a strict gluten-free lifestyle, there’s another, less understood phenomenon affecting countless individuals: non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS). Unlike celiac disease, NCGS does not cause detectable damage to the small intestine, yet it can trigger a range of distressing symptoms. From persistent bloating and abdominal pain to unexplained fatigue and brain fog, NCGS poses a unique challenge for those affected.
Table of Content:-
To understand this in detail, OnlyMyHealth interacted with Dr Kiran Dhake, Corporate Wellness Physician, Mumbai.
While gluten insensitivity or non-celiac gluten sensitivity can often exhibit a similar set of symptoms to that of undiagnosed celiac disease, the two entities are different. Dr Dhake said, “NCGS is characterised by GI tract related symptoms and non GI tract symptoms due to gluten ingestion, in the absence of celiac disease and wheat allergy.”
Causes

1. Unknown Mechanism
According to Dr Dhake, the exact mechanism is not well understood. “Activation of the immune system, direct toxic properties of gluten and cellular toxicity properties of certain molecules are implicated,” he said.
Also read: Can You Develop Celiac Disease When You're Older?
2. Gluten
Dr Dhake says that it is speculated that gluten could be the cause of NCGS. Studies have shown that gluten brings in the cascade of toxic events to cellular function, thereby affecting cell structure, mobility and chemical balance.
3. Intolerance to other proteins
“Certain individuals may exhibit a reaction to proteins present in gluten-containing cereals that activates the immune system and leads to NCGS and celiac disease,” Dhake said.

4. FODAMPs
Research postulates that FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols) –various complex carbohydrate chains that are present in gluten-containing grains (called as fructans) have been identified as a possible cause of gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with NCGS.
Symptoms
Dr Dhake helped us list down these common symptoms of NCGS
1. GI tract Symptoms: These symptoms may mimic celiac disease. Symptoms are bloating, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea or constipation and flatulence.

2. Non-GI symptoms: Wide spectrum of non-GI symptoms is associated with NCGS.
- Neurological: Headache, migraine, tingling numbness in hands and legs [ peripheral neuropathy]
- Muscle tone and coordination disorder [ Dystonia, myoclonus, ataxia]
- Movement disorder [ Chorea, tremors, restless leg syndrome, Parkinsonism.]
- Mental Health disorders: Attention deficit disorder, eating disorder, autism, anxiety, depression, hallucinations.
- Allergic disorders: Asthma, atopic dermatitis, eczema, IgE mediated allergy
- Iron deficiency anaemia/folate deficiency.
Also read: Celiac Disease: Know About Its Signs And Symptoms
Treatment
The effective management is initiated after excluding the possibility of celiac disease and allergic to wheat /wheat products. “Adopting a diet which is “free of gluten” is the key factor and it is advised to follow the diet meticulously to see whether the symptoms improve or subside, partially or completely,” Dr Dhake said. As gluten containing food products, wheat, barley, contain essential nutrients, a gluten free diet may lead to deficiency of the nutrients. “To ensure, affected individuals receive enough nutrients, multivitamin, mineral, calcium and fibre supplements are advised,” Dr Dhake said.
Difference Between Celiac and Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity
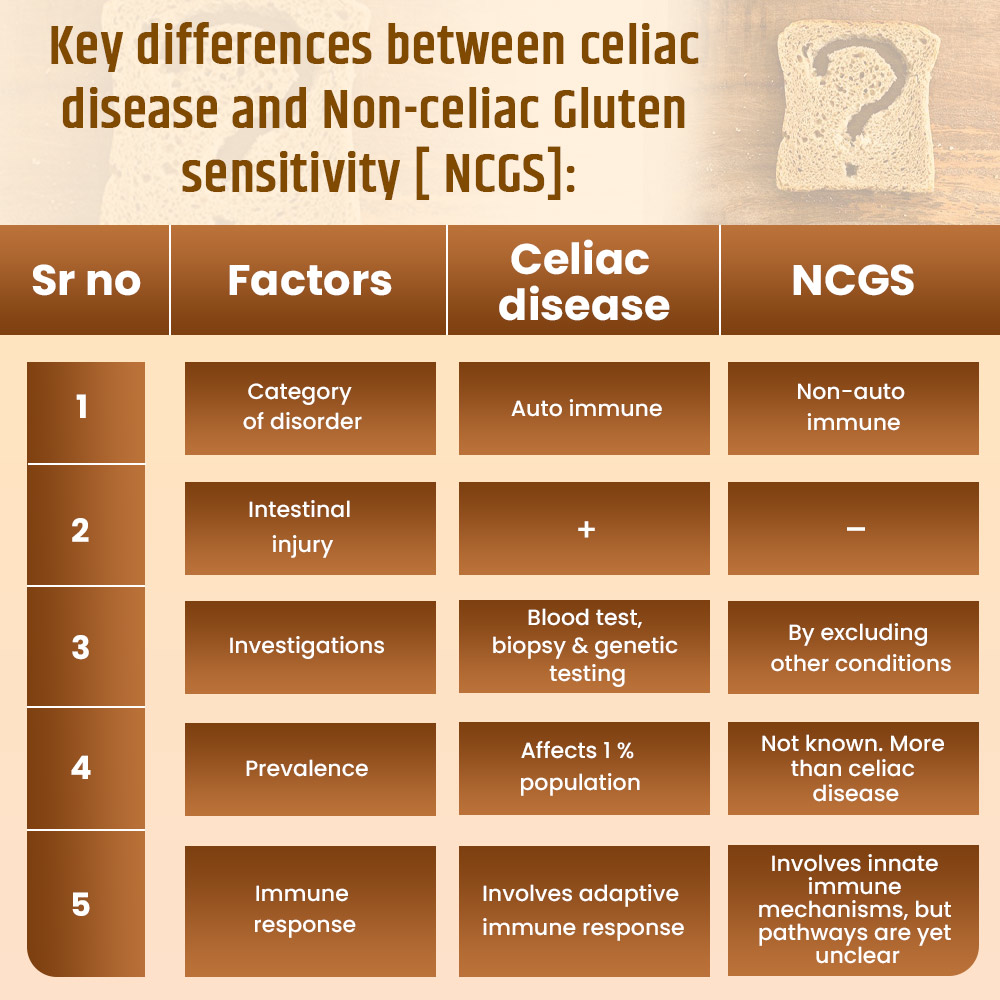
Conclusion
Though Gluten is one the quintessential components and a key source for fibre, protein and other vital nutrients for the body, it is also known to exert intolerance in certain groups of individuals. The best strategy in the prevention and treatment of this disease group is --early recognition of the symptoms, appropriate investigations and strict adherence to gluten free dietary regime.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version